|
St. Martial School
The Saint Martial School was a medieval music, medieval school of music composition centered in the Abbey of Saint Martial, Limoges, France. Most active from the 9th to 12th centuries, some scholars describe its practices, music, and manuscripts as 'Aquitanian'. It is known for the composition of Trope (music), tropes, sequence (poetry), sequences, and early organum. In this respect, it was an important precursor to the Notre Dame School. Adémar de Chabannes and his uncle Roger de Chabannes who introduced Adémar in the craftship of a notating cantor, were important proponents of this school whose hands had only be recently discovered by studies of James Grier between 1995 and 2005. They invented a local variant of a vertically precise organisation of notation and a new form of local tonary, they reorganised existing chant manuscripts, and they developed the libellum structure of a new type of sequentiary troper whose organisation was new at their time, but played a key role for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Music
Medieval music encompasses the sacred music, sacred and secular music of Western Europe during the Middle Ages, from approximately the 6th to 15th centuries. It is the Dates of classical music eras, first and longest major era of Western classical music and is followed by the Renaissance music; the two eras comprise what musicologists generally term as early music, preceding the common practice period. Following the traditional division of the Middle Ages, medieval music can be divided into #Early medieval music (500–1000), Early (500–1000), #High medieval music (1000–1300), High (1000–1300), and #Late medieval music (1300–1400), Late (1300–1400) medieval music. Medieval music includes liturgical music used for the church, other sacred music, and secular music, secular or non-religious music. Much medieval music is purely vocal music, such as Gregorian chant. Other music used only instruments or both voices and instruments (typically with the instruments accompanime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
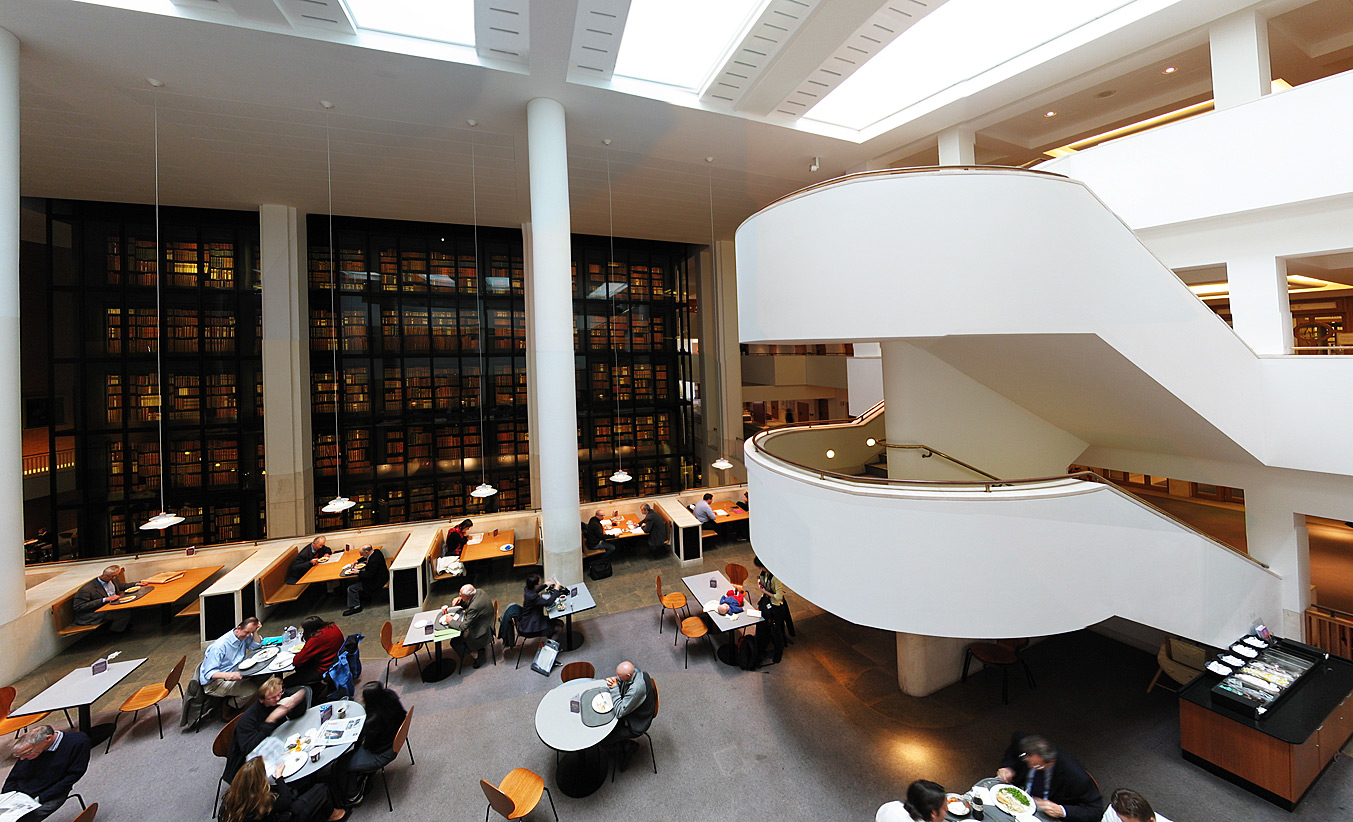
British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom. Based in London, it is one of the largest libraries in the world, with an estimated collection of between 170 and 200 million items from multiple countries. As a legal deposit library, it receives copies of all books produced in the United Kingdom and Ireland, as well as a significant proportion of overseas titles distributed in the United Kingdom. The library operates as a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. The British Library is a major research library, with items in many languages and in many formats, both print and digital: books, manuscripts, journals, newspapers, magazines, sound and music recordings, videos, play-scripts, patents, databases, maps, stamps, prints, drawings. The Library's collections include around 14 million books, along with substantial holdings of manuscripts and items dating as far back as 2000 BC. The library maintains a programme for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluny Abbey
Cluny Abbey (; , formerly also ''Cluni'' or ''Clugny''; ) is a former Benedictine monastery in Cluny, Saône-et-Loire, France. It was dedicated to Saints Peter and Paul. The abbey was constructed in the Romanesque architectural style, with three churches built in succession from the 4th to the early 12th centuries. The earliest basilica was the world's largest church until the St. Peter's Basilica construction began in Rome. Cluny was founded by Duke William I of Aquitaine in 910. He nominated Berno as the first abbot of Cluny, subject only to Pope Sergius III. The abbey was notable for its stricter adherence to the Rule of St. Benedict, whereby Cluny became acknowledged as the leader of western monasticism. In 1790 during the French Revolution, the abbey was sacked and mostly destroyed, with only a small part surviving. Starting around 1334, the Abbots of Cluny maintained a townhouse in Paris known as the Hôtel de Cluny, which has been a public museum since 1843. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Maur Abbey
Saint-Maur Abbey (), originally called the Abbaye des Fossés, is a former abbey now subsumed in the Saint-Maur-des-Fossés suburb of Paris, France. The remains and the domain of the abbey have been transformed into a pleasure park named ''Parc de l'abbaye''. The former abbey building has been replaced by a square at the corner of Avenue de Condé and Rue de l'Abbaye. Some ruins remain, such as the Rabelais tower, the 19th century Bourières villa and the old fortifications. The remains of the abbey have been classified as historical monuments since 13 June 1988. History Foundation An abbey with a church (known as "Abbatiale I"), it was built in 639, under the regency of Queen Nanthild, mother of Clovis II, on a ruined ''castrum'', located in a peninsula formed by a meander of the Marne (river), Marne, on the territory of the future commune of Saint-Maur by a deacon of Paris named Blidegisilus. It took the name of "Saint-Pierre-du-Fossé" referring to the terrain of the place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbey Of Saint Denis
The Basilica of Saint-Denis (, now formally known as the ) is a large former medieval abbey church and present cathedral in the commune of Saint-Denis, a northern suburb of Paris. The building is of singular importance historically and architecturally as its choir, completed in 1144, is widely considered the first structure to employ all of the elements of Gothic architecture. The basilica became a place of pilgrimage and a necropolis containing the tombs of the kings of France, including nearly every king from the 10th century to Louis XVIII in the 19th century. Henry IV of France came to Saint-Denis formally to renounce his Protestant faith and become a Catholic. The queens of France were crowned at Saint-Denis, and the regalia, including the sword used for crowning the kings and the royal sceptre, were kept at Saint-Denis between coronations. The site originated as a Gallo-Roman cemetery in late Roman times. The archaeological remains still lie beneath the cathedral; the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notre Dame School
The Notre-Dame school or the Notre-Dame school of polyphony refers to the group of composers working at or near the Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris from about 1160 to 1250, along with the music they produced. The only composers whose names have come down to us from this time are Léonin and Pérotin. Both were mentioned by an anonymous English student, known as Anonymous IV, who was either working or studying at Notre-Dame later in the 13th century. In addition to naming the two composers as "the best composers of organum," and specifying that they compiled the big book of organum known as the '' Magnus Liber Organi'', he provides a few tantalizing bits of information on the music and the principles involved in its composition. Pérotin is the first composer of ''organum quadruplum''—four-voice polyphony—at least the first composer whose music has survived, since complete survivals of notated music from this time are scarce. Léonin, Pérotin and the other anonymous co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, Fashion capital, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the French art, arts and Science and technology in France, sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleury Abbey
Fleury Abbey (Floriacum) in Saint-Benoît-sur-Loire, Loiret, France, founded in about 640, is one of the most celebrated Benedictine monasteries of Western Europe, and possesses the relics of St. Benedict of Nursia. Its site on the banks of the Loire has always made it easily accessible from Orléans, a center of culture unbroken since Roman times. In 2010, the abbey had over forty monks led by the abbot Etienne Ricaud. Abbo of Fleury (died 1004) a monk and abbot of Fleury was a theologian of wide-ranging intellect; his life was written by the chronicler Aimoin, also a monk of Fleury. Andrew of Fleury (writing 1043) wrote ''Miracula sancti Benedicti''. Hugh of Fleury (died after 1118) was a monk of Fleury known for his chronicles and other writings. Churches Anscar Vonier, writing in the ''Catholic Encyclopedia'' says that "from the very start the abbey boasted of two churches, one in honour of St. Peter and the other in honour of the Blessed Virgin." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epistle
An epistle (; ) is a writing directed or sent to a person or group of people, usually an elegant and formal didactic letter. The epistle genre of letter-writing was common in ancient Egypt as part of the scribal-school writing curriculum. The letters in the New Testament from Apostles to Christians are usually referred to as epistles. Those traditionally attributed to Paul are known as Pauline epistles and the others as catholic (i.e., "general") epistles. Ancient Egyptian epistles The ancient Egyptians wrote epistles, most often for pedagogical reasons. Egyptologist Edward Wente (1990) speculates that the Fifth-dynasty Pharaoh Djedkare Isesi—in his many letters sent to his viziers—was a pioneer in the epistolary genre. Its existence is firmly attested during the Sixth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, and is prominently featured in the educational guide ''The Book of Kemit'' written during the Eleventh Dynasty. A standardized formulae for epistolary compositions exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organum
''Organum'' () is, in general, a plainchant melody with at least one added voice to enhance the harmony, developed in the Middle Ages. Depending on the mode and form of the chant, a supporting bass line (or '' bourdon'') may be sung on the same text, the melody may be followed in parallel motion (parallel ), or a combination of both of these techniques may be employed. As no real independent second voice exists, this is a form of heterophony. In its earliest stages, ''organum'' involved two musical voices: a Gregorian chant melody, and the same melody transposed by a consonant interval, usually a perfect fifth or fourth. In these cases the composition often began and ended on a unison, the added voice keeping to the initial tone until the first part has reached a fifth or fourth, from where both voices proceeded in parallel harmony, with the reverse process at the end. ''Organum'' was originally improvised; while one singer performed a notated melody (the ''vox principalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence (music)
In music, a sequence is the restatement (music), restatement of a motif (music), motif or longer melody, melodic (or harmony (music), harmonic) passage at a higher or lower pitch (music), pitch in the same voice.Benward and Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.111-12. Seventh Edition. . It is one of the most common and simple methods of elaborating a melody in eighteenth and nineteenth century classical music (Classical period (music), Classical period and Romantic music). Characteristics of sequences: *Two segments, usually no more than three or four *Usually in only one direction: continually higher or lower *Segments continue by same interval distance It is possible for melody or harmony to form a sequence without the other participating. There are many types of sequences, each with a unique pattern. Listed below are some examples. Melodic sequences In a melody, a real sequence is a sequence where the subsequent segments are exact transposition (music) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosula
The word trope or tropus may refer to a variety of different concepts in medieval, 20th-, and 21st-century music. The term ''trope'' derives from the Greek (''tropos''), "a turn, a change", related to the root of the verb (''trepein''), "to turn, to direct, to alter, to change". The Latinised form of the word is ''tropus''. In music, a trope is adding another section, or trope to a plainchant or section of plainchant, thus making it appropriate to a particular occasion or festival. Medieval music From the 9th century onward, trope refers to additions of new music to pre-existing chants in use in the Western Christian Church. Three types of addition are found in music manuscripts: # new melismas without text (mostly unlabelled or called "trope" in manuscripts) # addition of a new text to a pre-existing melisma (more often called ''prosula'', ''prosa'', ''verba'' or ''versus'') # new verse or verses, consisting of both text and music (mostly called trope, but also ''laude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |