|
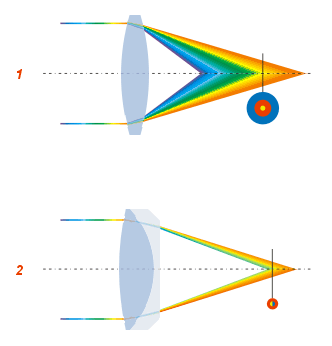
Stigmatism
In geometric optics, stigmatism refers to the image-formation property of an optical system which focuses a single point source in one phase optics space into a single point in image space. Two such points are called a stigmatic pair of the optical system. Many optical systems, even those exhibiting optical aberrations, including astigmatism, have at least one stigmatic pair. Stigmatism is applicable only in the approximation provided by geometric optics Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician .... In reality, image formation is, at best diffraction-limited, and point-like images are not possible due to the wave nature of light. References * {{cite book , first=Dietrich , last=Korsch , year=1991 , title=Reflective Optics , publisher=Academic Press , isbn=0-12-421 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astigmatism (optical Systems)
An optical system with astigmatism is one where rays that propagate in two perpendicular planes have different foci. If an optical system with astigmatism is used to form an image of a cross, the vertical and horizontal lines will be in sharp focus at two different distances. The term comes from the Greek α- (''a-'') meaning "without" and στίγμα (''stigma''), "a mark, spot, puncture". Forms of astigmatism There are two distinct forms of astigmatism. The first is a third-order aberration, which occurs for objects (or parts of objects) away from the optical axis. This form of aberration occurs even when the optical system is perfectly symmetrical. This is often referred to as a "monochromatic aberration", because it occurs even for light of a single wavelength. This terminology may be misleading, however, as the ''amount'' of aberration can vary strongly with wavelength in an optical system. The second form of astigmatism occurs when the optical system is not symmetri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Optics
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a '' geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. Originally developed to model the physical world, geometry has applications in almost all sciences, and also in art, architecture, and other activities that are related to graphics. Geometry also has applications in areas of mathematics that are apparently unrelated. For example, methods of algebraic geometry are fundamental in Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, a problem that was stated in terms of elementary arithmetic, and remained unsolved for several centuries. Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Aberrations
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as lenses and mirrors, that causes the ''image'' created by the optical system to not be a faithful reproduction of the ''object'' being observed. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred, distorted in shape or have color fringing or other effects not seen in the object, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which is not sharp. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Limited
In optics, any optical instrument or systema microscope, telescope, or camerahas a principal limit to its resolution due to the physics of diffraction. An optical instrument is said to be diffraction-limited if it has reached this limit of resolution performance. Other factors may affect an optical system's performance, such as lens imperfections or aberrations, but these are caused by errors in the manufacture or calculation of a lens, whereas the diffraction limit is the maximum resolution possible for a theoretically perfect, or ideal, optical system. The diffraction-limited angular resolution, in radians, of an instrument is proportional to the wavelength of the light being observed, and inversely proportional to the diameter of its objective's entrance aperture. For telescopes with circular apertures, the size of the smallest feature in an image that is diffraction limited is the size of the Airy disk. As one decreases the size of the aperture of a telescopic lens, diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |