|
State Court For The German Reich
The State Court for the German Reich (, ) was the constitutional court of the Weimar Republic. Its jurisdiction was limited to disputes concerning the legal organisation of the state. The court was established in 1921 and ceased functioning in February 1933, shortly after Adolf Hitler became chancellor of Germany. The State Court's primary area of jurisdiction was in disputes over the interpretation and application of the Weimar Constitution and of the constitutions of the individual States of the Weimar Republic, federal states. Such cases included the implementation of national laws by the states and disputes within a state regarding its own constitution. The court could not rule on whether a Reich law was compatible with the Reich constitution or a state law with a national law. The State Court's most famous case concerned the legality of the Reich government's removal of the legally elected government of the state of Free state of prussia, Prussia in 1932 (the ''Preussenschlag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free State Of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
The Free State of Mecklenburg-Strelitz () was a state of the Weimar Republic established in 1918 following the German Revolution which had overthrown the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz. The state lasted until the Nazi Party (NSDAP) came to power in Germany and merged the state with the neighbouring Free State of Mecklenburg-Schwerin to form a united state of Mecklenburg on 1 January, 1934. Government The state parliament consisted of a ''landtag'' of 35 members, elected for a term of four years by universal suffrage. The state administration, headed by a Minister of State was responsible to the ''landtag'' and could be removed by a vote of no confidence. For most of the Weimar period, the governments were headed by either a Social Democrat or a Nationalist. However, following the Nazi seizure of power at the national level, they enacted the " Second Law on the Coordination of the States with the Reich" which established more direct control over the states by means of the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courts And Tribunals Disestablished In 1945
A court is an institution, often a government entity, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and administer justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. Courts generally consist of judges or other judicial officers, and are usually established and dissolved through legislation enacted by a legislature. Courts may also be established by constitution or an equivalent constituting instrument. The practical authority given to the court is known as its jurisdiction, which describes the court's power to decide certain kinds of questions, or petitions put to it. There are various kinds of courts, including trial courts, appellate courts, administrative courts, international courts, and tribunals. Description A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Leipzig
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Supreme Courts
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
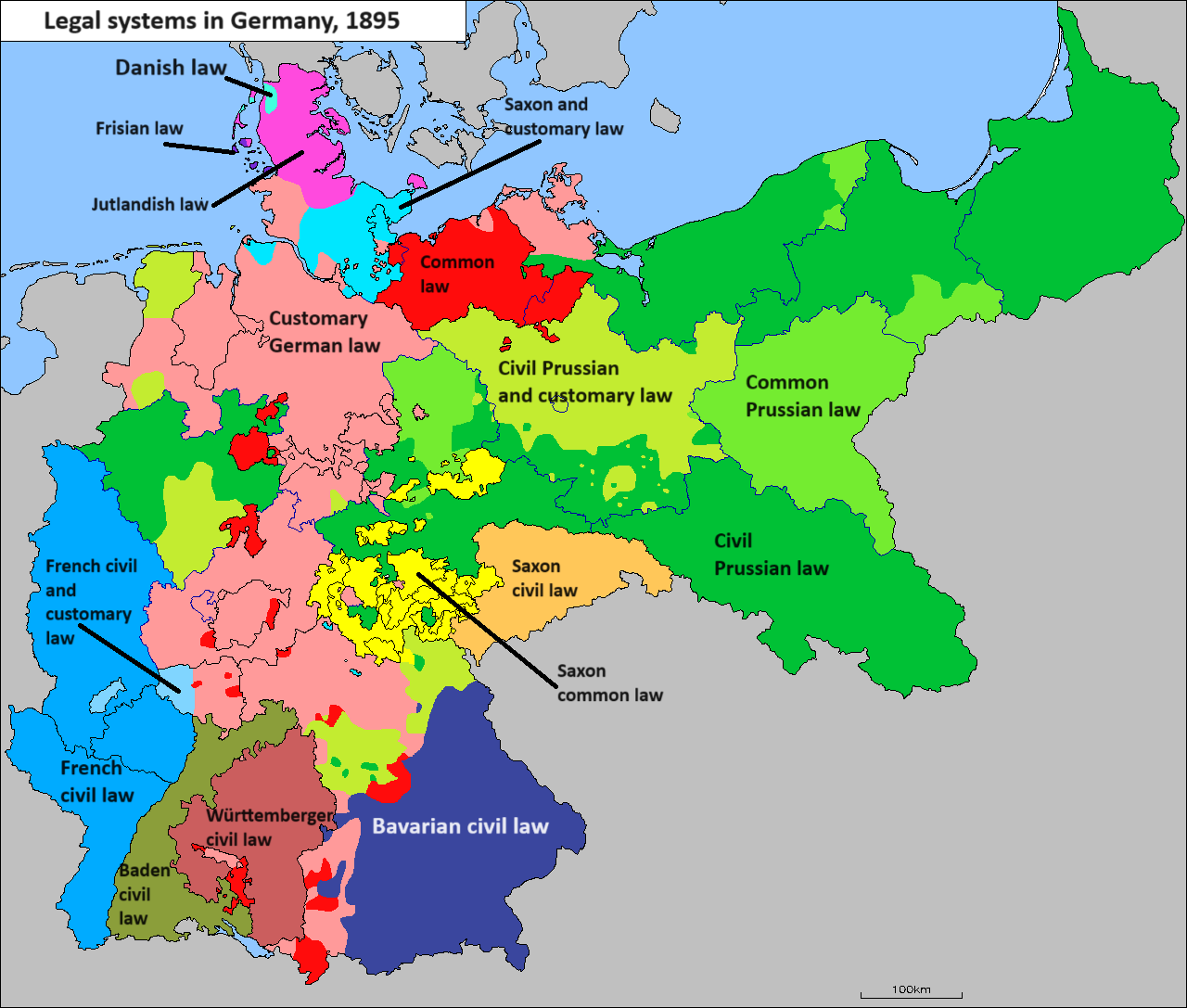
Legal History Of Germany
The law of Germany (), that being the modern German legal system (), is a system of civil law which is founded on the principles laid out by the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, though many of the most important laws, for example most regulations of the civil code (''Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch'', or BGB) were developed prior to the 1949 constitution. It is composed of public law (''öffentliches Recht''), which regulates the relations between a citizen/person and the state (including criminal law) or two bodies of the state, and the private law, (''Privatrecht'') which regulates the relations between two people or companies. It has been subject to a wide array of influences from Roman law, such as the Justinian Code the Corpus Juris Civilis, and to a lesser extent the Napoleonic Code. History German law has been subject to many influences over the centuries. Until Medieval times the Early Germanic Law, derived from the Salic Law of the Salian Franks and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Führer Principle
( , spelled ''Fuehrer'' when the umlaut is unavailable) is a German word meaning "leader" or "guide". As a political title, it is strongly associated with Adolf Hitler, the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945. Hitler officially called himself ''der Führer und Reichskanzler'' (the Leader and Chancellor of the Reich) after the death of President Paul von Hindenburg in 1934, as well as the subsequent merging of the offices of ''Reichspräsident'' and ''Reichskanzler''. Nazi Germany cultivated the ("leader principle"), and Hitler was generally known as simply ("the Leader"). In compound words, the use of remains common in German and is used in words such as (travel guide), ( museum docent), ( mountain guide), or (leader of the opposition). However, because of its strong association with Hitler, the isolated word itself usually has negative connotations when used with the meaning of "leader", especially in political contexts. The word has cognates in the Scandi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Schmitt
Carl Schmitt (11 July 1888 – 7 April 1985) was a German jurist, author, and political theorist. Schmitt wrote extensively about the effective wielding of political power. An authoritarian conservative theorist, he was noted as a critic of parliamentary democracy, liberalism, and cosmopolitanism. His works covered political theory, legal theory, continental philosophy, and political theology. However, they are controversial, mainly due to his intellectual support for, and active involvement with, Nazism. In 1933, Schmitt joined the Nazi Party and utilized his legal and political theories to provide ideological justification for the regime. However, he later lost favour among senior Nazi officials and was ultimately removed from his official positions within the party. The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' writes that "Schmitt was an acute observer and analyst of the weaknesses of liberal constitutionalism and liberal cosmopolitanism. But there can be little doubt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Rudolf Huber
Ernst Rudolf Huber (8 June 1903 – 28 October 1990) was a German jurist, noted as a constitutional historian and for his attempts to provide a legal underpinning for the Nazi regime. Life and work Huber studied law in Bonn under Carl Schmitt. He received a PhD in 1926 for a work on state church law, and his habilitation in 1931 for a work on economic administrative law, which he was instrumental in establishing as a field of study. In 1933, he was called to teach in Kiel, and subsequently also taught law in Leipzig after 1937 and in Strasbourg from 1941 to 1944. Like Georg Dahm and Karl Larenz, Huber (who joined the Nazi Party on 1 May 1933) belonged to the "Kiel school" of constitutional law, which attempted to legitimize the '' Führerstaat'', Adolf Hitler's dictatorship, by constructing a legal structure to anchor it in the German state as the source of all legitimate power. In doing so, Huber was influential in shaping the law of Nazi Germany and in recruiting others to tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Von Papen
Franz Joseph Hermann Michael Maria von Papen, (; 29 October 18792 May 1969) was a German politician, diplomat, Prussian nobleman and army officer. A national conservative, he served as Chancellor of Germany in 1932, and then as Vice-Chancellor under Adolf Hitler from 1933 to 1934. Papen is largely remembered for his role in bringing Hitler to power. Born into a wealthy family of Westphalian Catholic aristocrats, Papen served in the Prussian Army from 1898 onward and was trained as an officer of the German General Staff. He served as a military attaché in Mexico and the United States from 1913 to 1915, while also covertly organising acts of sabotage in the United States and quietly backing and financing Mexican forces in the Mexican Revolution on behalf of German military intelligence. After being expelled as persona non grata by the United States State Department in 1915, he served as a battalion commander on the Western Front of World War I and finished his war service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Article 48 (Weimar Constitution)
Article 48 of the constitution of the Weimar Republic of Germany (1919–1933) allowed the Reich president, under certain circumstances, to take emergency measures without the prior consent of the Reichstag. This power came to be understood to include the promulgation of emergency decrees. It was used frequently by Reich President Friedrich Ebert of the Social Democratic Party to deal with both political unrest and economic emergencies. Later, under President Paul von Hindenburg and the presidential cabinets, Article 48 was called on more and more often to bypass a politically fractured parliament and to rule without its consent. After the Nazi Party's rise to power in the early 1930s, the law allowed Chancellor Adolf Hitler, with decrees issued by Hindenburg, to create a totalitarian dictatorship by seemingly legal means. Text History Background The Weimar National Assembly, which was responsible for writing a constitution for a new, democratic Germany following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German military and political leader who led the Imperial German Army during the First World War and later became President of Germany (1919–1945), President of Germany from 1925 until his death in 1934. He played a key role in the Nazi seizure of power in 1933 when he appointed Adolf Hitler as Chancellor of Germany. Hindenburg was born to a family of minor Prussian nobility in the Grand Duchy of Posen. Upon completing his education as a cadet, he enlisted in the Third Regiment of Foot Guards as a second lieutenant. He saw combat during the Austro-Prussian War, Austro-Prussian and Franco-Prussian War, Franco-Prussian wars. In 1873, he was admitted to the prestigious Preußische Hauptkadettenanstalt, War Academy in Berlin, where he studied before being appointed to the General Staff Corps. In 1885, he was promoted to major and became a member of the German General Staff. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |