|
Standard Model (other)
Standard model may refer to: * Standard Model of particle physics * The mathematical formulation of the Standard Model of particle physics * The Standard Solar Model of solar astrophysics * The Lambda-CDM model, the standard model of big bang cosmology * Standard model (cryptography) * Intended interpretation of a syntactical system, called standard model in mathematical logic * The standard models of set theory * The Standard Model (Exhibition) held in Stockholm, 2009 See also * Cosmological model Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of fu ... * The Standardmodell rifle, a German weapon {{mathdab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Model
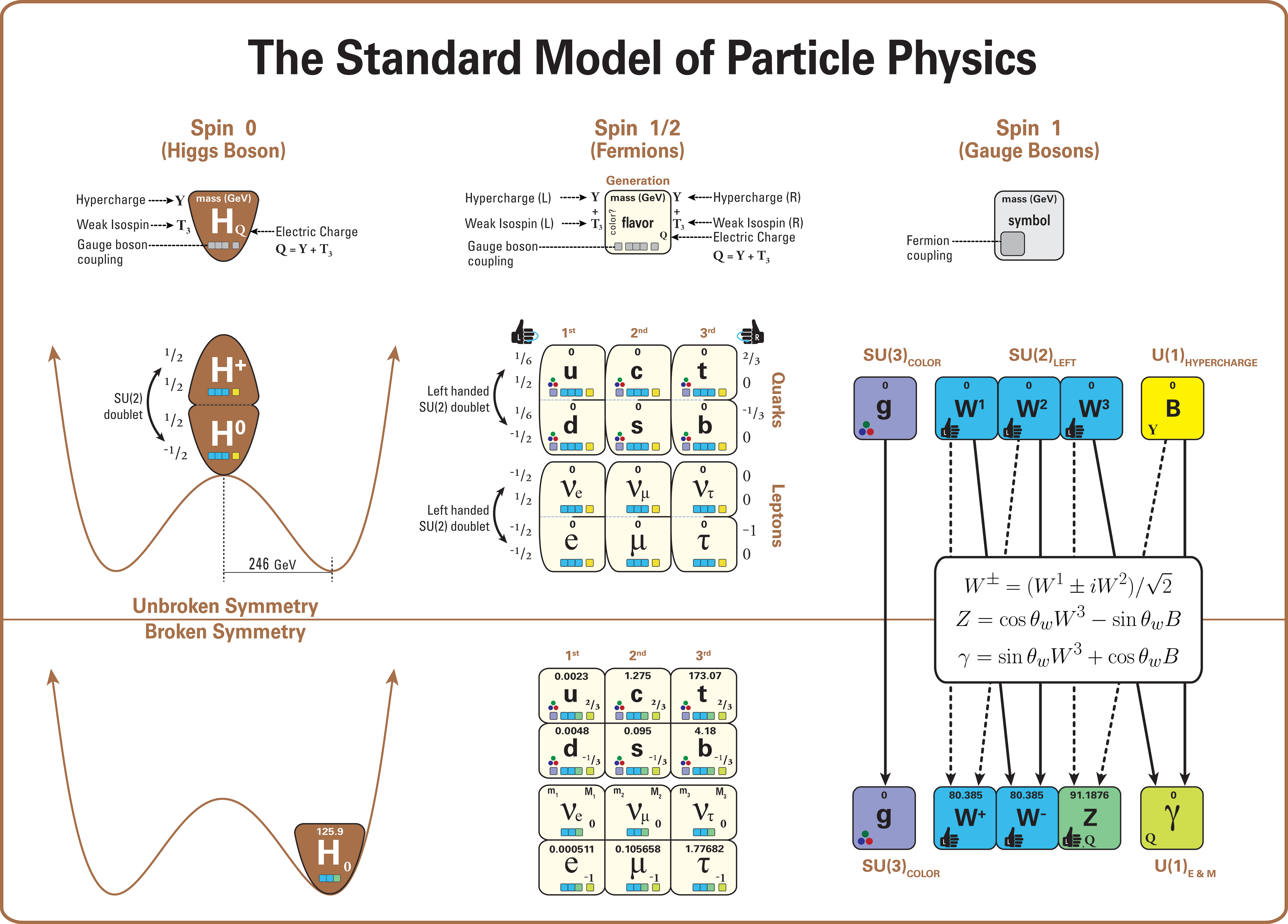
The Standard Model of particle physics is the Scientific theory, theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetism, electromagnetic, weak interaction, weak and strong interactions – excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles. It was developed in stages throughout the latter half of the 20th century, through the work of many scientists worldwide, with the current formulation being finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, proof of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and the Higgs boson (2012) have added further credence to the Standard Model. In addition, the Standard Model has predicted various properties of weak neutral currents and the W and Z bosons with great accuracy. Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated some success in providing experimental predictions, it leaves some physics be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Model (mathematical Formulation)
This article describes the mathematics of the Standard Model of particle physics, a gauge quantum field theory containing the internal symmetries of the unitary product group . The theory is commonly viewed as describing the fundamental set of particles – the leptons, quarks, gauge bosons and the Higgs boson. The Standard Model is renormalizable and mathematically self-consistent; however, despite having huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some unexplained phenomena. In particular, although the physics of special relativity is incorporated, general relativity is not, and the Standard Model will fail at energies or distances where the graviton is expected to emerge. Therefore, in a modern field theory context, it is seen as an effective field theory. Quantum field theory The standard model is a quantum field theory, meaning its fundamental objects are ''quantum fields'', which are defined at all points in spacetime. Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda-CDM Model
The Lambda-CDM, Lambda cold dark matter, or ΛCDM model is a mathematical model of the Big Bang theory with three major components: # a cosmological constant, denoted by lambda (Λ), associated with dark energy; # the postulated cold dark matter, denoted by CDM; # ordinary matter. It is the current ''standard model'' of Big Bang cosmology, as it is the simplest model that provides a reasonably good account of: * the existence and structure of the cosmic microwave background; * the large-scale structure in the distribution of galaxies; * the observed abundances of hydrogen (including deuterium), helium, and lithium; * the accelerating expansion of the universe observed in the light from distant galaxies and supernovae. The model assumes that general relativity is the correct theory of gravity on cosmological scales. It emerged in the late 1990s as a concordance cosmology, after a period when disparate observed properties of the universe appeared mutually inconsistent, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Model (cryptography)
In cryptography the standard model is the model of computation in which the adversary is only limited by the amount of time and computational power available. Other names used are bare model and plain model. Cryptographic schemes are usually based on complexity assumptions, which state that some problems, such as factorization, cannot be solved in polynomial time. Schemes that can be proven secure using only complexity assumptions are said to be secure in the standard model. Security proofs are notoriously difficult to achieve in the standard model, so in many proofs, cryptographic primitives are replaced by idealized versions. The most common example of this technique, known as the random oracle model, involves replacing a cryptographic hash function with a genuinely random function. Another example is the generic group model, where the adversary is given access to a randomly chosen encoding of a group, instead of the finite field or elliptic curve groups used in practice. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intended Interpretation
An interpretation is an assignment of meaning to the symbols of a formal language. Many formal languages used in mathematics, logic, and theoretical computer science are defined in solely syntactic terms, and as such do not have any meaning until they are given some interpretation. The general study of interpretations of formal languages is called formal semantics. The most commonly studied formal logics are propositional logic, predicate logic and their modal analogs, and for these there are standard ways of presenting an interpretation. In these contexts an interpretation is a function that provides the extension of symbols and strings of an object language. For example, an interpretation function could take the predicate symbol T and assign it the extension \. All our interpretation does is assign the extension \ to the non-logical symbol T, and does not make a claim about whether T is to stand for tall and \mathrm for Abraham Lincoln. On the other hand, an interpretation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Model (set Theory)
In set theory, a standard model for a theory ''T'' is a model ''M'' for ''T'' where the membership relation ∈''M'' is the same as the membership relation ∈ of a set theoretical universe ''V'' (restricted to the domain of ''M''). In other words, ''M'' is a substructure of ''V.'' A standard model ''M'' that satisfies the additional transitivity condition that ''x'' ∈ ''y ∈'' ''M'' implies ''x'' ∈ ''M'' is a standard transitive model (or simply a transitive model). Usually, when one talks about a model ''M'' of set theory, it is assumed that ''M'' is a set model, i.e. the domain of ''M'' is a set in ''V.'' If the domain of ''M'' is a proper class, then ''M'' is a class model. An inner model In set theory, a branch of mathematical logic, an inner model for a theory ''T'' is a substructure of a model ''M'' of a set theory that is both a model for ''T'' and contains all the ordinals of ''M''. Definition Let ''L'' = ⟨∈� ... is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Model (Exhibition)
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetic, weak and strong interactions – excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles. It was developed in stages throughout the latter half of the 20th century, through the work of many scientists worldwide, with the current formulation being finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, proof of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and the Higgs boson (2012) have added further credence to the Standard Model. In addition, the Standard Model has predicted various properties of weak neutral currents and the W and Z bosons with great accuracy. Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated some success in providing experimental predictions, it leaves some physical phenomena unexplained and so falls short of being a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Model
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate.For an overview, see Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed those physical laws to be understood. Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began in 1915 with the development of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond the Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |