|
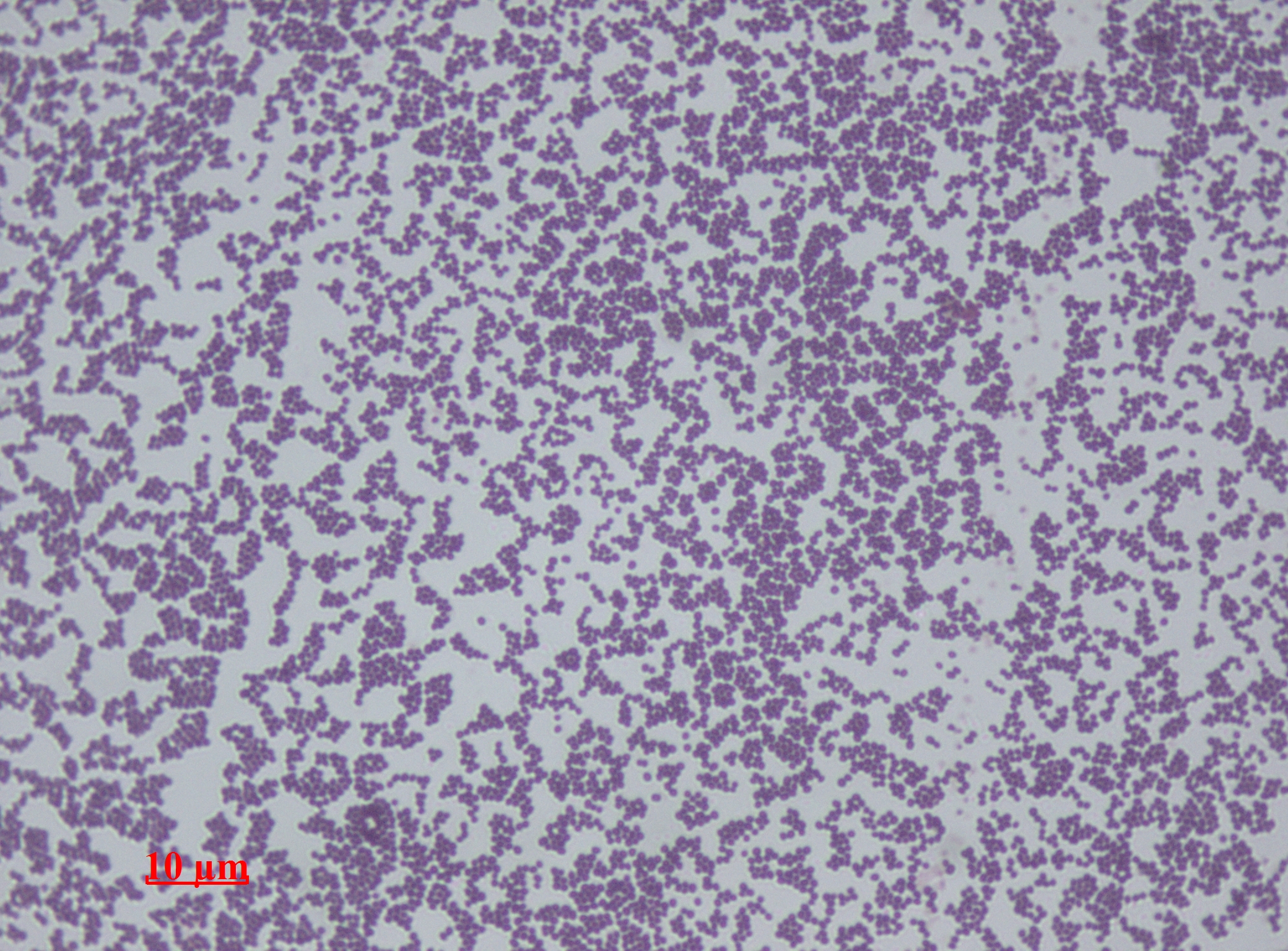
Staphylococcus Hominis
''Staphylococcus hominis'' is a coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus ''Staphylococcus'', consisting of Gram-positive, spherical cells in clusters. It occurs very commonly as a harmless commensal on human and animal skin and is known for producing thioalcohol compounds that contribute to body odour. Like many other coagulase-negative staphylococci, ''S. hominis'' may occasionally cause infection in patients whose immune systems are compromised, for example by chemotherapy or predisposing illness. Description Colonies of ''S. hominis'' are small, usually 1–2 mm in diameter after 24 hours' incubation at 35 °C, and white or tan in colour. Occasionally, strains are resistant to novobiocin and may be confused with other resistant species (e.g. ''S. saprophyticus''). It is one of only two species of ''Staphylococcus'' to display sensitivity to desferrioxamine, the other being ''S. epidermidis''. Unlike ''S. epidermidis'', ''S. hominis'' produces acid from treh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coagulase
Coagulase is a protein enzyme produced by several microorganisms that enables the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. In the laboratory, it is used to distinguish between different types of '' Staphylococcus'' isolates. Importantly, '' S. aureus'' is generally coagulase-positive, meaning that a positive coagulase test would indicate the presence of ''S. aureus'' or any of the other 11 coagulase-positive ''Staphylococci''. A negative coagulase test would instead show the presence of coagulase-negative organisms such as ''S. epidermidis'' or ''S. saprophyticus''. However, it is now known that not all ''S. aureus'' are coagulase-positive. Whereas coagulase-positive ''Staphylococci'' are usually pathogenic, coagulase-negative ''Staphylococci'' are more often associated with opportunistic infection. It is also produced by '' Yersinia pestis''. Coagulase reacts with prothrombin in the blood. The resulting complex is called ''staphylothrombin'', which enables the enzyme to act as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trehalose
Trehalose (from Turkish '' tıgala'' – a sugar derived from insect cocoons + -ose) is a sugar consisting of two molecules of glucose. It is also known as mycose or tremalose. Some bacteria, fungi, plants and invertebrate animals synthesize it as a source of energy, and to survive freezing and lack of water. Extracting trehalose was once a difficult and costly process, but around 2000, the Hayashibara company ( Okayama, Japan) discovered an inexpensive extraction technology from starch. Trehalose has high water retention capabilities, and is used in food, cosmetics and as a drug. A procedure developed in 2017 using trehalose allows sperm storage at room temperatures. Structure Trehalose is a disaccharide formed by a bond between two α-glucose units. It is found in nature as a disaccharide and also as a monomer in some polymers. Two other isomers exist, α,β-trehalose, otherwise known as neotrehalose, and β,β-trehalose (also referred to as isotrehalose). Neotrehalose has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nosocomial
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital settings, it is sometimes instead called a healthcare–associated infection. Such an infection can be acquired in hospital, nursing home, rehabilitation facility, outpatient clinic, diagnostic laboratory or other clinical settings. Infection is spread to the susceptible patient in the clinical setting by various means. Health care staff also spread infection, in addition to contaminated equipment, bed linens, or air droplets. The infection can originate from the outside environment, another infected patient, staff that may be infected, or in some cases, the source of the infection cannot be determined. In some cases the microorganism originates from the patient's own skin microbiota, becoming opportunistic after surgery or other procedures that compromise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, and meningitis caused by methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Blood levels may be measured to determine the correct dose. Vancomycin is also taken by mouth as a treatment for severe ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis. When taken by mouth it is poorly absorbed. Common side effects include pain in the area of injection and allergic reactions. Occasionally, hearing loss, low blood pressure, or bone marrow suppression occur. Safety in pregnancy is not clear, but no evidence of harm has been found, and it is likely safe for use when breastfeeding. It is a type of glycopeptide antibiotic and works by blocking the construction of a cell wall. Vancomycin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958. It is on the Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Morphology
In microbiology, colonial morphology refers to the visual appearance of bacterial or fungal colonies on an agar plate. Examining colonial morphology is the first step in the identification of an unknown microbe. The systematic assessment of the colonies' appearance, focusing on aspects like size, shape, colour, opacity, and consistency, provides clues to the identity of the organism, allowing microbiologists to select appropriate tests to provide a definitive identification. Procedure When a specimen arrives in the microbiology laboratory, it is inoculated into an agar plate and placed in an incubator to encourage microbial growth. Because the appearance of microbial colonies changes as they grow, colonial morphology is examined at a specific time after the plate is inoculated. Usually, the plate is read at 18–24 hours post-inoculation, but times may differ for slower-growing organisms like fungi. The microbiologist examines the appearance of the colony, noting specific feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannose
Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation are associated with mutations in enzymes involved in mannose metabolism. Mannose is not an essential nutrient; it can be produced in the human body from glucose, or converted into glucose. Mannose provides 2–5 kcal/g. It is partially excreted in the urine. Etymology The root of both "mannose" and "mannitol" is manna, which the Bible describes as the food supplied to the Israelites during their journey in the region of Sinai. Several trees and shrubs can produce a substance called manna, such as the "manna tree" ('' Fraxinus ornus'') from whose secretions mannitol was originally isolated. Structure Mannose commonly exists as two different-sized rings, the pyranose (six-membered) form and the furanose (five-membered) form. Eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melezitose
Melezitose, also spelled melicitose, is a nonreducing trisaccharide sugar that is produced by many plant sap eating insects, including aphids such as ''Cinara pilicornis'', by an enzyme reaction. This is beneficial to the insects, as it reduces the stress of osmosis by reducing their own water potential. The melezitose is part of the honeydew which acts as an attractant for ants and also as a food for bees. This is useful to the aphids as they have a symbiotic relationship with ants. Melezitose can be partially hydrolyzed to glucose and turanose the latter of which is an isomer of sucrose Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula . For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refi .... References {{Carbohydrates Trisaccharides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turanose
Turanose is a reducing disaccharide. The -isomer is naturally occurring. Its systematic name is α--glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-α--fructofuranose. It is an analog of sucrose not metabolized by higher plants, but rather acquired through the action of sucrose transporters for intracellular carbohydrate signaling. In addition to its involvement in signal transduction, -(+)-turanose can also be used as a carbon source by many organisms including numerous species of bacteria and fungi. at Sigma-Aldrich
Sigma-Aldrich (formally MilliporeSigma) is an American chemical, life science, and biotechnology company that is owned by the German chemical conglomerate Merck Group.
Sigma-Aldrich wa ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. Because it has antimicrobial and antiviral properties, it is widely used in wound and burn treatments approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Conversely, it is also used as a bacterial culture medium. It can be used as an effective marker to measure liver disease. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature. Structure Although achiral, glycerol is prochiral with respect to reactions of one of the two primary alcohols. Thus, in substituted derivatives, the stereospecific numbering labels the molecule with a "sn-" prefix before the stem name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superiorly by the imaginary plane between the superior borders of the first rib, clavicle and scapula (above which are considered part of the neck), medially by the serratus anterior muscle and thoracolumbar fascia, anteriorly by the pectoral muscles and posteriorly by the subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi muscle. The soft skin covering the lateral axilla contains many hair and sweat glands. In humans, the formation of body odor happens mostly in the axilla. These odorant substances have been suggested by some to serve as pheromones, which play a role related to mate selection, although this is a controversial topic within the scientific community. The underarms seem more important than the pubic area for emitting bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus ''Staphylococcus''. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified salt tolerant strains of ''S. epidermi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of '' Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from grc, σταφυλή, staphylē, bunch of grapes), and suffixed by the Modern (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staph bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at risk of infection. Staphylococcus includes at least 43 species. Of these, nine have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |