|
Standpipe At EFWE , part of a drilling rig
{{disambig ...
Standpipe may refer to: * Standpipe (firefighting), a rigid vertical or horizontal pipe to which fire hoses can be connected * Standpipe (street), an external freestanding pipe to provide running water in areas with no other water supply * Standpipe water towers * Standpipe (plumbing), a vertical pipe attached to a p-trap for rapid high-volume wastewater drainage such as from washing machines * Standpipe piezometer, a device that monitors groundwater levels through a borehole * Rig standpipe Rig or RIG may refer to: Objects and structures * Rig (fishing), an arrangement of items used for fishing * Drilling rig, a structure housing equipment used to drill or extract oil from underground * Rig (stage lighting) * rig, a horse-drawn ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standpipe (firefighting)
A standpipe or riser is a type of rigid water piping which is built into multi-story buildings in a vertical position, or into bridges in a horizontal position, to which fire hoses can be connected, allowing manual application of water to the fire. Within the context of a building or bridge, a standpipe serves the same purpose as a fire hydrant. ''NFPA 14 - Standard for the Installation of Standpipe and Hose Systems'' regulates the design of standpipe system in the United States. Some standpipe systems are combined with fire sprinkler systems, using common pipes to supply both the sprinklers and hose connections. Types of standpipe systems Fire standpipes have two broad types: "Wet" and "Dry". The terms describe their state during normal, non-firefighting situations. Dry standpipe Dry standpipe systems do not contain water in the piping during normal, non-firefighting situations. Water is only introduced when needed for firefighting purposes. Manual Dry Standpipe System - A st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standpipe (street)
A standpipe is a freestanding pipe fitted with a tap which is installed outdoors to dispense water in areas which do not have a running water supply to the buildings. Use In the United Kingdom, an "Emergency Drought Order" permits a water company to shut off the primary water supply to homes, and to supply water instead from tanks or standpipes in the streets. This was done in some areas during the 1976 heat wave, for example. In some Middle Eastern, Caribbean and North African countries a standpipe is used as a communal water supply for neighbourhoods which lack individual housing water service. In areas such as Morocco, standpipes often yield unreliable service and lead to water scarcity for large numbers of people.Guillaume Benoit and Aline Comeau, ''A Sustainable Future for the Mediterranean'' (2005) 640 pages Freeze resistance In areas where the air or surface ground temperatures reach below freezing point for part or all of the year, some standpipes are equipped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
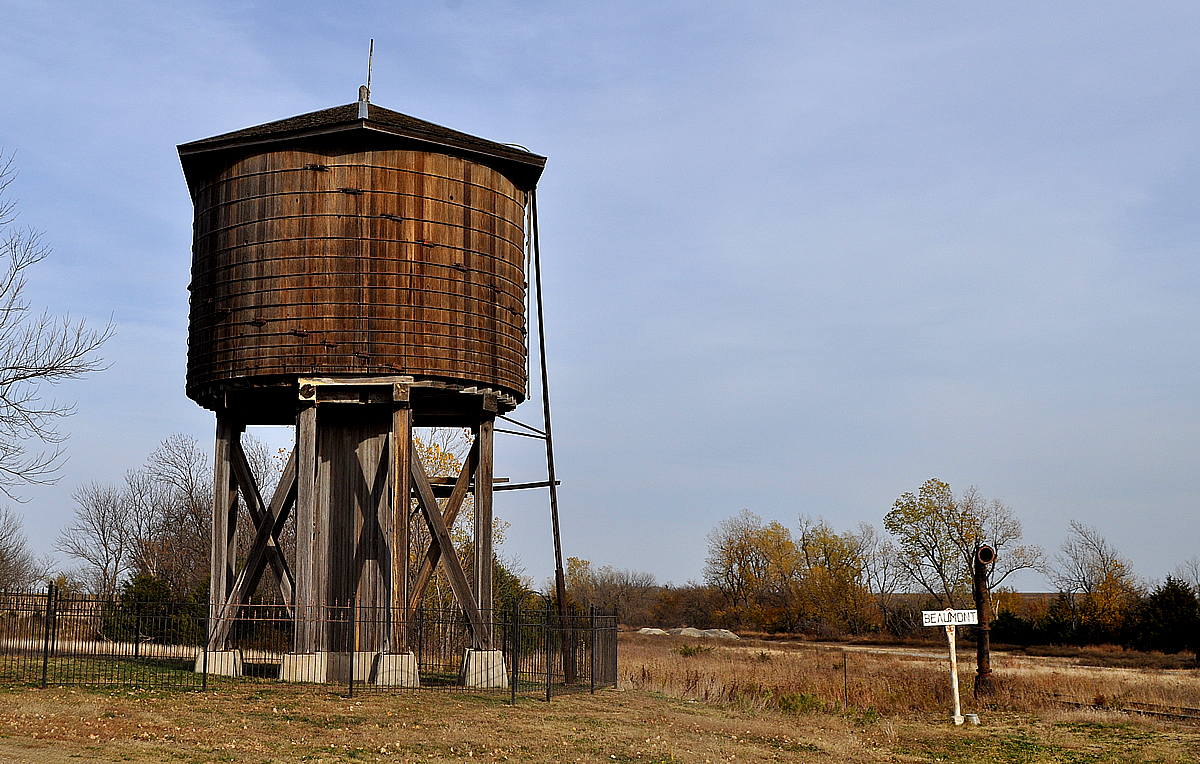
Water Tower
A water tower is an elevated structure supporting a water tank constructed at a height sufficient to pressurize a water distribution system, distribution system for potable water, and to provide emergency storage for fire protection. Water towers often operate in conjunction with underground or surface service reservoirs, which store treated water close to where it will be used. Other types of water towers may only store raw (non-potable) water for fire protection or industrial purposes, and may not necessarily be connected to a public water supply. Water towers are able to supply water even during power outages, because they rely on hydrostatic pressure produced by elevation of water (due to gravity) to push the water into domestic and industrial water distribution systems; however, they cannot supply the water for a long time without power, because a pump is typically required to refill the tower. A water tower also serves as a reservoir to help with water needs during peak us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
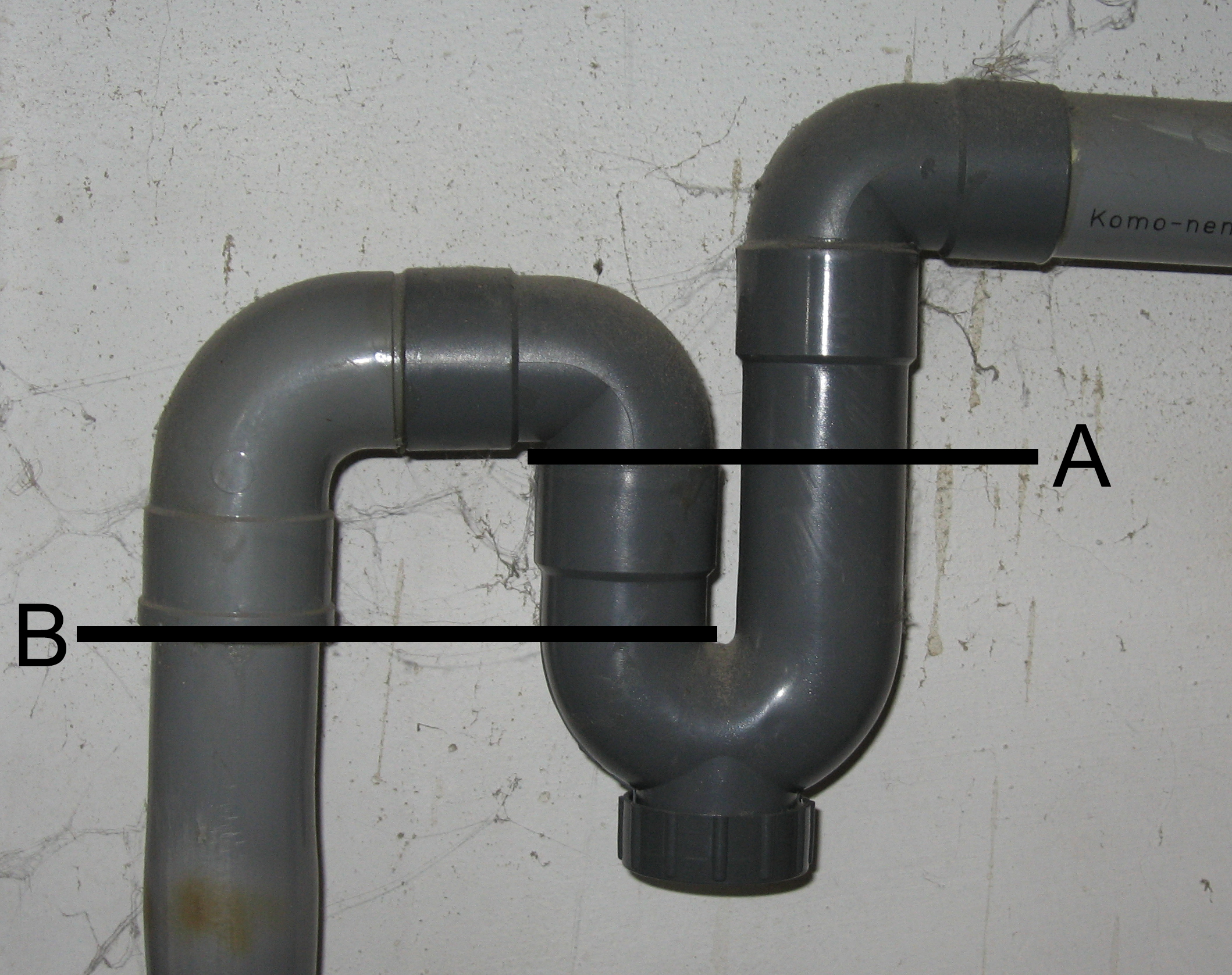
Standpipe (plumbing)
In plumbing, a trap is a U-shaped portion of pipe designed to trap liquid or gas to prevent unwanted flow; most notably sewer gases from entering buildings while allowing waste materials to pass through. In oil refineries, traps are used to prevent hydrocarbons and other dangerous gases and chemical fumes from escaping through drains. In heating systems, the same feature is used to prevent thermo-siphoning which would allow heat to escape to locations where it is not wanted. Similarly, some pressure gauges are connected to systems using U bends to maintain a local gas while the system uses liquid. For decorative effect, they can be disguised as complete loops of pipe, creating more than one U for added efficacy. General description In domestic applications, traps are typically U, S, Q, or J-shaped pipe (material), pipe located below or within a plumbing fixture. An S-shaped trap is also known as an S-bend. It was invented by Alexander Cumming in 1775 but became known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
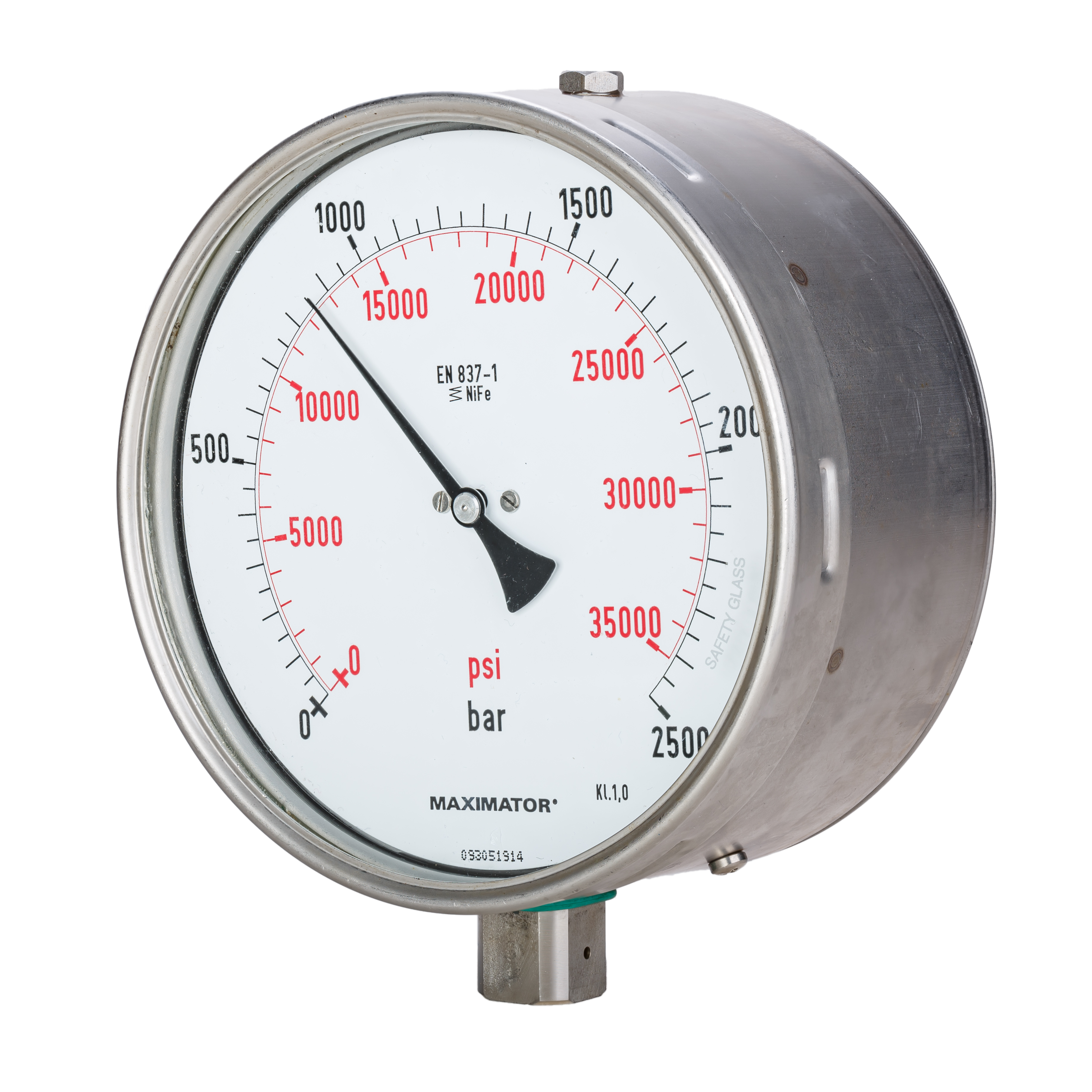
Piezometer
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in unit of measurement, units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |