 |
Strain Partitioning
In structural geology, strain partitioning is the distribution of the total strain experienced on a rock, area, or region, in terms of different strain intensity and strain type (i.e. pure shear, simple shear, dilatation). This process is observed on a range of scales spanning from the grain – crystal scale to the plate – lithospheric scale, and occurs in both the brittle and plastic deformation regimes. The manner and intensity by which strain is distributed are controlled by a number of factors listed below. Influencing factors All four of these factors below may individually or in combination contribute toward the distribution of strain. Therefore, each of these factors must be taken into consideration when analyzing how and why strain is partitioned: : anisotropy such as preexisting structures, compositional layering, or cleavage planes. Isotropic lines "separate mutually orthogonal principle trajectories on each side. In a plane-strain field, the strain is zero at iso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Structural Geology
Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation ( strain) in the rocks, and ultimately, to understand the stress field that resulted in the observed strain and geometries. This understanding of the dynamics of the stress field can be linked to important events in the geologic past; a common goal is to understand the structural evolution of a particular area with respect to regionally widespread patterns of rock deformation (e.g., mountain building, rifting) due to plate tectonics. Use and importance The study of geologic structures has been of prime importance in economic geology, both petroleum geology and mining geology. Folded and faulted rock strata commonly form traps that accumulate and concentrate fluids such as petroleum and natural gas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Transpression
In geology, transpression is a type of Strike-slip fault, strike-slip deformation that deviates from simple shear because of a simultaneous component of shortening perpendicular to the fault plane. This movement ends up resulting in oblique shear. It is generally very unlikely that a deforming body will experience "pure" shortening or "pure" strike-slip. The relative amounts of shortening and strike-slip can be expressed in the convergence angle alpha which ranges from zero (ideal strike-slip) to 90 degrees (ideal convergence). During shortening, unless material is lost, transpression produces vertical thickening in the crust. Transpression that occurs on a regional scale along Tectonic plate, plate boundaries is characterized by oblique convergence. More locally, transpression occurs within restraining bends in strike-slip Fault (geology), fault zones. Transpressional structures Transpressional shear zones are characterized by an association of structures that suggest zone-norma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
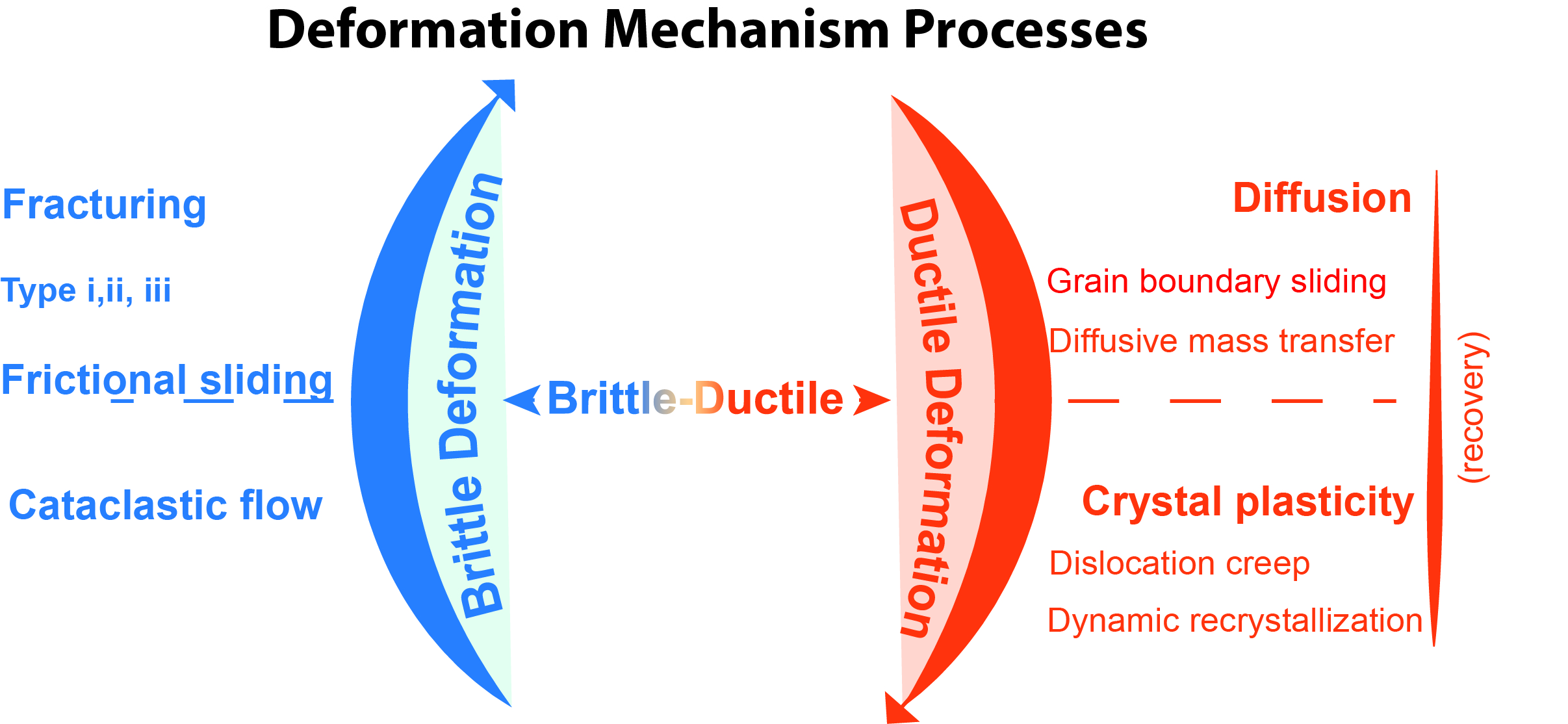 |
Deformation Mechanisms
In geology and materials science, a deformation mechanism is a process occurring at a microscopic scale that is responsible for deformation: changes in a material's internal structure, shape and volume. The process involves planar discontinuity and/or displacement of atoms from their original position within a crystal lattice structure. These small changes are preserved in various microstructures of materials such as rocks, metals and plastics, and can be studied in depth using optical or digital microscopy. Processes Deformation mechanisms are commonly characterized as brittle, ductile, and brittle-ductile. The driving mechanism responsible is an interplay between internal (e.g. composition, grain size and lattice-preferred orientation) and external (e.g. temperature and fluid pressure) factors. These mechanisms produce a range of micro-structures studied in rocks to constrain the conditions, rheology, dynamics, and motions of tectonic events. More than one mechanism may be ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspars and the ''alkali'' (potassium-sodium) feldspars. Feldspars make up about 60% of the Earth's crust and 41% of the Earth's continental crust by weight. Feldspars crystallize from magma as both intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and are also present in many types of metamorphic rock. Rock formed almost entirely of calcic plagioclase feldspar is known as anorthosite. Feldspars are also found in many types of sedimentary rocks. Etymology The name ''feldspar'' derives from the German , a compound of the words ' ("field") and ("flake"). had long been used as the word for "a rock easily cleaved into flakes"; was introduced in the 18th century as a more specific term, referring perhaps to its comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of Silicon dioxide, SiO2. Quartz is, therefore, classified structurally as a Silicate mineral#Tectosilicates, framework silicate mineral and compositionally as an oxide mineral. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into fragile elastic plates. This characteristic is described as ''perfect basal cleavage''. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites. Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, and fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing, and in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost". Properties and structure The mica group comprises 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in the monoclinic system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Micas are translucent to opa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Deformation Mechanisms (Passchier And Trouw)
Deformation can refer to: * Deformation (engineering), changes in an object's shape or form due to the application of a force or forces. ** Deformation (physics), such changes considered and analyzed as displacements of continuum bodies. * Deformation (meteorology), a measure of the rate at which the shapes of clouds and other fluid bodies change. * Deformation (mathematics), the study of conditions leading to slightly different solutions of mathematical equations, models and problems. * Deformation (volcanology), a measure of the rate at which the shapes of volcanoes change. * Deformation (biology), a harmful mutation or other deformation in an organism. See also * Deformity (medicine), a major difference in the shape of a body part or organ compared to its common or average shape. * Plasticity (physics) In physics and materials science, plasticity (also known as plastic deformation) is the ability of a solid material to undergo permanent Deformation (engineering), defo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Rheological
Rheology (; ) is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a fluid (liquid or gas) state but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied forcRheology is the branch of physics that deals with the deformation and flow of materials, both solids and liquids.W. R. Schowalter (1978) Mechanics of Non-Newtonian Fluids Pergamon The term ''rheology'' was coined by Eugene C. Bingham, a professor at Lafayette College, in 1920 from a suggestion by a colleague, Markus Reiner.The Deborah Number The term was inspired by the of |
|
|
Conceptual Illustration Of Strain Factorization
Conceptual may refer to: Philosophy and Humanities *Concept *Conceptualism *Philosophical analysis (Conceptual analysis) *Theoretical definition (Conceptual definition) *Thinking about Consciousness (Conceptual dualism) *Pragmatism (Conceptual pragmatism) * Paradigm (Conceptual scheme) * Abstract and concrete (Conceptual object) * Conceptual attrition, an idea of Beverley Skeggs *Conceptual proliferation *Conceptual history *Conceptual necessity Linguistics and Semantics *Conceptual schema *Conceptual metaphor *Conceptual model *Conceptual blending *Conceptual semantics *Conceptual dictionary * Conceptual change *Conceptual dependency theory *Conceptual domain in Frame semantics (linguistics) *Inferential role semantics (Conceptual role semantics) Psychology *Priming (psychology) (Conceptual priming) *Spatial–temporal reasoning (Visuo-conceptual) *Conceptual act model of emotion *Conceptual space Science *Conceptual physics *Conceptual economy *Conceptual model (computer scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Homogeneous And Partitioned Strain Within Transpressive And Transtensive Tectonic Regimes
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains () are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the British Columbia Coast, Coast of British Columbia south to the Fraser River. The mountain range's name derives from its proximity to the sea coast, and it is often referred to as the Coast Range. The range includes volcanic and non-volcanic mountains and the extensive ice fields of the Pacific Ranges, Pacific and Boundary Ranges, and the northern end of the volcano, volcanic system known as the Cascade Volcanoes. The Coast Mountains are part of a larger mountain system called the Pacific Coast Ranges or the Pacific Mountain System, which includes the Cascade Range, the Insular Mountains, the Olympic Mountains, the Oregon Coast Range, the California Coast Ranges, the Saint Elias Mountains and the Chugach Mountains. The Coast Mountains are also part of the American Cordilleraa Spanish term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |