|
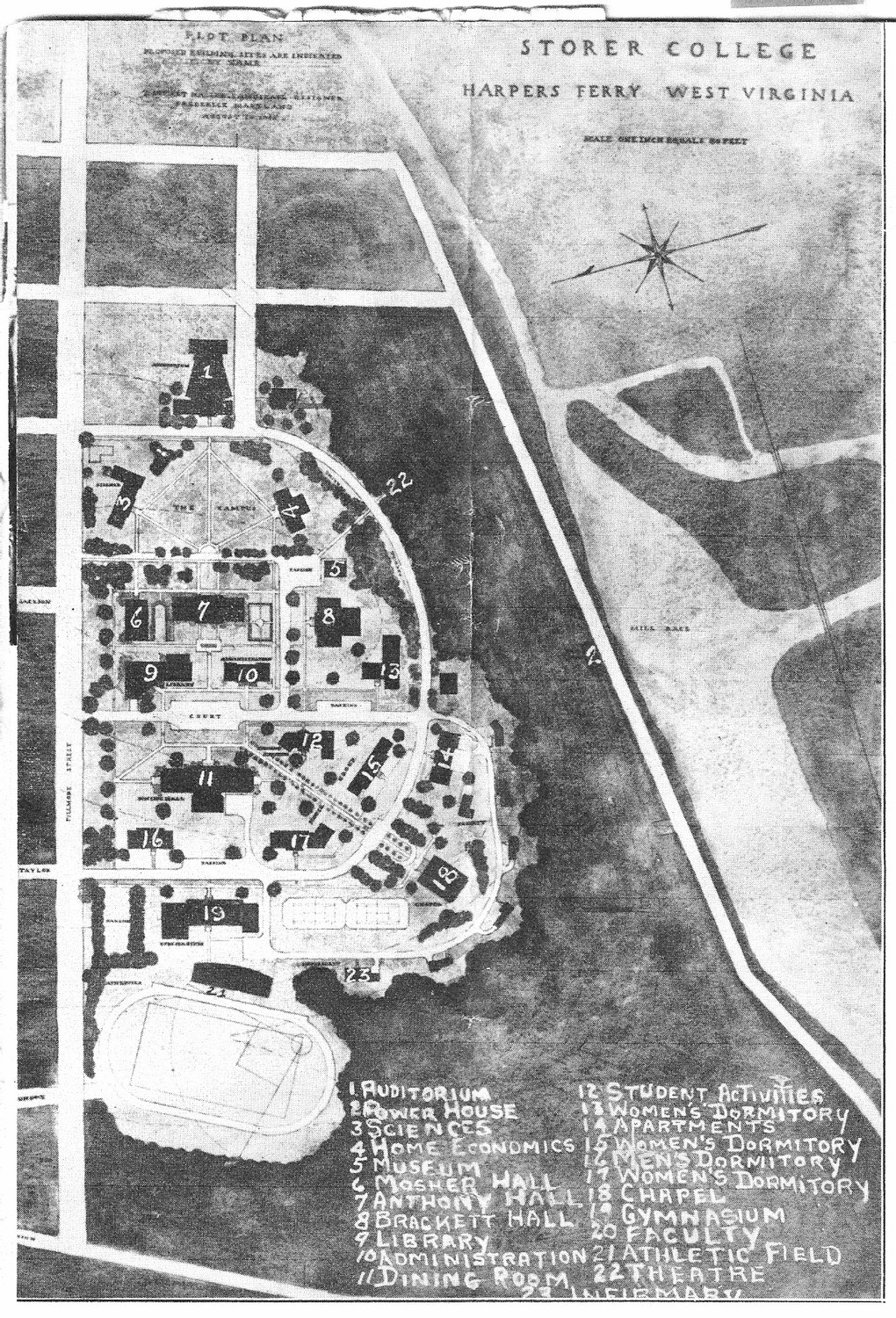
Storer College
Storer College was a historically black college in Harpers Ferry, West Virginia, that operated from 1867 to 1955. A national icon for Black Americans, in the town where the 'end of American slavery began', as Frederick Douglass famously put it, it was a unique institution whose focus changed several times. There is no one category of college into which it fits neatly. Sometimes white students studied alongside Black students, which at the time was prohibited by law at state-supported schools in West Virginia and the other Southern states, and sometimes in the North. In the twentieth century, Storer was at the center of the growing protest movement against Jim Crow treatment that would lead to the NAACP and the Civil Rights Movement. The first American meeting of the predecessor of the NAACP, the Niagara Movement, was held at Storer in 1906. John Brown's Fort, the main symbol of the end of slavery in the United States, was located from 1909 until 1968 on the Storer campus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpers Ferry, West Virginia
Harpers Ferry is a historic town in Jefferson County, West Virginia. It is located in the lower Shenandoah Valley. The population was 285 at the 2020 census. Situated at the confluence of the Potomac and Shenandoah rivers, where the U.S. states of Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia meet, it is the easternmost town in West Virginia. During the American Civil War, it was the northernmost point of Confederate-controlled territory. An 1890 history book on the town called it "the best strategic point in the whole South." The town was formerly spelled Harper's Ferry with an apostrophe, so named because in the 18th century it was the site of a ferry service owned and operated by Robert Harper. The United States Board on Geographic Names, whose Domestic Name Committee is reluctant to include apostrophes in official place names, established the standard spelling of "Harpers Ferry" by 1891. By far, the most important event in the town's history was John Brown's raid on the Harpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shenandoah River
The Shenandoah River is the principal tributary of the Potomac River, long with two forks approximately long each,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 in the U.S. states of Virginia and West Virginia. The river and its tributaries drain the central and lower Shenandoah Valley and the Page Valley in the Appalachians on the west side of the Blue Ridge Mountains, in northwestern Virginia and the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia. There is a hydroelectric plant along the Shenandoah river constructed in 2014 by Dominion. Course The Shenandoah River is formed northeast of Front Royal near Riverton, by the confluence of the South Fork and the North Fork. It flows northeast across Warren County, passing underneath Interstate 66 from its formation. Beyond the I-66 bridge the river flows through a set of bends before turning to the northeast again, crossing into Clarke County below I-66. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal School
A normal school or normal college is an institution created to train teachers by educating them in the norms of pedagogy and curriculum. In the 19th century in the United States, instruction in normal schools was at the high school level, turning out primary school teachers. Most such schools are now called teacher training colleges or teachers' colleges, currently require a high school diploma for entry, and may be part of a comprehensive university. Normal schools in the United States, Canada and Argentina trained teachers for primary schools, while in Europe, the equivalent colleges typically educated teachers for primary schools and later extended their curricula to also cover secondary schools. In 1685, St. Jean-Baptiste de La Salle, founder of the Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools, founded what is generally considered the first normal school, the ''École Normale'', in Reims, Champagne, France. The term "normal" in this context refers to the goal of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ex Libris (West Virginia University Libraries)
Ex Libris may refer to: *An Ex Libris (bookplate), a label affixed to a book to indicate ownership *Ex Libris (band), a Dutch metal band *Ex Libris (bookshop), a Swiss retail company * "Ex Libris" (''Charmed''), a 2000 episode of the television series ''Charmed'' *'' Ex Libris: Confessions of a Common Reader'', a 1998 collection of essays by Anne Fadiman *Ex Libris (game), a party game *Ex Libris Group, an Israeli software company that sells library automation software * Exlibris (music label), subsidiary of Danish publisher Gyldendal. *'' Ex Libris: The New York Public Library'', a 2017 American documentary film * Ex Libris, an imprint of Rizzoli International Publications See also *''Rex Libris ''Rex Libris'' is a science fiction / humor comic book series written and illustrated by James Turner. It was published quarterly from 2005–2008 by Slave Labor Graphics. Publication history Thirteen issues were published from August 2005 to Oc ...'', a comic book series by James Turne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Park, Maine
Ocean Park is a village in the town of Old Orchard Beach in York County, Maine, United States. A historic family style summer community affiliated with the Free Will Baptists, the community is located in southern Old Orchard Beach on Saco Bay. Ocean Park continues to be a dry community to this day. Rooted in the Chautauqua tradition, it is occasionally referred to as "Chautauqua-by-the-Sea." The ZIP Code for Ocean Park is 04063. History The main institutional buildings in Ocean Park were mainly constructed in the 1880s in a Classical Revival style. The site was home to a large Free Will Baptist meeting site, organized in 1881 largely by Bates College President Oren B. Cheney. One of the prominent buildings is the Free Baptist Tabernacle Temple, a large octagonal meeting hall serving as the central gathering place of the camp. The style was similar to other prominent summer church camp meetings such those at Ocean Grove, New Jersey and Wesleyan Grove on Martha's Vineyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oren Cheney
Oren Burbank Cheney (December 10, 1816 – December 22, 1903) was an American politician, minister, and statesman who was a key figure in the abolitionist movement in the United States during the later 19th century. Along with textile tycoon Benjamin Bates, he founded the first coeducational university in New England (the Bates College) which is widely considered his ''magnum opus.'' Cheney is one of the most extensively covered subjects of Neoabolitionism, for his public denouncement of slavery, involuntary servitude, and advocation for fair and equal representation, egalitarianism, and personal sovereignty. Cheney's main social ideology was that of egalitarianism; he personally voiced his disdain for racial inequality, social elitism, and socioeconomic depravation regularly, in controversial speeches and articles. He was ordained a minister in his early twenties, became the headmaster at Parsonsfield, Maine, and illegally harbored and transferred slaves to safety during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Storer
John Storer (January 18, 1796 – October 23, 1867) was a merchant and philanthropist from Sanford, Maine, who was the namesake of Storer College in Harpers Ferry, West Virginia. Life and career Storer was born in 1796 in Wells, Maine, and was a Congregationalist. He started working as a clerk for the firm of Smith & Porter in Kennebunk, Maine, but on their recommendation, and with their financing, he set up his own shop in Sanford in 1820. He eventually owned stores throughout the state of Maine and made numerous lucrative investments. Storer was "an avowed Whig", later a Republican. No one in Sanford was more in favor of the Union cause. As told by the wife of Rev. Oren B. Cheney, founder of Bates College, a Freewill Baptist school in Maine, Cheney suggested to Storer that his desire to donate to "the colored race" could finance a Free Baptist school for former slaves. Storer offered a $10,000 matching grant to the Freewill Baptists for a " colored school" in the South, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
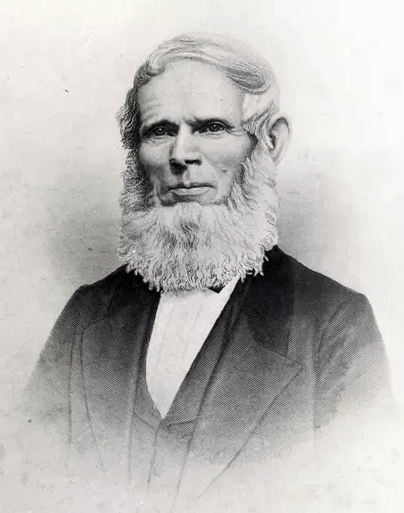
Nathan Cook Brackett
Nathan Cook Brackett (1836–1910) was an abolitionist, Free Will Baptist pastor, first president of Storer College, and chairman and co-founder of Bluefield State College. Nathan Brackett was born in Phillips, Maine in 1836 and starting in 1857 attended Bates College (then called the Maine State Seminary) and then Colby College (then called Waterville College) and finally Dartmouth College for his senior year. After graduating from Dartmouth in 1864 and becoming ordained as a Free Will Baptist pastor, Brackett joined the U.S. Christian Commission in the Shenandoah Valley assisting soldiers and freed slaves. In 1865 the New England's Freewill Baptist Home Mission Society sponsored Brackett in establishing a primary school for former slaves and in supervising several dozen northern women from the North who were teaching in Free Will Baptist schools throughout the Shenandoah Valley. Also in 1865 Brackett married Louise Wood of Lewiston, Maine, who was also an 1860 alumna of Bates (Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Virginia & Regional History Center
The West Virginia & Regional History Center (WVRHC), is the largest archival collection housing documents and manuscripts involving West Virginia and the surrounding central Appalachian region. Because of name changes over the years, it is sometimes referred to as the "West Virginia Collection." The WVRHC is the Special Collections division of the WVU Libraries. According to the University, the Center holds over 36,000 linear feet of manuscripts, 100,000 books, 100,000 pamphlets, 1,200 newspaper titles, over 1 million photographs and prints, 5,000 maps, and 40,000 microfilms, as well as oral histories, films and folk music recordings. Through donations, the WVRHC provides access to and preserves information on the history and cultural aspects of West Virginia and the central Appalachian Region. History The Center was created in the 1920s when WVU history professor Charles Ambler began to actively seek support for the preservation of state historical records and resources. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Virginia History
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב maarav 'west' from עֶרֶב erev 'evening'. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigation (in a place where magnetic north is the same dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedmen's Bureau
The Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands, usually referred to as simply the Freedmen's Bureau, was an agency of early Reconstruction, assisting freedmen in the South. It was established on March 3, 1865, and operated briefly as a U.S. government agency, from 1865 to 1872, after the American Civil War, to direct "provisions, clothing, and fuel...for the immediate and temporary shelter and supply of destitute and suffering refugees and freedmen and their wives and children". Background and operations In 1863, the American Freedmen's Inquiry Commission was established. Two years later, as a result of the inquiry the Freedmen's Bureau Bill was passed, which established the Freedmen's Bureau as initiated by U.S. President Abraham Lincoln. It was intended to last for one year after the end of the Civil War. The Bureau became a part of the United States Department of War, as Congress provided no funding for it. The War Department was the only agency with funds the Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Baptists
Free Will Baptists are a group of General Baptist denominations of Christianity that teach free grace, free salvation and free will. The movement can be traced back to the 1600s with the development of General Baptism in England. Its formal establishment is widely linked to the English theologian, Thomas Helwys who led the Baptist movement to believe in general atonement. He was an advocate of religious liberty at a time when to hold to such views could be dangerous and punishable by death. He died in prison as a consequence of the religious persecution of Protestant dissenters under King James I. In 1702 Paul Palmer would go on to establish the movement in North Carolina and in 1727 formed the Free Will Baptist Church of Chowan. Many Calvinists became Free Will Baptists in the 19th century. With the establishment of Free Will Baptists in the South, Benjamin Randall developed the movement in the Northeastern United States, specifically Maine, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |