|
Stannate
In chemistry, the term stannate or tinnate refers to compounds of tin (Sn). Stannic acid (Sn(OH)4), the formal precursor to stannates, does not exist and is actually a hydrate of SnO2. The term is also used in naming conventions as a suffix; for example the hexachlorostannate ion is . In materials science, two kinds of tin oxyanions are distinguished: *''orthostannates'' contain discrete units (e.g. K4SnO4) or have a spinel structure (e.g. Mg2SnO4) *''metastannates'' with a stoichiometry MIISnO3, MSnO3 which may contain polymeric anions or may be sometimes better described as mixed oxides These materials are semiconductors."Preparation, characterization and structure of metal stannates: a new family of photocatalysts for organic pollutants degradation." ''Handbook of Photocatalysts'' (2010), pp. 493–510. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., Hauppauge, NY Examples * Barium stannate, BaSnO3 (a metastannate) * Cobalt stannate, Co2SnO4, primary constituent of the pigment cerulean bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Stannate
Sodium stannate, formally sodium hexahydroxostannate(IV), is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2 n(OH)6 This colourless salt forms upon dissolving metallic tin or tin(IV) oxide in sodium hydroxide and is used as a stabiliser for hydrogen peroxide. In older literature, stannates are sometimes represented as having the simple oxyanion SnO32−, in which case this compound is sometimes named as sodium stannate–3–water and represented as Na2SnO3·3H2O, a hydrate with three waters of crystallisation. The anhydrous form of sodium stannate, Na2SnO3, is recognised as a distinct compound with its own CAS Registry Number, and a distinct material safety data sheet. Alkali metal stannate compounds are prepared by dissolving elemental tin in a suitable metal hydroxide, in the case of sodium stannate by the reaction: :Sn + 2 NaOH + 4 H2O → Na2 n(OH)6 + 2 H2 A similar reaction occurs when tin dioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stannic Acid
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the so-called "tin cry", as a result of twinning in tin crystals. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, . Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element on Earth, making up 0.00022% of its crust, and with 10 stable isotopes, it has the largest number of stable isotopes in the periodic table, due to its magic number of protons. It has two main allotropes: at room temperature, the stable allotrope is β-tin, a silvery-white, ductility, malleable metal; at low temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium Stannate
Barium stannate is an oxide of barium and tin with the chemical formula Ba Sn O3. It is a wide band gap semiconductor with a perovskite crystal A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ... structure. References {{tin compounds Barium compounds Stannates Semiconductor materials Perovskites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerulean
The color cerulean (American English) or caerulean (British English, Commonwealth English), is a variety of the hue of blue that may range from a light azure blue to a more intense sky blue. Cerulean may also be mixed with the hue of green. The first recorded use of ''cerulean'' as a color name in English was in 1590. The word is derived from the Latin word '' caeruleus'' (), "dark blue, blue, or blue-green", which in turn probably derives from , diminutive of , "heaven, sky". "Cerulean blue" is the name of a blue-green pigment consisting of cobalt stannate (). The pigment was first synthesized in the late eighteenth century by Albrecht Höpfner, a Swiss chemist, and it was known as Höpfner blue during the first half of the nineteenth century. Art suppliers began referring to cobalt stannate as cerulean in the second half of the nineteenth century. It was not widely used by artists until the 1870s when it became available in oil paint. Pigment characteristics The primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysprosium Stannate
Dysprosium stannate ( Dy2 Sn2 O7) is an inorganic compound, a ceramic of the stannate family, with pyrochlore structure. Dysprosium stannate, like dysprosium titanate and holmium stannate, is a spin ice material. In 2009, quasiparticles resembling magnetic monopoles In particle physics, a magnetic monopole is a hypothetical particle that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). A magnetic monopole would have a net north or south "magnetic charge". ... were observed at low temperature and high magnetic field. References Dysprosium compounds Stannates {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin(IV) Oxide
Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in tin chemistry. It is a colourless, diamagnetic, amphoteric solid. Structure Tin(IV) oxide crystallises with the rutile structure. As such the tin atoms are six coordinate and the oxygen atoms three coordinate. SnO2 is usually regarded as an oxygen-deficient n-type semiconductor. Hydrous forms of SnO2 have been described as stannic acid. Such materials appear to be hydrated particles of SnO2 where the composition reflects the particle size. Preparation Tin(IV) oxide occurs naturally. Synthetic tin(IV) oxide is produced by burning tin metal in air. Annual production is in the range of 10 kilotons. SnO2 is reduced industrially to the metal with carbon in a reverberatory furnace at 1200–1300 °C. Reactions The reaction from tin(IV) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead-tin Yellow
Lead-tin yellow is a yellow pigment, of historical importance in oil painting, sometimes called the "Yellow of the Old Masters" because of the frequency with which it was used by those famous painters. Nomenclature The name lead-tin yellow is a modern label. During the thirteenth to eighteenth centuries when it was in widest use, it was known by a variety of names. In Italy, it was ''giallorino'' or ''giallolino''. In other countries of Europe, it was massicot, (Spanish), (German), ''general'' (English) or (Portuguese). All of these names were often applied to other yellow pigments as well as lead-tin yellow. Composition Lead-tin yellow historically occurred in two varieties. The first and more common one, today known as "Type I", was a lead stannate, an oxide of lead and tin with the chemical formula Pb2SnO4. The second, "Type II", was a silicate with the formula .Hermann Kühn, 1967, "Blei-Zinn-Gelb und seine Verwendung in der Malerei", ''Farbe und Lack'' 73: 938-949 Lead- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stannite (ion)
The stannite ion is . It can be formed by adding strong base to stannous hydroxide. The stannite ion is a strong reducing agent; also, it may disproportionate to tin metal plus stannate ion. There are stannite compounds, for example, sodium stannite, . See also * Stannate In chemistry, the term stannate or tinnate refers to compounds of tin (Sn). Stannic acid (Sn(OH)4), the formal precursor to stannates, does not exist and is actually a hydrate of SnO2. The term is also used in naming conventions as a suffix; for ... Oxyanions References {{Chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinel
Spinel () is the magnesium/aluminium member of the larger spinel group of minerals. It has the formula in the cubic crystal system. Its name comes from the Latin word , a diminutive form of ''spine,'' in reference to its pointed crystals. Properties Spinel crystallizes in the isometric system; common crystal forms are octahedron, octahedra, usually Crystal twinning, twinned. It has no true Cleavage (crystal), cleavage, but shows an octahedral Parting (crystal), parting and a conchoidal fracture. Its Mohs scale of mineral hardness, hardness is 8, its specific gravity is 3.5–4.1, and it is transparent to opaque with a vitreous to dull Lustre (mineralogy), luster. It may be colorless, but is usually various shades of red, lavender (color), lavender, blue, green, brown, black, or yellow. Chromium(III) causes the red color in spinel from Burma. Some spinels are among the most famous gemstones; among them are the Black Prince's Ruby and the "Timur ruby" in the British Crown Jewels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping levels are present in the same crystal, they form a semiconductor junction. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits. Semiconductor devices can display a range of different useful properties, such as passing current more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Science Publishers, Inc
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems, but causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. This type is usually created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. If the orbital period of the system is a few days or less, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to draw accreted matter onto its surface, creating a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmosphere, mostly consisting of hydrogen, is heated by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicate
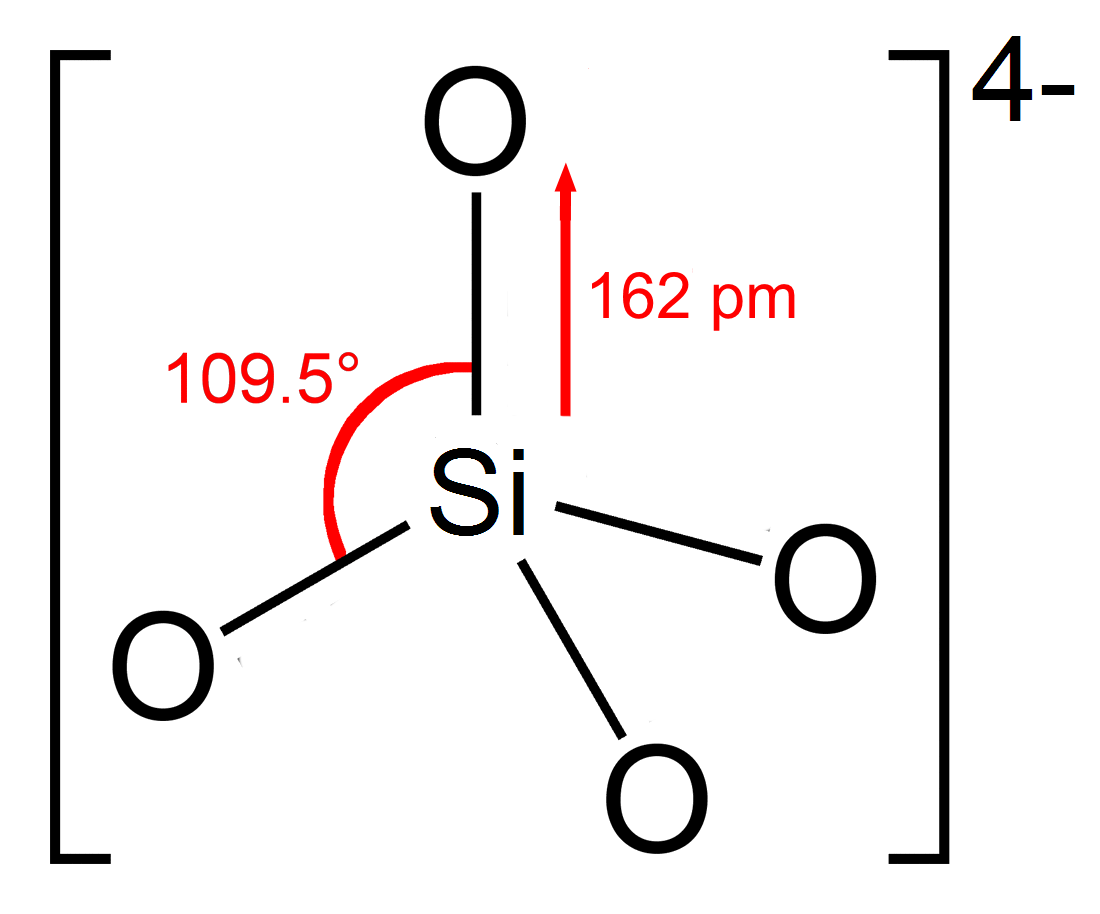
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate . Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In most silicates, a silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |