|
Steeple Claydon
Steeple Claydon is a village and civil parish in the Buckinghamshire district of the ceremonial county of Buckinghamshire, England. The village is about south of Buckingham, west of Winslow and northwest of Waddesdon. The 2011 Census recorded the parish population as 2,278. History The toponym "Claydon" is derived from the Old English for "clay hill". The Domesday Book of 1086 records the area (including nearby Botolph Claydon, East Claydon and Middle Claydon) as ''Claindone''. The affix "steeple" refers to the steeple of the Church of England parish church, which is prominent in the village. The manor of Steeple Claydon was once a royal possession. It was given as a wedding gift to Robert D'Oyly by King Henry I because D'Oyly was marrying one of the king's former mistresses. Later, after changing hands several times it came into the possession of King Edward IV when his grandfather the Earl of March left it to him. The manor house has since been pulled down. Thomas Chalon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert D'Oyly (Osney)
Robert D'Oyly was a 12th-century English nobleman, son of Nigel D'Oyly, and nephew of Robert D'Oyly, founder of Oxford Castle. Robert married Edith Forne, daughter of Lord Greystoke, who had been King Henry I of England's concubine, in 1120. The marriage also meant Robert became Lord of the Manor of Cleydon.''Victoria County History of Oxford Volume IV'' by Alan Crossley, 1969 In 1129, he was persuaded by his wife to build the Church of St Mary, in the Isle of Osney, near Oxford Castle, for the use of Augustine Monks—this was to become Osney Abbey. By 1141 Robert had inherited his father's position of Lord of Oxford Castle and Baron Hocknorton and it was he that declared his support for Empress Matilda against King Stephen, giving her protection in Oxford between 1141 and the winter of 1142. It is because of this action that Stephen came to Oxford and besieged the castle for three months, burning the city down in the process. Matilda supposedly escaped by dressing in white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community School (England And Wales)
A community school in England and Wales is a type of state-funded school in which the local education authority employs the school's staff, is responsible for the school's admissions and owns the school's estate. The formal use of this name to describe a school derives from the School Standards and Framework Act 1998.School Standards and Framework Act 1998 Her Majesty's Stationery Office. Board School [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Baldock
George Henry Ivor Baldock (Greek: Τζορτζ Μπόλντοκ; born 9 March 1993) is a professional footballer who plays as a right back for club Sheffield United. Born in England, he plays for the Greece national team. Club career Milton Keynes Dons Baldock was born in Buckingham, Buckinghamshire. He started his career playing for Milton Keynes Dons' academy team. His older brother Sam Baldock also played for the club. 2009–10 Baldock made his first-team debut for Milton Keynes Dons on 1 May 2010 in the League One clash with Brighton & Hove Albion at the Stadium:mk which ended in 0–0 draw, coming on as a substitute for Daniel Powell in the 81st minute. 2010–11 Baldock made his full debut for the club on the last day of the 2010–11 season in a League One match against Oldham Athletic. 2011–12 On 30 October 2011, he joined Northampton Town on a month's loan. In March 2012 he joined Tamworth on loan, along with teammate Charlie Collins. He made his debut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sam Baldock
Samuel Edward Thomas Baldock (born 15 March 1989) is an English professional footballer who plays as a striker for Oxford United. He grew up in the village of Steeple Claydon, Buckinghamshire, while attending the Royal Latin School in Buckingham. Club career Milton Keynes Dons Baldock was born in Buckingham, Buckinghamshire. Having joined the Wimbledon F.C. youth system following the club's 2003 relocation to Milton Keynes, Baldock signed as a trainee in July 2004, just after the club renamed itself as Milton Keynes Dons. Danny Wilson handed Baldock his first team debut on 20 December 2005 in the 2–1 Football League Trophy loss to Colchester United as a late substitute in his only appearance of the season. Martin Allen as Dons manager for the 2006–07 season gave Baldock two further games in the first team in his only year in charge. Baldock failed to score as a substitute in either game as the Dons lost 4–1 away to Brighton & Hove Albion in the Football Leag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War, in which she organised care for wounded soldiers at Constantinople. She significantly reduced death rates by improving hygiene and living standards. Nightingale gave nursing a favourable reputation and became an icon of Victorian culture, especially in the persona of "The Lady with the Lamp" making rounds of wounded soldiers at night. Recent commentators have asserted that Nightingale's Crimean War achievements were exaggerated by the media at the time, but critics agree on the importance of her later work in professionalising nursing roles for women. In 1860, she laid the foundation of professional nursing with the establishment of her nursing school at St Thomas' Hospital in London. It was the first secular nursing school in the world an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
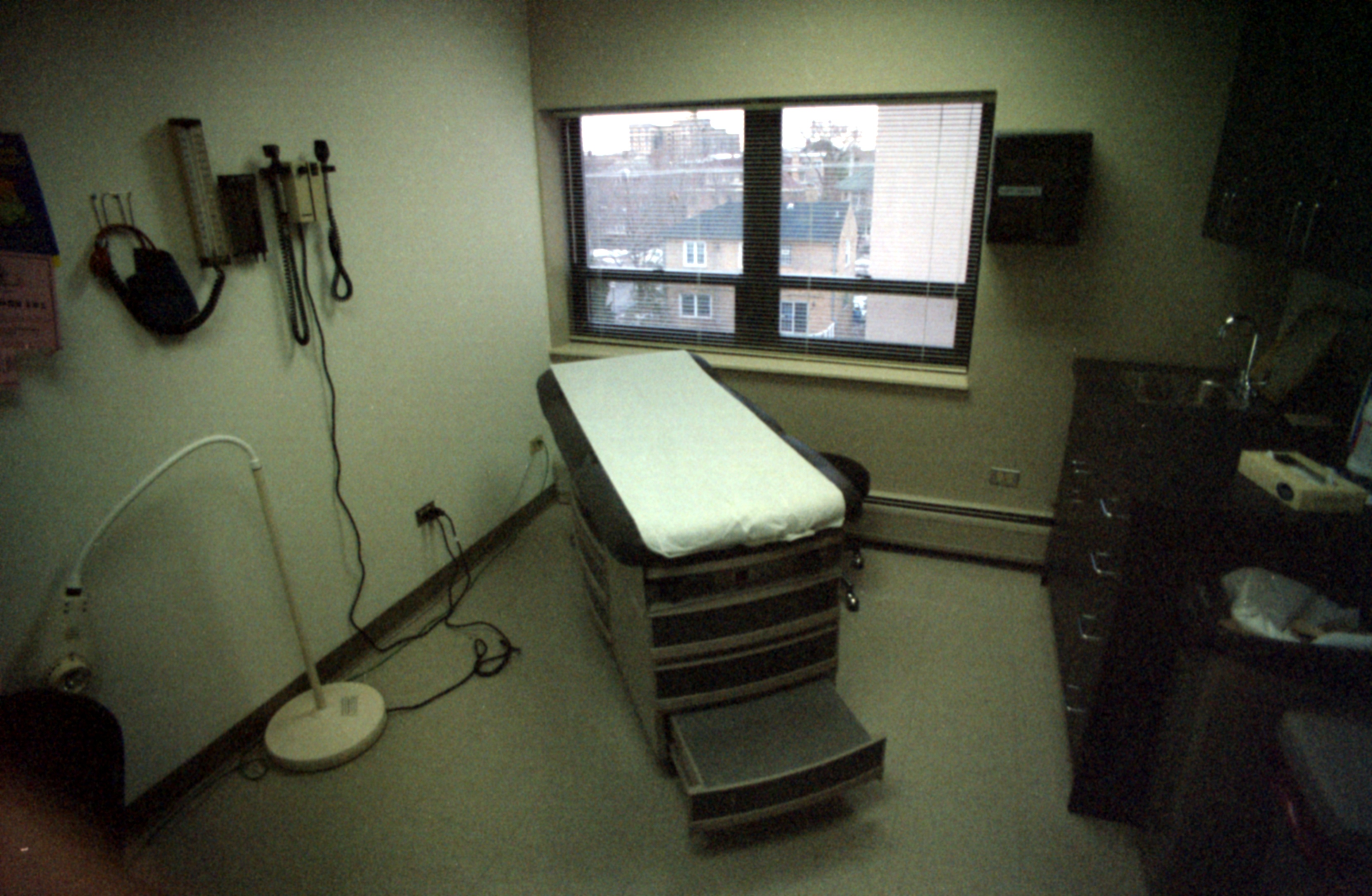
Doctor's Office
A doctor's office in American English, a doctor's surgery in British English, or a doctor's practice, is a medical facility in which one or more medical doctors, usually general practitioners (GP), receive and treat patients. Description Doctors' offices are the primary place where ambulatory care is given, and are often the first place that a sick person would go for care, except in an emergency, in which case one would go to an emergency department at a hospital. In developed countries, where health services are guaranteed by the state in some form, most medical visits to doctors take place in their offices. In the United States, where this is not the case, many people who cannot afford health insurance or doctor's visits must either go to free or reduced-cost clinics or an emergency department at a hospital for care, instead of a doctor's office. For healthy people, most visits to doctors' offices revolve around a once-yearly recommended physical examination. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish & Chips
Fish and chips is a popular hot dish consisting of fried fish in crispy batter, served with chips. The dish originated in England, where these two components had been introduced from separate immigrant cultures; it is not known who created the culinary fusion that became the emblematic British meal. Often considered Britain's national dish, fish and chips is a common take-away food in the United Kingdom and numerous other countries, particularly in English-speaking and Commonwealth nations. Fish and chip shops first appeared in the UK in the 1860s, and by 1910, there were over 25,000 fish and chip shops across the UK. By the 1930s there were over 35,000 shops, but the trend reversed, and by 2009 there were only approximately 10,000. The British government safeguarded the supply of fish and chips during the First World War, and again in the Second World War; it was one of the few foods in the UK not subject to rationing during the wars. History The UK tradition of ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Office
A post office is a public facility and a retailer that provides mail services, such as accepting letters and parcels, providing post office boxes, and selling postage stamps, packaging, and stationery. Post offices may offer additional services, which vary by country. These include providing and accepting government forms (such as passport applications), and processing government services and fees (such as road tax, postal savings, or bank fees). The chief administrator of a post office is called a postmaster. Before the advent of postal codes and the post office, postal systems would route items to a specific post office for receipt or delivery. During the 19th century in the United States, this often led to smaller communities being renamed after their post offices, particularly after the Post Office Department began to require that post office names not be duplicated within a state. Name The term "post-office" has been in use since the 1650s, shortly after the leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
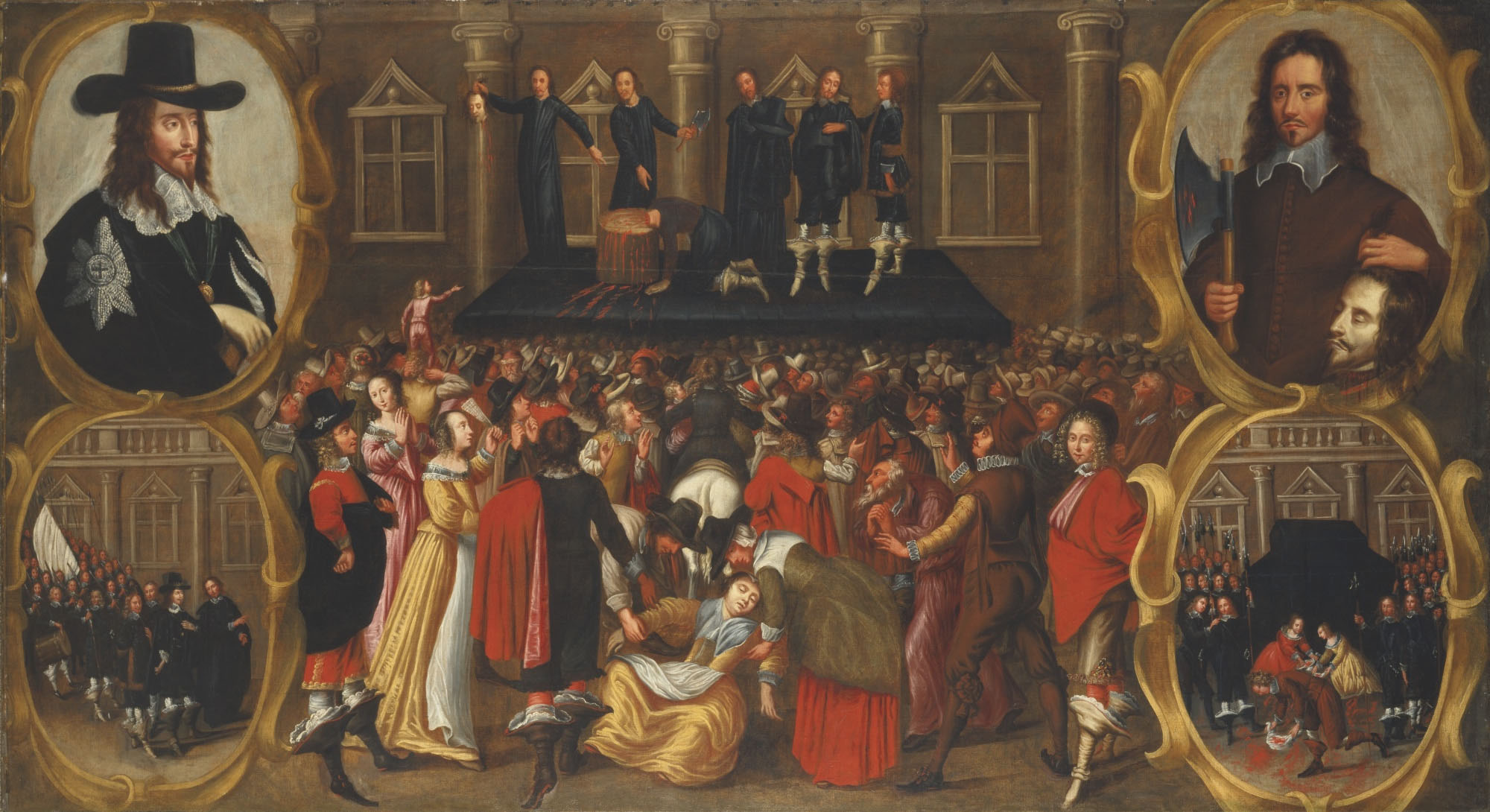
Regicide
Regicide is the purposeful killing of a monarch or sovereign of a polity and is often associated with the usurpation of power. A regicide can also be the person responsible for the killing. The word comes from the Latin roots of ''regis'' and ''cida'' (''cidium''), meaning "of monarch" and "killer" respectively. In the British tradition, it refers to the judicial execution of a king after a trial, reflecting the historical precedent of the trial and execution of Charles I of England. The concept of regicide has also been explored in media and the arts through pieces like ''Macbeth'' (Macbeth's killing of King Duncan) and '' The Lion King''. History In Western Christianity, regicide was far more common prior to 1200/1300. Sverre Bagge counts 20 cases of regicide between 1200 and 1800, which means that 6% of monarchs were killed by their subjects. He counts 94 cases of regicide between 600 and 1200, which means that 21.8% of monarchs were killed by their subjects. He a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Chaloner (regicide)
Thomas ChalonerIn some contemporary records, likHouse of Commons Journal Volume 8 9 June 1660 his name is also spelt Thomas Challoner (1595–1661) was an English politician, commissioner at the trial of Charles I and signatory to his death warrant. He was born at Steeple Claydon, Buckinghamshire, and was the son of the courtier Sir Thomas Chaloner. In January 1649 he and his younger brother, James Chaloner (1602–1660), served as two of the 135 commissioners of the court that tried King Charles I. Subsequently Thomas Chaloner signed the King's death warrant, whilst James did not. In 1660, at the restoration of the monarchy under Charles II, Chaloner was excluded from the Indemnity and Oblivion Act, which gave a general pardon, and escaped to the Continent to avoid a trial for high treason. He died at Middelburg in the Netherlands ) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manor House
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals with manorial tenants and great banquets. The term is today loosely applied to various country houses, frequently dating from the Late Middle Ages, which formerly housed the landed gentry. Manor houses were sometimes fortified, albeit not as fortified as castles, and were intended more for show than for defencibility. They existed in most European countries where feudalism was present. Function The lord of the manor may have held several properties within a county or, for example in the case of a feudal baron, spread across a kingdom, which he occupied only on occasional visits. Even so, the business of the manor was directed and controlled by regular manorial courts, which appointed manorial officials such as the bailiff, granted copyhol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |