|
Stable Diffusion WebUI Forge
AUTOMATIC1111 Stable Diffusion Web UI (SD WebUI, A1111, or Automatic1111) is an open source generative artificial intelligence program that allows users to generate images from a text prompt. It uses Stable Diffusion as the base model for its image capabilities together with a large set of extensions and features to customize its output. History ''SD WebUI'' was released on GitHub on August 22, 2022, by AUTOMATIC1111, 1 month after the initial release of Stable Diffusion. At the time, Stable Diffusion could only be run via the command line. ''SD WebUI'' quickly rose in popularity and has been described as "the most popular tool for running diffusion models locally." A user study of six StableDiffusion users showed that all participants had used SD WebUI at least once. The study showed that users ascribe SD WebUI's popularity to its ease of installation and support for open source tools. ''SD WebUI'' is one of the most popular user interfaces for Stable Diffusion, together with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language and first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000 and introduced new features such as list comprehensions, cycle-detecting garbage collection, reference counting, and Unicode support. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision that is not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2 was discontinued with version 2.7.18 in 2020. Python consistently ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variational Autoencoder
In machine learning, a variational autoencoder (VAE), is an artificial neural network architecture introduced by Diederik P. Kingma and Max Welling, belonging to the families of probabilistic graphical models and variational Bayesian methods. Variational autoencoders are often associated with the autoencoder model because of its architectural affinity, but with significant differences in the goal and mathematical formulation. Variational autoencoders are probabilistic generative models that require neural networks as only a part of their overall structure, as e.g. in VQ-VAE. The neural network components are typically referred to as the encoder and decoder for the first and second component respectively. The first neural network maps the input variable to a latent space that corresponds to the parameters of a variational distribution. In this way, the encoder can produce multiple different samples that all come from the same distribution. The decoder has the opposite function, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Register
''The Register'' is a British technology news website co-founded in 1994 by Mike Magee, John Lettice and Ross Alderson. The online newspaper's masthead sublogo is "''Biting the hand that feeds IT''." Their primary focus is information technology news and opinions. Situation Publishing Ltd is listed as the site's publisher. Drew Cullen is an owner and Linus Birtles is the managing director. Andrew Orlowski was the executive editor before leaving the website in May 2019. History ''The Register'' was founded in London as an email newsletter called ''Chip Connection''. In 1998 ''The Register'' became a daily online news source. Magee left in 2001 to start competing publications '' The Inquirer'', and later the '' IT Examiner'' and '' TechEye''.Walsh, Bob (2007). ''Clear Blogging: How People Blogging Are Changing the World and How You Can Join Them.'' Apress, In 2002, ''The Register'' expanded to have a presence in London and San Francisco, creating ''The Register USA'' at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flux (text-to-image Model)
Flux (also known as FLUX.1) is a text-to-image model developed by Black Forest Labs, based in Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany. Black Forest Labs were founded by former employees of Stability AI. As with other text-to-image models, Flux generates images from natural language descriptions, called '' prompts''. History Black Forest Labs were founded in 2024 by Robin Rombach, Andreas Blattmann, and Patrick Esser, former employees of Stability AI. All three founders had previously researched the artificial intelligence image generation at Ludwig Maximillian University of Munich as research assistants under Björn Ommer. They published their research results on image generation in 2022, which resulted in creation of Stable Diffusion. Investors in Black Forest Labs included venture capital firm Andreessen Horowitz, Brendan Iribe, Michael Ovitz, Garry Tan, and Vladlen Koltun. The company received an initial investment of million. In August 2024, Flux was integrated into the Grok ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
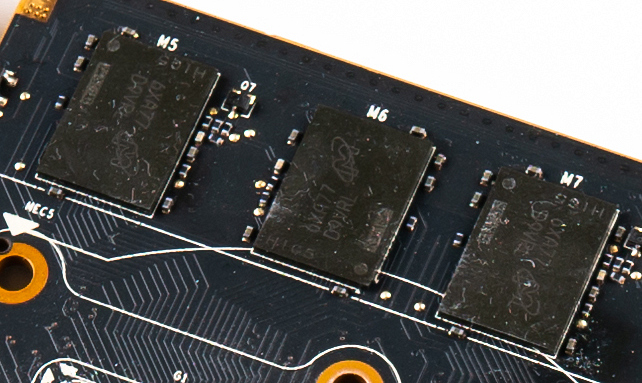
VRAM
Video random access memory (VRAM) is dedicated computer memory used to store the pixels and other graphics data as a framebuffer to be rendered on a computer monitor. This is often different technology than other computer memory, to facilitate being read rapidly to draw the image. In some systems this memory cannot be read/written using the same methods as normal memory; it is not memory mapped. Description While a computer has system RAM, most contemporary graphics cards have access to a dedicated set of memory known as VRAM. In contrast, a GPU which shares system memory has a Unified Memory Architecture, or shared graphics memory. System RAM and VRAM has been segregated due to the bandwidth requirements of GPUs, and to achieve lower latency since VRAM is physically closer to the GPU die. Modern VRAM is found in a BGA package soldered onto the graphics card. Like the GPU itself, the VRAM is cooled by the GPU heatsink. Technologies * Video RAM (dual-ported DRAM), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fooocus
Fooocus is an open source generative artificial intelligence program that allows users to generate images from a text prompt. It uses Stable Diffusion XL as the base model for its image capabilities as well as a collection of default settings and prompts to make the image generation process more streamlined. History ''Fooocus'' was created by Lvmin Zhang, a doctoral student at Stanford University who previously studied at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and Soochow University. He is also the main author of ControlNet, which has been adopted by many other Stable Diffusion interfaces, such as AUTOMATIC1111 and ComfyUI. As of 9 July 2024, the project had 38.1k stars on GitHub. Features ''Fooocus''' main feature is that it is easy to set up and does not require users to manually configure model parameters to achieve desirable results. According to the project, it uses GPT-2 to automatically add more detail to the user's prompts. It includes common extensions such LCM low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Diffusion
Stable Diffusion is a deep learning, text-to-image model released in 2022. It is primarily used to generate detailed images conditioned on text descriptions, though it can also be applied to other tasks such as inpainting, outpainting, and generating image-to-image translations guided by a text prompt. Stable Diffusion is a latent diffusion model, a kind of deep generative neural network developed by the CompVis group at LMU Munich. The model has been released by a collaboration of Stability AI, CompVis LMU, and Runway with support from EleutherAI and LAION. In October 2022, Stability AI raised US$101 million in a round led by Lightspeed Venture Partners and Coatue Management. Stable Diffusion's code and model weights have been released publicly, and it can run on most consumer hardware equipped with a modest GPU with at least 8 GB VRAM. This marked a departure from previous proprietary text-to-image models such as DALL-E and Midjourney which were accessible only via clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion Model
In machine learning, diffusion models, also known as diffusion probabilistic models, are a class of latent variable models. They are Markov chains trained using variational inference. The goal of diffusion models is to learn the latent structure of a dataset by modeling the way in which data points diffuse through the latent space. In computer vision, this means that a neural network is trained to denoise images blurred with Gaussian noise by learning to reverse the diffusion process. Three examples of generic diffusion modeling frameworks used in computer vision are denoising diffusion probabilistic models, noise conditioned score networks, and stochastic differential equations. Diffusion models were introduced in 2015 with a motivation from non-equilibrium thermodynamics. Diffusion models can be applied to a variety of tasks, including image denoising, inpainting, super-resolution, and image generation. For example, an image generation model would start with a random noise image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Scaling
In computer graphics and digital imaging, image scaling refers to the resizing of a digital image. In video technology, the magnification of digital material is known as upscaling or resolution enhancement. When scaling a vector graphic image, the graphic primitives that make up the image can be scaled using geometric transformations, with no loss of image quality. When scaling a raster graphics image, a new image with a higher or lower number of pixels must be generated. In the case of decreasing the pixel number (scaling down) this usually results in a visible quality loss. From the standpoint of digital signal processing, the scaling of raster graphics is a two-dimensional example of sample-rate conversion, the conversion of a discrete signal from a sampling rate (in this case the local sampling rate) to another. Mathematical Image scaling can be interpreted as a form of image resampling or image reconstruction from the view of the Nyquist sampling theorem. According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inpainting
Inpainting is a conservation process where damaged, deteriorated, or missing parts of an artwork are filled in to present a complete image. This process is commonly used in image restoration. It can be applied to both physical and digital art mediums such as oil or acrylic paintings, chemical photographic prints, sculptures, or digital images and video. With its roots in physical artwork, such as painting and sculpture, traditional inpainting is performed by a trained art conservator who has carefully studied the artwork to determine the mediums and techniques used in the piece, potential risks of treatments, and ethical appropriateness of treatment. History The modern use of inpainting can be traced back to Pietro Edwards (1744–1821), Director of the Restoration of the Public Pictures in Venice, Italy. Using a scientific approach, Edwards focused his restoration efforts on the intentions of the artist. It was during the 1930 International Conference for the Study o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine-tuning (deep Learning)
In deep learning, fine-tuning is an approach to transfer learning in which the weights of a pre-trained model are trained on new data. Fine-tuning can be done on the entire neural network, or on only a subset of its layers, in which case the layers that are not being fine-tuned are "frozen" (not updated during the backpropagation step). A model may also be augmented with "adapters" that consist of far fewer parameters than the original model, and fine-tuned in a parameter-efficient way by tuning the weights of the adapters and leaving the rest of the model's weights frozen. For some architectures, such as convolutional neural networks, it is common to keep the earlier layers (those closest to the input layer) frozen because they capture lower-level features, while later layers often discern high-level features that can be more related to the task that the model is trained on. Models that are pre-trained on large and general corpora are usually fine-tuned by reusing the model's p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Affero General Public License
The GNU Affero General Public License (GNU AGPL) is a free, copyleft license published by the Free Software Foundation in November 2007, and based on the GNU General Public License, version 3 and the Affero General Public License. The Free Software Foundation has recommended that the GNU AGPLv3 be considered for any software that will commonly be run over a network.List of free-software licences on the FSF website "''We recommend that developers consider using the GNU AGPL for any software which will commonly be run over a network.''" The Free Software Foundation explains the need for the license in the case when a free program is run on a server: The GNU Affero General Public License is a modified version of the ordinary GNU GPL version 3. It has one added requirement: if you ... |