|
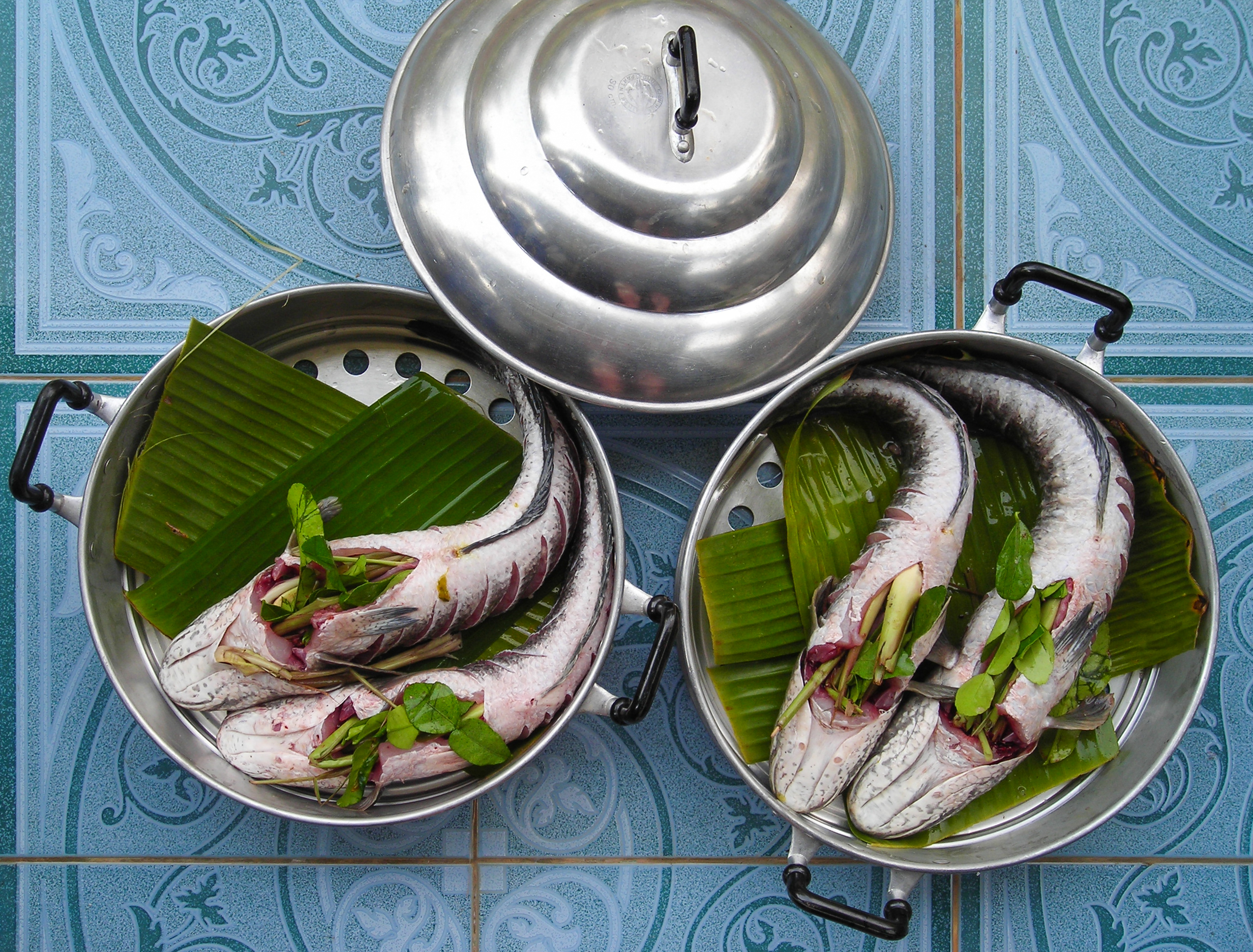
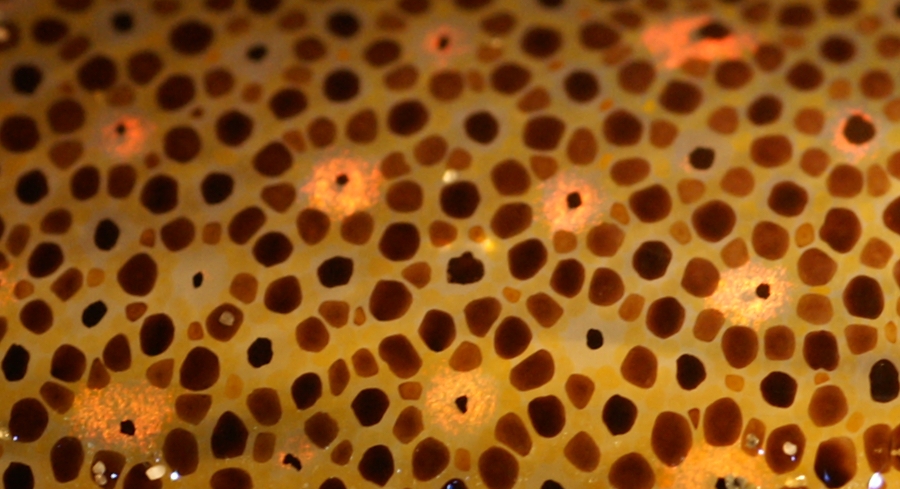
Starry Flounder
The starry flounder (''Platichthys stellatus''), also known as the grindstone, emery wheel and long-nosed flounder, is a common flatfish found around the margins of the North Pacific. The distinctive features of the starry flounder include the combination of black and white-to-orange bar on the dorsal and anal fins, as well as the skin covered with scales modified into tiny star-shaped plates or tubercles (thus both the common name and species epithet), resulting in a rough feel. The eyed side is black to dark brown, while the lower side is white or cream-colored. Although classed as "righteye flounders," individuals may have their eyes on either the right or left side. They have been recorded at up to 91 cm and 9 kg. Starry flounders are inshore fish, ranging up estuaries well into the freshwater zone, to the first riffles, with young found as much as 120 km inland. In marine environments, they occur as deep as 375 m. They glide over the bottom by rippling th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussia, Prussian zoologist, botanist, Ethnography, ethnographer, Exploration, explorer, Geography, geographer, Geology, geologist, Natural history, natural historian, and Taxonomy, taxonomist. He studied natural sciences at various universities in Germany in the early modern period, early modern Germany and worked primarily in the Russian Empire between 1767 and 1810. Life and work Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, Kingdom of Prussia, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University of Göttingen. In 1760, he moved to the University of Leiden and passed his doctor's degree at the age of 19. Pallas travelled throughout the Dutch Republic and to London, improving his medical and surgical knowledge. He then settled at The Hague, and his new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; , "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before Alaska Purchase, 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain of 14 main, larger volcanic islands and 55 smaller ones. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, with the archipelago encompassing the Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska, Aleutians West Census Area and the Aleutians East Borough, Alaska, Aleutians East Borough. The Commander Islands, located further to the west, belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai, of the Russian Far East. The islands form part of the Aleutian Arc of the Northern Pacific Ocean, and occupy a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) that extends westward roughly from the Alaska Peninsula, Alaskan Peninsula mainland, in the direction of the Kamchatka Peninsula; the archipelago acts as a border between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphon (mollusc)
A siphon is an anatomical structure which is part of the body of aquatic molluscs in three Class (biology), classes: Gastropoda, Bivalvia and Cephalopoda (members of these classes include saltwater and freshwater snails, clams, octopus, squid and relatives). Siphons in molluscs are tube-like structures in which water (or, more rarely, air) flows. The water flow is used for one or more purposes such as animal locomotion, locomotion, feeding, respiration (physiology), respiration, and reproduction. The siphon is part of the mantle (mollusc), mantle of the mollusc, and the water flow is directed to (or from) the Mantle (mollusc)#The mantle cavity, mantle cavity. A single siphon occurs in some gastropods. In those bivalves which have siphons, the siphons are paired. In cephalopods, there is a single siphon or funnel which is known as a hyponome. In gastropods In some (but not all) sea snails, Marine (ocean), marine gastropod molluscs, the animal has an anterior extension of the man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
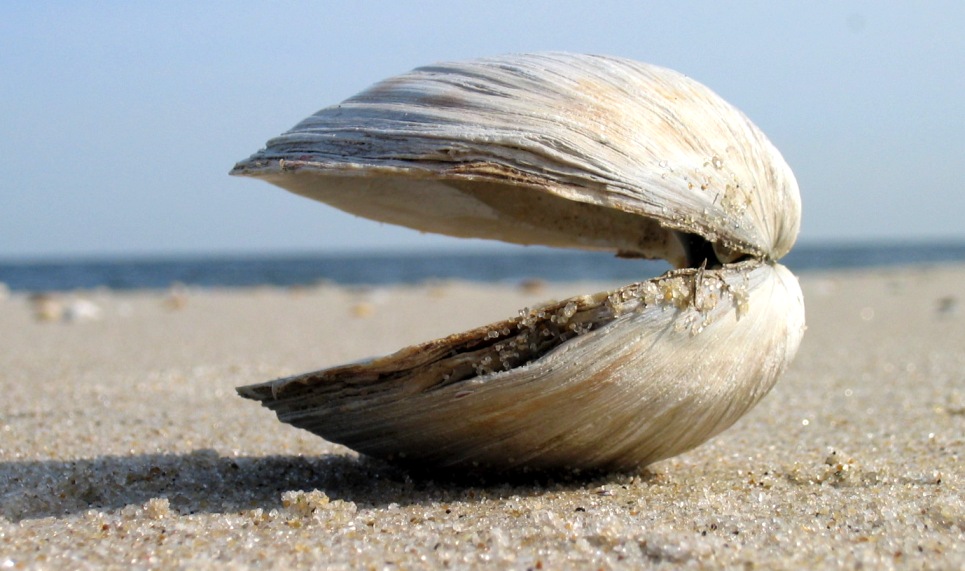
Clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams have two shells of equal size connected by two adductor muscles and have a powerful burrowing foot. They live in both freshwater and marine environments; in salt water they prefer to burrow down into the mud and the turbidity of the water required varies with species and location; the greatest diversity of these is in North America. Clams in the culinary sense do not live attached to a substrate (whereas oysters and mussels do) and do not live near the bottom (whereas scallops do). In culinary usage, clams are commonly eaten marine bivalves, as in clam digging and the resulting soup, clam chowder. Many edible clams such as palourde clams are ovoid or triangular; however, razor clams have an elongated parallel-sided shell, suggesting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate subphylum Vertebrata, i.e. vertebrates. Well-known Phylum, phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, molluscs, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxon, taxa have a greater number and diversity of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 10 Micrometre, μm (0.0004 in) myxozoans to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are actually sister chordate subphyla to Vertebrata, being more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the "invertebrates" para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clams
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams have two shells of equal size connected by two adductor muscles and have a powerful burrowing foot. They live in both freshwater and marine environments; in salt water they prefer to burrow down into the mud and the turbidity of the water required varies with species and location; the greatest diversity of these is in North America. Clams in the culinary sense do not live attached to a substrate (whereas oysters and mussels do) and do not live near the bottom (whereas scallops do). In culinary usage, clams are commonly eaten marine bivalves, as in clam digging and the resulting soup, clam chowder. Many edible clams such as palourde clams are ovoid or triangular; however, razor clams have an elongated parallel-sided shell, suggesting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopod A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...s. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for animal coloration, coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye color, eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescence, iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flounder
Flounders are a group of flatfish species. They are demersal fish, found at the bottom of oceans around the world; some species will also enter estuary, estuaries. Taxonomy The name "flounder" is used for several only distantly related species, though all are in the suborder Pleuronectoidei (families Achiropsettidae, Bothidae, Pleuronectidae, Paralichthyidae, and Samaridae). Some of the better known species that are important in fisheries are: * Western Atlantic ** Gulf flounder – ''Paralichthys albigutta'' ** Paralichthys lethostigma, Southern flounder – ''Paralichthys lethostigma'' ** Summer flounder (also known as ''fluke'') – ''Paralichthys dentatus'' ** Winter flounder – ''Pseudopleuronectes americanus'' * European waters **European flounder – ''Platichthys flesus'' **Witch (righteye flounder), Witch flounder – ''Glyptocephalus cynoglossus'' * North Pacific ** Halibut – ''Hippoglossus stenolepis'' ** Olive flounder – ''Paralichthys olivaceus'' Eye migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish ( Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish ( Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish ( Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Fish
Many species of fish are caught by humans and consumed as food in virtually all regions around the world. Their meat has been an important dietary source of protein and other nutrients in the human diet. The English language does not have a special culinary name for food prepared from fish like with other animals (as with '' pig'' vs. ''pork''), or as in other languages (such as Spanish '' pez'' vs. '' pescado''). In culinary and fishery contexts, ''fish'' may include so-called shellfish such as molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms; but, more expansively, ''seafood'' covers both fish and other marine life used as food. Since 1961, the average annual increase in global apparent food fish consumption (3.2 percent) has outpaced population growth (1.6 percent) and exceeded the increase in consumption of meat from all terrestrial animals except poultry (4.9 percent), both combined (2.8 percent) and individually (bovine, ovine, porcine, et cetera). In ''per capita'' terms, food f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Barbara County, California
Santa Barbara County, officially the County of Santa Barbara (), is a County (United States), county located in Southern California. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 448,229. The county seat is Santa Barbara, California, Santa Barbara, and the largest city is Santa Maria, California, Santa Maria. Santa Barbara County comprises the Santa Maria-Santa Barbara, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area. Most of the county is part of the California Central Coast. Mainstays of the county's economy include engineering, resource extraction (particularly petroleum extraction and diatomaceous earth mining), winemaking, agriculture, and education. The software development and tourism industries are important employers in the southern part of the county. Having a blend of both Southern California, Southern and Northern California influences, Santa Barbara County often considered the cultural and geographical boundary between Southern California and Northern California. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Ynez River
The Santa Ynez River is one of the largest rivers on the Central Coast, California, Central Coast of California. It is long, ArcExplorer Geographic information system, GIS data viewer. flowing from east to west through the Santa Ynez Valley, reaching the Pacific Ocean at Surf, near Vandenberg Space Force Base and the city of Lompoc, California, Lompoc. The river drains the north slope of the Santa Ynez Mountains, the south slope of the San Rafael Mountains, as well as much of the southern half of Santa Barbara County. Its drainage basin is in area. ArcExplorer Geographic information system, GIS data viewer. The river's flow is highly variable. It usually dries up almost completely in the summer, but can become a raging torrent in the winter. The river has three dams which can impound a total of of water in wet years. History The river was first named by the Spanish Portolà expedition, first European land exploration of Alta California, which camped near the river mouth on Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |