|
Stephen W. Kearney
Stephen Watts Kearny (sometimes spelled Kearney) ( ) (August 30, 1794October 31, 1848) was one of the foremost antebellum frontier officers of the United States Army. He is remembered for his significant contributions in the Mexican–American War, especially the Conquest of California. The Kearny Code, proclaimed on September 22, 1846, in Santa Fe, established the law and government of the newly acquired territory of New Mexico and was named after him. His nephew was Major General Philip Kearny of American Civil War fame. Early years Stephen Watts Kearny was the fifteenth and youngest child of Philip and Susanna Watts Kearny. His father, who was of Irish ancestry (the family name had originally been O'Kearny), was a successful wine merchant and landowner in Perth Amboy, New Jersey, before the start of the American Revolution (1775–83). Kearny was born in Newark, New Jersey, the son of Philip Kearny Sr. and Susanna Watts. His maternal grandparents were the wealthy merchant Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Governors Of New Mexico
The governor of New Mexico is the head of government of New Mexico New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ... and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The governor has a duty to enforce state laws, the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the New Mexico Legislature, to convene the legislature at any time, and to grant pardons. Twenty-eight individuals have held the office of governor of New Mexico since the state's admission to the Union in 1912, two of whom— Edwin L. Mechem and Bruce King—served three non-consecutive terms. King holds the record as New Mexico's longest-serving governor, with 12 years of service. William C. McDonald, the first governor, took office on January 15, 1912. The first woman to serve as Governor was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, (April 25, 1846 – February 2, 1848) was an invasion of Second Federal Republic of Mexico, Mexico by the United States Army. It followed the 1845 American annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered its territory because it refused to recognize the Treaties of Velasco, signed by President Antonio López de Santa Anna after he was captured by the Texian Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was ''de facto'' an independent country, but most of its Anglo-American citizens who had moved from the United States to Texas after 1822 wanted to be annexed by the United States. Sectional politics over slavery in the United States had previously prevented annexation because Texas would have been admitted as a slave state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Kearny
Philip Kearny Jr. (; June 1, 1815 – September 1, 1862) was a United States Army officer, notable for his leadership in the Mexican–American War and American Civil War. He served in Emperor of the French, French Emperor Napoleon III's Imperial Guard (Napoleon III), Imperial Guard at the Battle of Solferino. The first U.S. citizen to be awarded the French ''Légion d’Honneur, Légion d'Honneur'', he was killed in action in the 1862 Battle of Chantilly. Early life and career Kearny was born in New York City to a wealthy Irish American family. His father and mother were Philip Kearny Sr., and Susan Watts. His maternal grandfather John Watts (New York politician), John Watts, the last Royal Recorder of New York City, was one of New York's wealthiest residents, who had vast holdings in ships, mills, factories, banks, and investment houses. Kearny's father was a Harvard-educated, New York City financier who owned his own brokerage firm and was also a founder of the New York Stock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
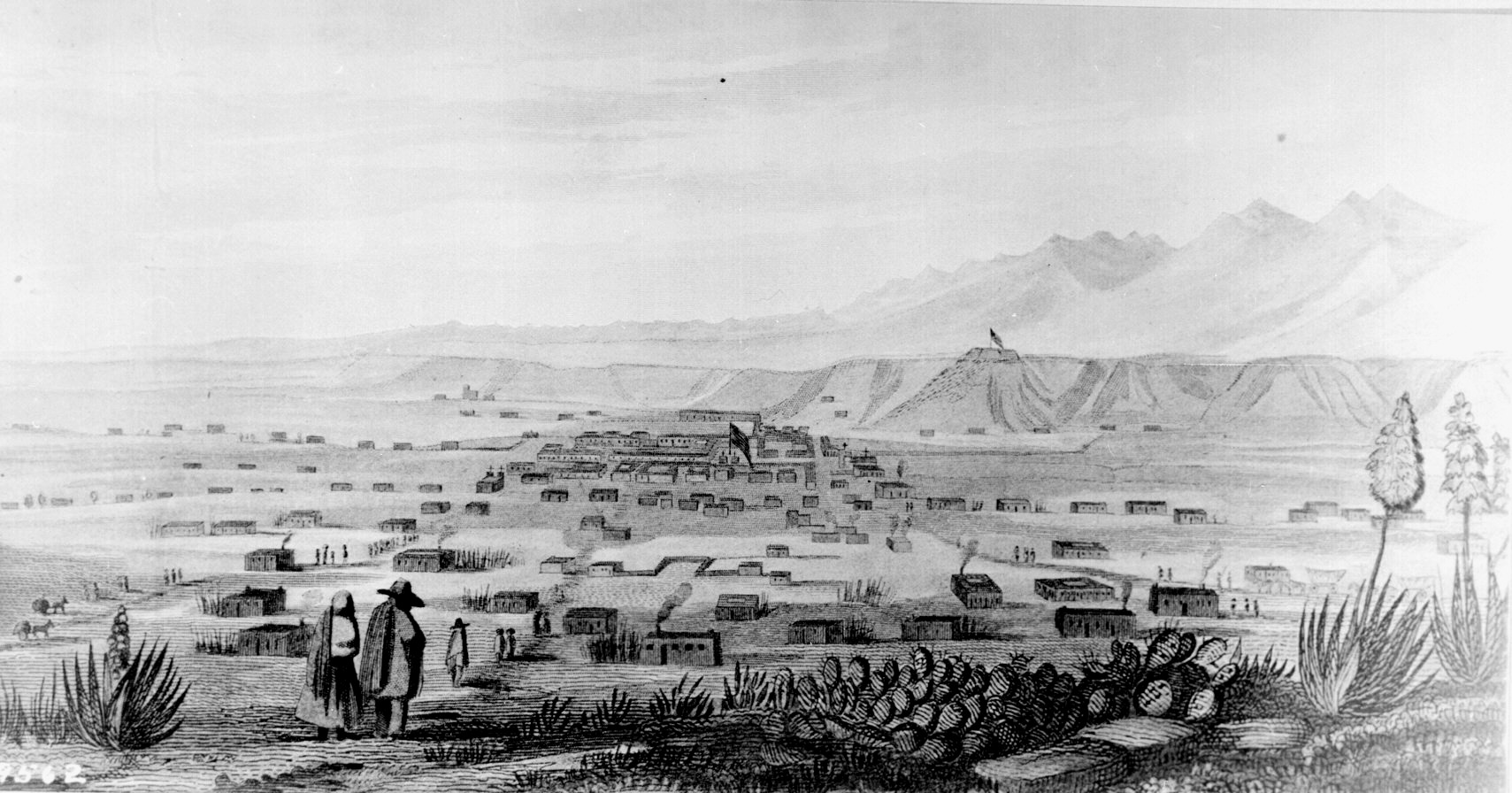
Santa Fe, New Mexico
Santa Fe ( ; , literal translation, lit. "Holy Faith") is the capital city, capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico, and the county seat of Santa Fe County. With over 89,000 residents, Santa Fe is the List of municipalities in New Mexico, fourth-most populous city in the state and the principal city of the Santa Fe metropolitan statistical area, which had 154,823 residents in 2020. Santa Fe is the third-largest city in the Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque–Santa Fe–Los Alamos, New Mexico, Los Alamos Albuquerque–Santa Fe–Los Alamos combined statistical area, combined statistical area, which had a population of 1,162,523 in 2020. Situated at the foothills of the Sangre de Cristo Mountains, the city is at the highest altitude of any U.S. state capital, with an elevation of 6,998 feet (2,133 m). Founded in 1610 as the capital of ', a province of New Spain, Santa Fe is the oldest List of capitals in the United States, state capital in the United States and the earliest E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of California
The Conquest of California, also known as the Conquest of Alta California or the California Campaign, was a military campaign during the Mexican–American War carried out by the United States in Alta California (modern-day California), then part of Mexico, lasting from 1846 to 1847, and ending with signing of the Treaty of Cahuenga by military leaders from both the Californios and Americans. Background When war was declared on May 13, 1846, between the United States and Mexico, it took almost three months for definitive word of Congress' declaration of war to reach the Pacific coast. U.S. consul Thomas O. Larkin, stationed in the pueblo of Monterey, California, Monterey, was concerned about the increasing possibility of war and worked to prevent bloodshed between the Americans and the small Mexican military garrison at the Presidio of Monterey, California, Presidio of Monterey, commanded by José Castro. United States Army Captain John C. Frémont, on a United States Army Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789).See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 It operates under the authority, direction, and control of the United States Secretary of Defense, United States secretary of defense. It is one of the six armed forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. The Army is the most senior branch in order of precedence amongst the armed services. It has its roots in the Continental Army, formed on 14 June 1775 to fight against the British for independence during the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783). After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontier
A frontier is a political and geographical term referring to areas near or beyond a boundary. Australia The term "frontier" was frequently used in colonial Australia in the meaning of country that borders the unknown or uncivilised, the boundary, border country, the borders of civilisation, or as the land that forms the furthest extent of what was frequently termed "the inside" or "settled" districts. The "outside" was another term frequently used in colonial Australia, this term seemingly covered not only the frontier but the districts beyond. Settlers at the frontier thus frequently referred to themselves as "the outsiders" or "outside residents" and to the area in which they lived as "the outside districts". At times one might hear the "frontier" described as "the outside borders". However the term "frontier districts" was seemingly used predominantly in the early Australian colonial newspapers whenever dealing with skirmishes between black and white in northern New S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The United States (1789–1849)
The history of the present-day United States began in roughly 15,000 BC with the arrival of Peopling of the Americas, the first people in the Americas. In the late 15th century, European colonization of the Americas, European colonization began and wars and epidemics largely decimated Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous societies. By the 1760s, the Thirteen Colonies, then part of British America and the Kingdom of Great Britain, were established. The Southern Colonies built an agricultural system on Slavery in the United States, slave labor and Atlantic slave trade, enslaving millions from Africa. After the British victory over the Kingdom of France in the French and Indian Wars, Parliament of Great Britain, Parliament imposed a series of taxes and issued the Intolerable Acts on the colonies in 1773, which were designed to end self-governance. Tensions between the colonies and British authorities subsequently intensified, leading to the American Revolutionary War, Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevet (military)
In military terminology, a brevet ( or ) is a warrant which gives commissioned officers a higher military rank as a reward without necessarily conferring the authority and privileges granted by that rank. The promotion would be noted in the officer's title (for example, "Bvt. Maj. Gen. Joshua L. Chamberlain" or "Bvt. Col. Arthur MacArthur"). It is not to be confused with a '' Brevet d'état-major'' in Francophone European military circles, where it is an award, nor should it be confused with temporary commissions. France In France, ''brevet'' is a word with a very broad meaning, which includes every document giving a capacity to a person. For instance, the various military speciality courses, such as military parachutism, are ended by the award of a brevet. The more important brevet in the French military is that of the École de guerre (''lit''. "school of war"), the French Staff College. Between 1870 and 1940, an ''officier breveté'' was a graduate of the ''École ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Army Major General Rank Insignia
Union commonly refers to: * Trade union, an organization of workers * Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets Union may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Union (band), an American rock group ** ''Union'' (Union album), 1998 * ''Union'' (Chara album), 2007 * ''Union'' (Toni Childs album), 1988 * ''Union'' (Cuff the Duke album), 2012 * ''Union'' (Paradoxical Frog album), 2011 * ''Union'', a 2001 album by Puya * ''Union'', a 2001 album by Rasa * ''Union'' (Son Volt album), 2019 * ''Union'' (The Boxer Rebellion album), 2009 * ''Union'' (Yes album), 1991 * "Union" (Black Eyed Peas song), 2005 Other uses in arts and entertainment * ''Union'' (film), a labor documentary released in 2024 * ''Union'' (Star Wars), a Dark Horse comics limited series * Union, in the fictional Alliance–Union universe of C. J. Cherryh * ''Union (Horse with Two Discs)'', a bronze sculpture by Christopher Le Brun, 1999–2000 * The Union (Marvel Team), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |