|
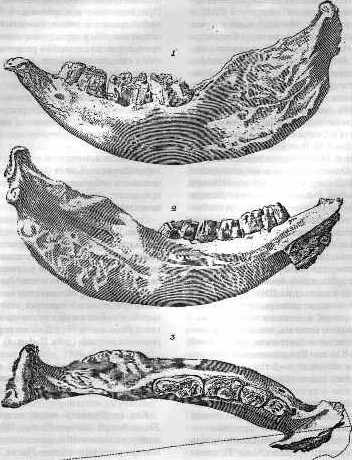
Stephanorhinus Kirchbergensis
''Stephanorhinus kirchbergensis'', also known as Merck's rhinoceros (or the less commonly, the forest rhinoceros) is an extinct species of rhinoceros belonging to the genus ''Stephanorhinus'' that lived from the end of the Early Pleistocene (around 800,000 years ago) until its extinction in the Late Pleistocene (surviving until at least 40,000 years ago and possibly later) in Eurasia. Its range spanned from Western Europe to East Asia. Among the last members of the genus, it co-existed alongside '' Stephanorhinus hemitoechus'' (the narrow-nosed or steppe rhinoceros) in the western part of its range. Description Merck's rhinoceros was a large rhinoceros, with a body mass in the range of , with a 2016 study estimating an average body weight of around . A particularly large specimen from Poland reached an estimated height at the withers of . It is one of the largest species of ''Stephanorhinus'', exceeding ''S. hundsheimensis'' and '' S. hemitoechus'' in size. The bones of the ske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephanorhinus
''Stephanorhinus'' is an extinct genus of two-horned rhinoceros native to Eurasia and North Africa that lived during the Late Pliocene to Late Pleistocene. Species of ''Stephanorhinus'' were the predominant and often only species of rhinoceros in much of temperate Eurasia, especially Europe, for most of the Pleistocene. The last two species of ''Stephanorhinus'' – Merck's rhinoceros (''S. kirchbergensis'') and the narrow-nosed rhinoceros (''S. hemitoechus'') – went extinct during the last glacial period. Etymology The first part of the name, ''Stephano-'', honours Stephen I, the first king of Hungary. (The genus name was coined by Kretzoi, a Hungarian.) The second part is from (Greek for "nose"), a typical suffix of rhinoceros genus names. Taxonomy The taxonomic history of ''Stephanorhinus'' is long and convoluted, as many species are known by numerous synonyms and different genera – typically ''Rhinoceros'' and '' Dicerorhinus'' – for the 19th and most of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Friedrich Von Jäger
Georg Friedrich Jäger, from 1850 Georg Friedrich von Jäger (25 December 1785 – 10 September 1866), was a German physician and paleontologist. Life Jäger was born in Stuttgart, the son of physician Christian Friedrich von Jäger and Luise Frieder. An older brother was Carl Christoph Friedrich von Jäger (1773–1828), and he was introduced to natural history at an early age. Georg Friedrich went to study medicine at the University of Tübingen, Tübingen University, receiving a degree in 1808. After travels through Switzerland and France (where Georges Cuvier, Cuvier allowed him to study collections at the Jardin des plantes, Jardin des Plantes) he returned to practice medicine in Stuttgart, and in 1817 he became a director of the royal natural history cabinet. In 1824 he published on Ichthyosaur, ichthyosaurs and plant fossils discovered by Albert Mohr. He continued publishing on plant fossils, and described some mammal and reptile fossils from Stuttgart. A species of Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
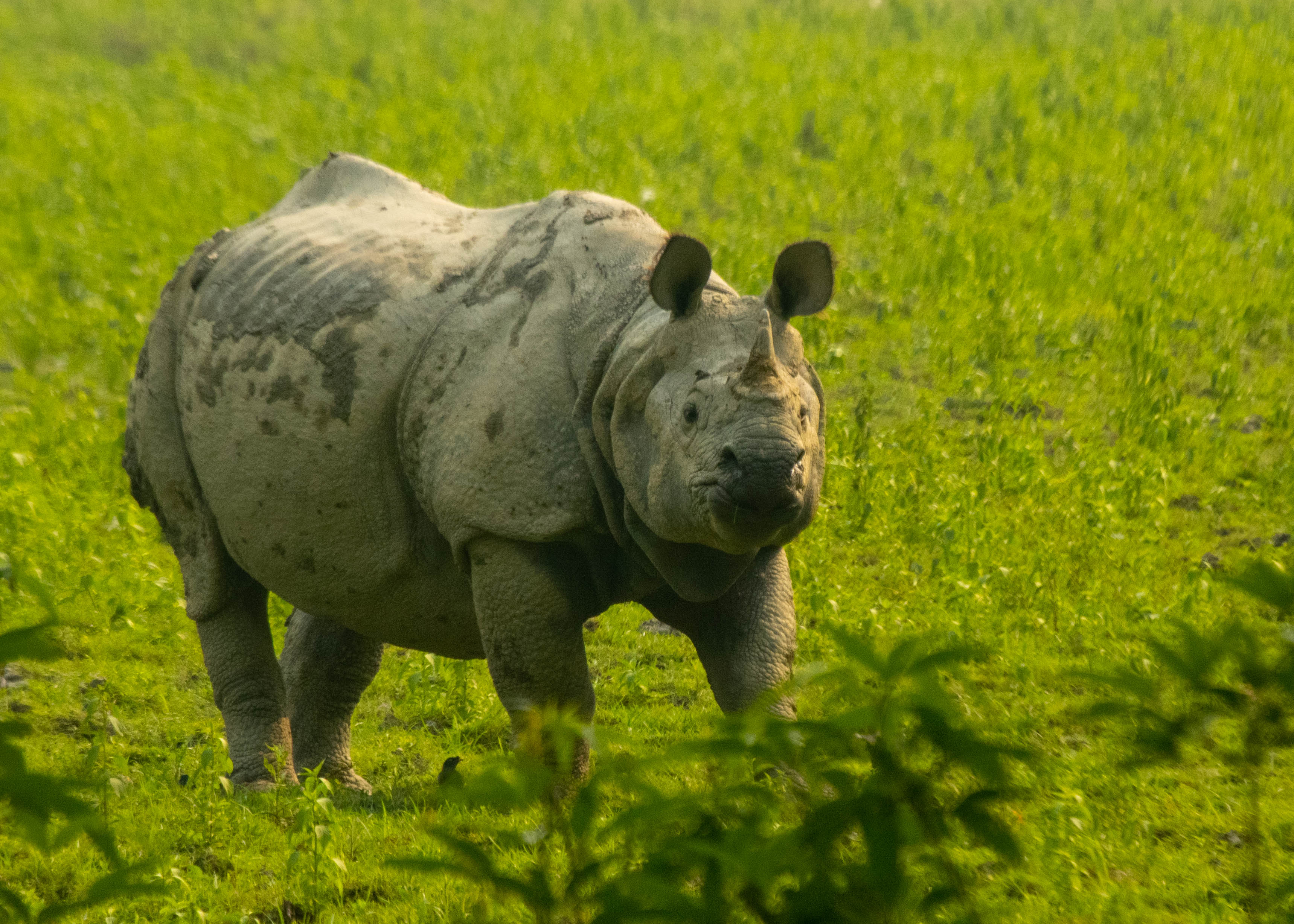
Indian Rhinoceros
The Indian rhinoceros (''Rhinoceros unicornis''), also known as the greater one-horned rhinoceros, great Indian rhinoceros or Indian rhino, is a species of rhinoceros found in the Indian subcontinent. It is the second largest living rhinoceros species, with adult males weighing and adult females . Its thick skin is grey-brown with pinkish skin folds. It has a single horn on its snout that grows up to long. Its upper legs and shoulders are covered in wart-like bumps, and it is nearly hairless aside from the eyelashes, ear fringes and tail brush. The Indian rhinoceros is native to the Indo-Gangetic Plain and occurs in 12 protected areas in northern India and southern Nepal. It is a Grazing (behaviour), grazer, eating mainly grass, but also twigs, leaves, branches, shrubs, flowers, fruits and aquatic plants. It is a largely solitary animal, only associating in the breeding season and when rearing calves. Females give birth to a single calf after a gestation of 15.7 months. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
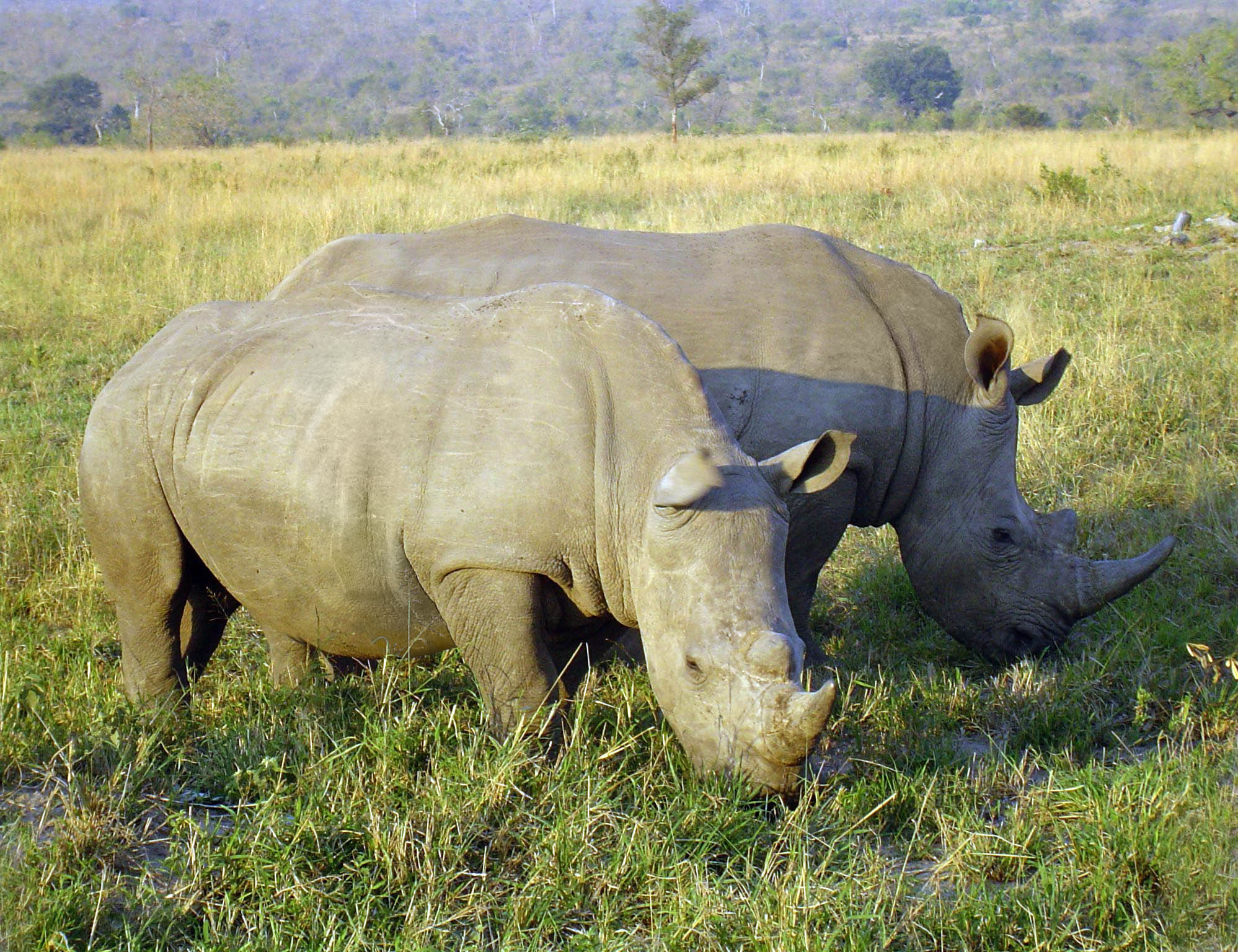
White Rhinoceros
The white rhinoceros, also known as the white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''), is the largest extant species of rhinoceros and the most Sociality, social of all rhino species, characterized by its wide mouth adapted for grazing (behaviour), grazing. The species includes two subspecies with dramatically different conservation outlooks: the southern white rhinoceros, with an estimated 17,464 individuals in the wild as of the end of 2023, and the northern white rhinoceros. The northern subspecies is critically endangered and on the brink of extinction; its last known male, Sudan (rhinoceros), Sudan, died in March 2018, leaving behind only a very small number of females in captivity. Both subspecies have faced significant threats, primarily from poaching for their horns and habitat loss, which contribute to the species' overall Conservation status, conservation status of Near Threatened. Naming One popular, though widely discredited, theory for the origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmotherium Sibiricum
''Elasmotherium'' is an extinction, extinct genus of large rhinoceros that lived in Eastern Europe, Central Asia and East Asia during Late Miocene through to the Late Pleistocene, with the youngest reliable dates of at least 39,000 years ago. It was the last surviving member of Rhinoceros#Rhinocerotidae, Elasmotheriinae, a distinctive group of rhinoceroses separate from the group that contains living rhinoceros (Rhinocerotinae). Five species are recognised. The genus first appeared in the Late Miocene in present-day China, likely having evolved from ''Sinotherium'', before spreading to the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Caucasus and Central Asia. The best known ''Elasmotherium'' species, ''E. sibiricum'', sometimes called the Siberian unicorn, was among the largest known rhinoceroses, with an estimated body mass of around , comparable to an elephant, and is often conjectured to have borne a single very large horn. However, no horn has ever been found, and other authors have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that inhabited northern Eurasia during the Pleistocene epoch. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was large, comparable in size to the largest living rhinoceros species, the white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''), and covered with long, thick hair that allowed it to survive in the extremely cold, harsh mammoth steppe. It had a massive hump reaching from its shoulder and fed mainly on herbaceous plants that grew in the steppe. Mummified carcasses preserved in permafrost and many bone remains of woolly rhinoceroses have been found. Images of woolly rhinoceroses are found among cave paintings in Europe and Asia, and evidence has been found suggesting that the species was hunted by humans. The range of the woolly rhinoceros contracted towards Siberia beginning around 17,000 years ago, with the youngest known r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatran Rhinoceros
The Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis''), also known as the Sumatran rhino, hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros, is a rare member of the family Rhinocerotidae and one of five extant species of rhinoceros; it is the only Extant taxon, extant species of the genus ''Dicerorhinus''. It is the smallest rhinoceros, although it is still a large mammal; it stands high at the shoulder, with a head-and-body length of and a tail of . The weight is reported to range from , averaging . Like both African species, it has two horns; the larger is the nasal horn, typically , while the other horn is typically a stub. A coat of reddish-brown hair covers most of the Sumatran rhino's body. The Sumatran rhinoceros once inhabited rainforests, swamps and cloud forests in India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and southwestern China, particularly in Sichuan. It is now critically endangered, with only five substantial populations in the wild: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piacenzian
The Piacenzian is in the international geologic time scale the upper stage (stratigraphy), stage or latest age (geology), age of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 3.6 ± 0.005 year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma and 2.58 Ma (million years ago). The Piacenzian is after the Zanclean and is followed by the Gelasian (part of the Pleistocene). The Piacenzian is roughly coeval with the European land mammal age MN 16, overlaps the late Chapadmalalan and early Uquian South American land mammal age and falls inside the more extensive Blancan North American land mammal age. It also correlates with the Astian, Redonian, Reuverian and Romanian regional stages of Europe, and the Waipipian and Mangapanian stages of New Zealand geologic time scale, New Zealand. Some authorities describe the British Red Crag Formation and Waltonian Stage as late Piacenzian, while others regard them as early Pleistocene. Carbon dioxide levels during the Piacenzian were similar to those of today, making this age, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Jakob Kaup
Johann Jakob von Kaup (10 April 1803 – 4 July 1873) was a German naturalist. A proponent of natural philosophy, he believed in an innate mathematical order in nature and he attempted biological classifications based on the Quinarian system. Kaup is also known for having coined popular prehistoric taxa like ''Pterosauria'', ''Machairodus'', ''Deinotherium'', ''Dorcatherium'', and ''Chalicotherium''. Biography He was born at Darmstadt. After studying at Göttingen and Heidelberg he spent two years at Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie, Leiden, where his attention was specially devoted to the amphibians and fishes. He then returned to Darmstadt as an assistant in the grand ducal museum, of which in 1840 he became inspector. In 1829 he published ''Skizze zur Entwickelungsgeschichte der europäischen Thierwelt'', in which he regarded the animal world as developed from lower to higher forms, from the amphibians through the birds to the beasts of prey; but subsequently he repudiated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The Botanical nomenclature, botanical and Zoological nomenclature, zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In nomenclature, botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a Binomial nomenclature, scientific name that applies to a taxon that now goes by a different scientific name. For example, Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different Binomial nomenclature, binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Oblitum
In zoological nomenclature, a ''nomen oblitum'' (plural: ''nomina oblita''; Latin for "forgotten name") is a disused scientific name which has been declared to be obsolete (figuratively "forgotten") in favor of another "protected" name. In its present meaning, the ''nomen oblitum'' came into being with the fourth edition (1999) of the ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature''. After 1 January 2000, a scientific name may be formally declared to be a ''nomen oblitum'' when it satisfy the following conditions: # No uses as a valid name in a scientific publication are known after 1899 (this criterion is taken on faith). # It is either a senior synonym (there is also a more recent name which applies to the same taxon, and which is in common use) or a senior homonym (it is spelled the same as another name, which is also in valid use). # The preferred junior synonym or homonym is shown to be in wide use, defined as appearing in 25 or more publications in the past 50 years (must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |