|
StarBase (biological Database)
StarBase is a database for decoding miRNA-mRNA, miRNA-lncRNA, miRNA- sncRNA, miRNA-circRNA, miRNA-pseudogene, protein-lncRNA, protein-ncRNA, protein-mRNA interactions, and ceRNA networks from CLIP-Seq (HITS-CLIP, PAR-CLIP PAR-CLIP (photoactivatable ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation) is a biochemical method for identifying the binding sites of cellular RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and microRNA-containing ribonucleoprotein complexes (miRNPs). ..., iCLIP, CLASH) and degradome sequencing data. StarBase provides miRFunction and ceRNAFunction web tools to predict the function of ncRNAs (miRNAs, lncRNAs, pseudogenes) and protein-coding genes from the miRNA and ceRNA regulatory networks. StarBase also developed Pan-Cancer Analysis Platform to decipher Pan-Cancer Analysis Networks of lncRNAs, miRNAs, ceRNAs, and RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) by mining clinical and expression profiles of 14 cancer types (including more than six thousand samples) from The Cancer Geno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance. A database management system (DBMS) is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS software additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICLIP
iCLIP (individual-nucleotide resolution CrossLinking and ImmunoPrecipitation) is a variant of the original CLIP method used for identifying protein-RNA interactions, which uses UV light to covalently bind proteins and RNA molecules to identify RNA binding sites of proteins. This crosslinking step has generally less background than standard RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) protocols, because the covalent bond formed by UV light allows RNA to be fragmented, followed by stringent purification, and this also enables CLIP to identify the positions of protein-RNA interactions. As with all CLIP methods, iCLIP allows for a very stringent purification of the linked protein-RNA complexes by stringent washing during immunoprecipitation followed by SDS-PAGE and transfer to nitrocellulose. The labelled protein-RNA complexes are then visualised for quality control, excised from nitrocellulose, and treated with proteinase to release the RNA, leaving only a few amino acids at the crosslink site of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
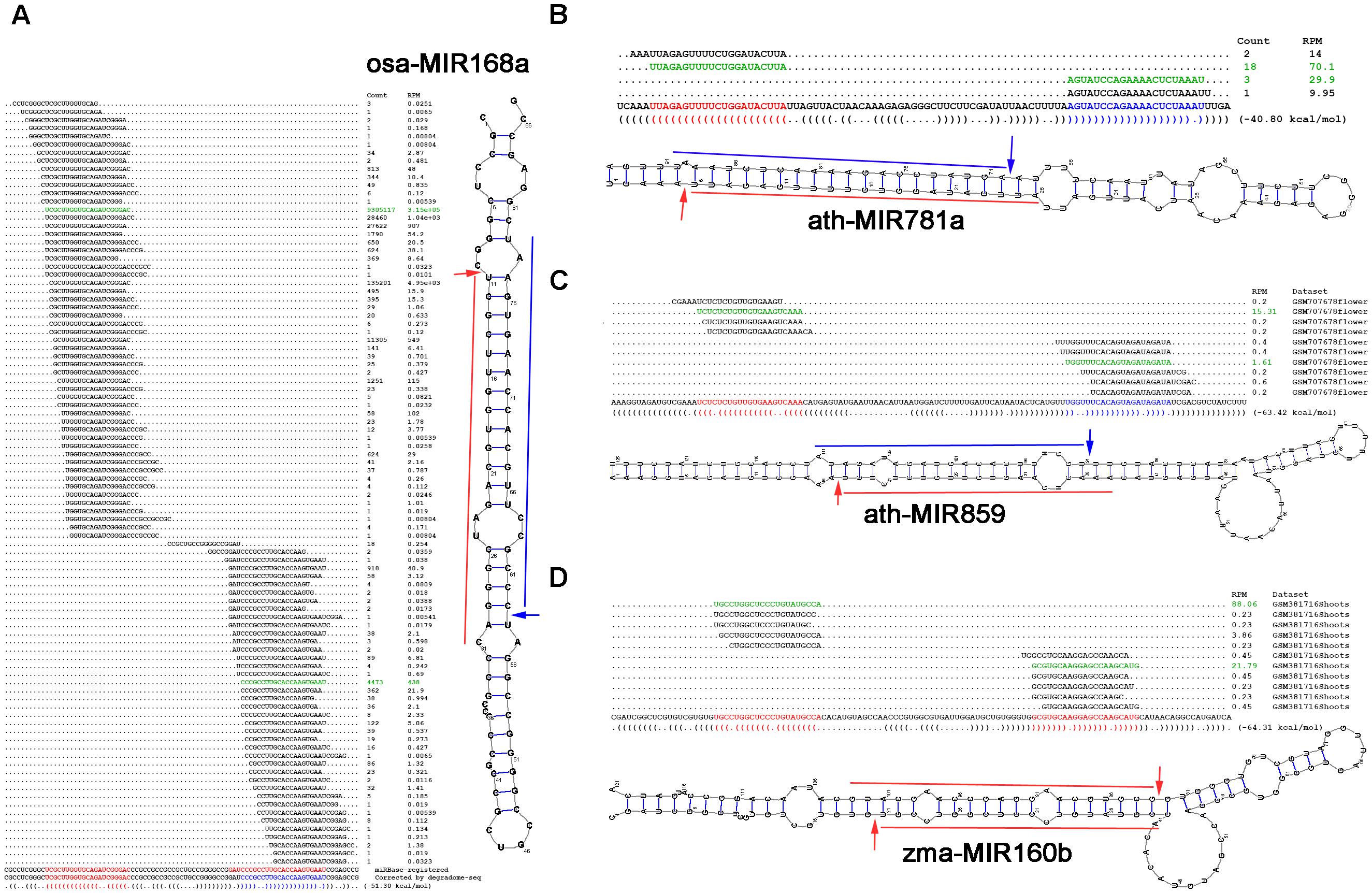
Degradome Sequencing
Degradome sequencing (Degradome-Seq), also referred to as parallel analysis of RNA ends (PARE), is a modified version of 5'-Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE) using high-throughput, deep sequencing methods such aIllumina's SBS technology The degradome encompasses the entire set of proteases that are expressed at a specific time in a given biological material, including tissues, cells, organisms, and biofluids. Thus, sequencing this degradome offers a method for studying and researching the process of RNA degradation. This process is used to identify and quantify RNA degradation products, or fragments, present in any given biological sample. This approach allows for the systematic identification of targets of RNA decay and provides insight into the dynamics of transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation. Degradome sequencing is a complex process which includes multiple steps such as isolating RNA fragments in a given sample as well as ligation and reverse transcrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicroRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs base-pair to complementary sequences in mRNA molecules, then gene silence said mRNA molecules by one or more of the following processes: (1) cleavage of mRNA strand into two pieces, (2) destabilization of mRNA by shortening its poly(A) tail, or (3) translation of mRNA into proteins. This last method of gene silencing is the least efficient of the three, and requires the aid of ribosomes. miRNAs resemble the small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. The human genome may encode over 1900 miRNAs, although more recent analysis s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicroRNA And MicroRNA Target Database
This microRNA database and microRNA targets databases is a compilation of databases and web portals and servers used for microRNAs and their targets. MicroRNAs MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miR ... (miRNAs) represent an important class of small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) that regulate gene expression by targeting messenger RNAs. microRNA target gene databases microRNA databases References Further reading * * External links starBase databaseStarScan toolCupid: simultaneous reconstruction of microRNA-target and ceRNA networksmiRBase databasedeepBase databaseTargetScanpicTarmiRecords databaseTarBase databaseTarget ID LibrarymiRTarBase database {{DEFAULTSORT:MicroRNA RNA MicroRNA Genetics databases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) is a project to catalogue the genomic alterations responsible for cancer using genome sequencing and bioinformatics. The overarching goal was to apply high-throughput genome analysis techniques to improve the ability to diagnose, treat, and prevent cancer through a better understanding of the genetic basis of the disease. TCGA was supervised by the National Cancer Institute's Center for Cancer Genomics and the National Human Genome Research Institute funded by the US government. A three-year pilot project, begun in 2006, focused on characterization of three types of human cancers: glioblastoma multiforme, lung squamous carcinoma, and ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. In 2009, it expanded into phase II, which planned to complete the genomic characterization and sequence analysis of 20–25 different tumor types by 2014. Ultimately, TCGA surpassed that goal, characterizing 33 cancer types including 10 rare cancers. The project initially set out to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-Cancer Analysis
Pan-cancer analysis aims to examine the similarities and differences among the genomic and cellular alterations found across diverse tumor types. International efforts have performed pan-cancer analysis on exomes and the whole genomes of cancers, the latter including their non-coding regions. In 2018, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Research Network used exome, transcriptome, and DNA methylome data to develop an integrated picture of commonalities, differences, and emergent themes across tumor types. In 2020, the International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC)/TCGA Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes project published a set of 24 papers analyzing whole cancer genomes and transcriptomic data from 38 tumor types. A comprehensive overview of the project is provided in its flagship paper. Another project, pan-cancer analysis of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) across human cancers, explored the expression, somatic copy number alteration, and mutation profiles of 1,542 RBPs in ∼7,000 cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degradome Sequencing
Degradome sequencing (Degradome-Seq), also referred to as parallel analysis of RNA ends (PARE), is a modified version of 5'-Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE) using high-throughput, deep sequencing methods such aIllumina's SBS technology The degradome encompasses the entire set of proteases that are expressed at a specific time in a given biological material, including tissues, cells, organisms, and biofluids. Thus, sequencing this degradome offers a method for studying and researching the process of RNA degradation. This process is used to identify and quantify RNA degradation products, or fragments, present in any given biological sample. This approach allows for the systematic identification of targets of RNA decay and provides insight into the dynamics of transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation. Degradome sequencing is a complex process which includes multiple steps such as isolating RNA fragments in a given sample as well as ligation and reverse transcrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAR-CLIP
PAR-CLIP (photoactivatable ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation) is a biochemical method for identifying the binding sites of cellular RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and microRNA-containing ribonucleoprotein complexes (miRNPs). The method relies on the incorporation of ribonucleoside analogs that are photoreactive, such as 4-thiouridine (4-SU) and 6-thioguanosine (6-SG), into nascent RNA transcripts by living cells. Irradiation of the cells by ultraviolet light of 365 nm wavelength induces efficient crosslinking of photoreactive nucleoside– labeled cellular RNAs to interacting RBPs. Immunoprecipitation of the RBP of interest is followed by isolation of the crosslinked and coimmunoprecipitated RNA. The isolated RNA is converted into a cDNA library and is deep sequenced using next-generation sequencing technology. Recently, PAR-CLIP have been applied to determine the transcriptome-wide binding sites of several known RBPs and microRNA-containing ribonucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicroRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs base-pair to complementary sequences in mRNA molecules, then gene silence said mRNA molecules by one or more of the following processes: (1) cleavage of mRNA strand into two pieces, (2) destabilization of mRNA by shortening its poly(A) tail, or (3) translation of mRNA into proteins. This last method of gene silencing is the least efficient of the three, and requires the aid of ribosomes. miRNAs resemble the small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. The human genome may encode over 1900 miRNAs, although more recent analysis s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HITS-CLIP
High-throughput sequencing of RNA isolated by crosslinking immunoprecipitation (HITS-CLIP, also known as CLIP-Seq) is a genome-wide means of mapping protein–RNA binding sites or RNA modification sites in vivo. HITS-CLIP was originally used to generate genome-wide protein-RNA interaction maps for the neuron-specific RNA-binding protein and splicing factor NOVA1 and NOVA2; since then a number of other splicing factor maps have been generated, including those for PTB, RbFox2, SFRS1, hnRNP C, and even N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) mRNA modifications. HITS-CLIP of the RNA-binding protein Argonaute has been performed for the identification of microRNA targets by decoding microRNA-mRNA and protein-RNA interaction maps in mouse brain, and subsequently in ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', embryonic stem cells and tissue culture cells. As a novel modification of HITS-CLIP, m6A-CLIP was developed to precisely map N6-Methyladenosine(m6A) locations in mRNA by UV-crosslinking m6A antibody to the tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |