|
Stonea
Stonea is a hamlet in Cambridgeshire, England, south east of March and part of the parish of Wimblington.Wimblington at Genuki.org.uk, accessed 20 September 2013 Stonea today consists of a scattered collection of farmsteads and houses, the majority sited along Sixteen Foot Bank, a man-made river which forms part of the . The largest settlement is on the bank near the Golden Lion pub. A former chapel is now a private residence. This part of Stonea is dissected by a staffed railway crossing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stonea Camp Bank And Ditch - Geograph
Stonea is a hamlet in Cambridgeshire, England, south east of March and part of the parish of Wimblington.Wimblington at Genuki.org.uk, accessed 20 September 2013 Stonea today consists of a scattered collection of farmsteads and houses, the majority sited along Sixteen Foot Bank, a man-made river which forms part of the . The largest settlement is on the bank near the Golden Lion pub. A former chapel is now a private residence. This part of Stonea is dissected by a staffed railway crossing on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
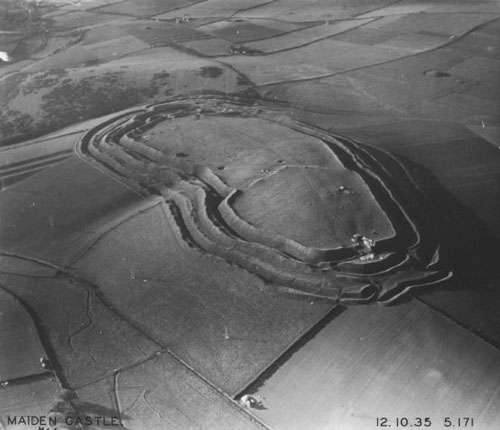
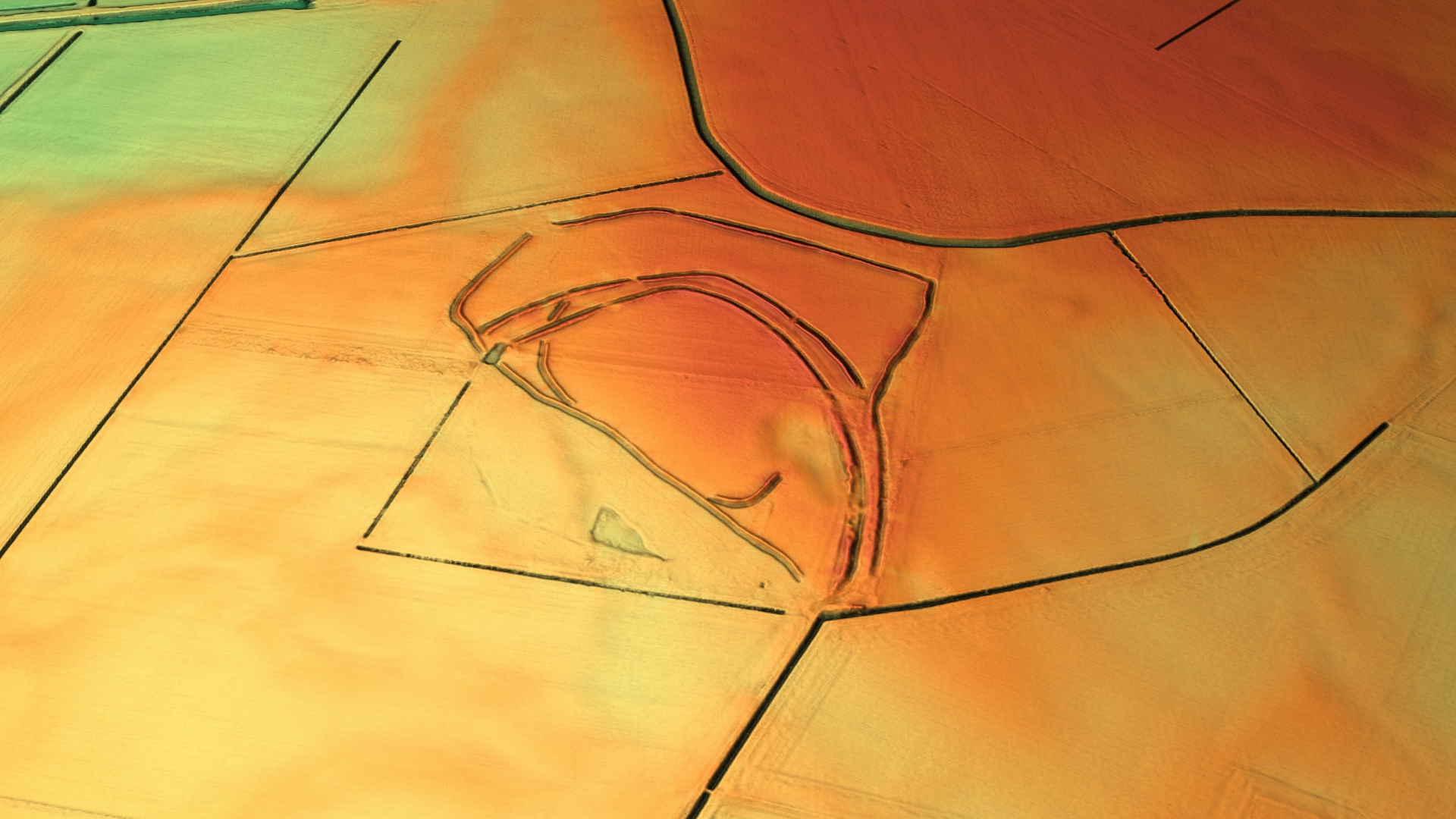
Stonea Camp
Stonea Camp is an Iron Age multivallate hill fort located at Stonea near March in the Cambridgeshire Fens. Situated on a gravel bank just above sea-level, it is the lowest hill fort in Britain. Around 500 BC, when fortification is thought to have begun at this site, this "hill" would have provided a significant area of habitable land amidst the flooded marshes of the fens. The site exhibits at least two phases of development over several hundred years of settlement, with a D-shaped set of earth banks surrounded by a larger, more formal set of banks and ditches. Roman control The fort is a possible site of the battle of 47 AD mentioned by Tacitus, between the Iceni tribe and a Roman auxiliary force under governor Ostorius Scapula. It has also been speculated that the remains relate to the campaign to subdue the Iceni after the Boudiccan Revolt. Human remains have been found around the site including sword-marked adult bones and the cleaved skull of a child, indicating that the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stonea Railway Station
Stonea railway station is a former railway station serving the small village of Stonea, Cambridgeshire Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a Counties of England, county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and North ....British Railways Atlas.1947. p.11 Although the station closed in 1966, the line is still in use. References External links Stonea station on navigable 1946 O. S. map Disused railway stations in Cambridgeshire Former Great Eastern Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1847 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1966 1847 establishments in England Fenland District {{EastEngland-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wimblington
Wimblington is a village in the Isle of Ely, Cambridgeshire, England, with a population of 1700 as of the 2001 census, including Stonea and increasing to 2,211 at the 2011 Census. History The place-name 'Wimblington' is first attested in a document of circa 975, where it appears as ''Wimblingetune''. The name means 'the town or settlement of Winebald's people'.Eilert Ekwall, ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Place-names'', p.521. Formerly a hamlet of the large Doddington parish, in 1874 it became a separate parish and a new church, St Peter's, was opened on 15 May of that year. The church was designed by Thomas Henry Wyatt. The village is effectively divided into two; a hamlet known as Eastwood End is separated from the main village by the A141 road, which was previously divided by the St Ives extension of the Great Eastern Railway line between March and Chatteris. Wimblington railway station closed in 1967. Wimblington won the ''Cambridgeshire Times'' and ''Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostorius Scapula
Publius Ostorius Scapula standing at the terrace of the Roman Baths (Bath) Publius Ostorius Scapula (died 52) was a Roman statesman and general who governed Britain from 47 until his death, and was responsible for the defeat and capture of Caratacus. Career Publius Ostorius Scapula was probably the son of Quintus Ostorius Scapula, the first joint commander of the Praetorian Guard appointed by Augustus and later prefect of Egypt. Nothing is known of his early career. He was suffect consul, probably in 46. In the winter of 47 he was appointed the second governor of Roman Britain by the emperor Claudius, succeeding Aulus Plautius. The south and east of the island was securely occupied and alliances had been made with tribes outside the Roman-controlled area, but other tribes continued to resist. Believing a new governor would be reluctant to campaign so late in the year, they staged attacks and uprisings. Ostorius disabused them of this notion and responded vigorously, attacking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceni
The Iceni ( , ) or Eceni were a Brittonic tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the west, and the Catuvellauni and Trinovantes to the south. In the Roman period, their capital was Venta Icenorum at modern-day Caistor St Edmund. Julius Caesar does not mention the Iceni in his account of his invasions of Britain in 55 and 54 BC, though they may be related to the Cenimagni, whom Caesar notes as living north of the River Thames at that time. The Iceni were a significant power in eastern Britain during Claudius' conquest of Britain in AD 43, in which they allied with Rome. Increasing Roman influence on their affairs led to revolt in AD 47, though they remained nominally independent under king Prasutagus until his death around AD 60. Roman encroachment after Prasutagus' death led his wife Boudica to launch a major revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post- Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of earthworks, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. Hillforts developed in the Late Bronze and Early Iron Age, roughly the start of the first millennium BC, and were used in many Celtic areas of central and western Europe until the Roman conquest. Nomenclature The spellings "hill fort", "hill-fort" and "hillfort" are all used in the archaeological literature. The ''Monument Type Thesaurus'' published by the Forum on Information Standards in Heritage lists ''hillfort'' as the preferred term. They all refer to an elevated site with one or more ramparts made of earth, stone and/or wood, with an external dit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Methodist
The Primitive Methodist Church is a Methodist Christian denomination with the holiness movement. It began in England in the early 19th century, with the influence of American evangelist Lorenzo Dow (1777–1834). In the United States, the Primitive Methodist Church had eighty-three parishes and 8,487 members in 1996. In Great Britain and Australia, the Primitive Methodist Church merged with other denominations, to form the Methodist Church of Great Britain in 1932 and the Methodist Church of Australasia in 1901. The latter subsequently merged into the Uniting Church in Australia in 1977. Beliefs The Primitive Methodist Church recognizes the dominical sacraments of Baptism and Holy Communion, as well as other rites, such as Holy Matrimony. History United Kingdom The leaders who originated Primitive Methodism were attempting to restore a spirit of revivalism as they felt was found in the ministry of John Wesley, with no intent of forming a new church. The leaders were Hugh B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fay Weldon
Fay Weldon CBE, FRSL (born Franklin Birkinshaw; 22 September 1931 – 4 January 2023) was an English author, essayist and playwright. Over the course of her 55-year writing career, she published 31 novels, including '' Puffball'' (1980), '' The Cloning of Joanna May'' (1989), ''Wicked Women'' (1995)'' and The Bulgari Connection'' (2000), but was most well-known as the writer of '' The Life and Loves of a She-Devil'' (1983) which was televised by the BBC in 1986. Married three times and with four children, Weldon was a self-declared feminist. Her work features what she described as "overweight, plain women". She said there were many reasons why she became a feminist, including the "appalling" lack of equal opportunities and the myth that women were supported by male relatives. Early life Weldon was born Franklin Birkinshaw to a literary family in Birmingham, England, on 22 September 1931. Her maternal grandfather, Edgar Jepson (1863–1938), her uncle Selwyn Jepson and her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tales Of The Unexpected Episodes
This is a list of episodes of the British anthology drama series, '' Tales of the Unexpected''. Series overview Episodes Series 1 (1979) Nine episodes. First broadcast: Saturdays on ITV – 24 March to 19 May 1979 Series 2 (1980) Sixteen episodes. First broadcast: ITV – Saturdays 1 March to 14 June 1980 Series 3 (1980) Nine episodes. First broadcast: Saturdays, Sundays and a Friday on ITV – 9 to 30 August and 9 November to 19 December 1980 Series 4 (1981) Seventeen episodes. First broadcast: Sundays and a Saturday on ITV – 5 April to 26 July and 26 December 1981. Series 5 (1982–1983) Eighteen episodes. First broadcast: Sundays on ITV – 25 April 1982 to 2 January 1983 Series 6 (1983) Fourteen episodes. Series 7 (1984) Fifteen episodes. First broadcast: Saturdays and Sundays on ITV – 12 May to 21 October 1984 Series 8 (1985) Four episodes. First broadcast: 1 Saturday and 3 Sundays on ITV – 30 March and 14 to 28 July 1985 Series 9 (1987� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procurator (Roman)
Procurator (plural: ''Procuratores'') was a title of certain officials (not magistrates) in ancient Rome who were in charge of the financial affairs of a province, or imperial governor of a minor province. Fiscal officers A fiscal procurator (''procurator Augusti'') was the chief financial officer of a province during the Principate (30 BC – AD 284). A fiscal procurator worked alongside the '' legatus Augusti pro praetore'' (imperial governor) of his province but was not subordinate to him, reporting directly to the emperor. The governor headed the civil and judicial administration of the province and was the commander-in-chief of all military units deployed there. The procurator, with his own staff and agents, was in charge of the province's financial affairs, including the following primary responsibilities: *the collection of taxes, especially the land tax (''tributum soli''), poll tax (''tributum capitis''), and the ''portorium'', an imperial duty on the carriage of goods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |