|
Sri Lanka Myna
The Sri Lanka hill myna or Ceylon myna (''Gracula ptilogenys'') is a myna, a member of the starling family. This bird is endemic to Sri Lanka. This passerine is typically found in forest and cultivation. The Sri Lanka myna builds a nest in a hole. The normal clutch is two eggs. These 25 cm long birds have green-glossed black plumage, purple-tinged on the head and neck. There are large white wing patches, which are obvious in flight. The strong legs are bright yellow, and there are yellow wattles on the nape. The different shape and position of the wattles and the stouter orange-red bill distinguish this species from the southern hill myna, which also occurs in Sri Lankan forests. The sexes are similar in plumage, but can be distinguished by iris color, which is pale in females and dark in males. Juveniles have a duller bill and smaller wattles, and are less glossy overall. Like most starlings, the Sri Lanka myna is fairly omnivorous, eating fruit, nectar and insects. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Blyth
Edward Blyth (23 December 1810 – 27 December 1873) was an English zoologist who worked for most of his life in India as a curator of zoology at the Asiatic Society, Royal Asiatic Society of Bengal in Calcutta. He set about updating the museum's catalogues, publishing a ''Catalogue of the Birds of the Asiatic Society'' in 1849. He was prevented from doing much fieldwork himself, but received and described bird specimens from Allan Octavian Hume, A.O. Hume, Samuel Tickell, Robert Swinhoe among others. His ''Natural History of the Cranes'' was published posthumously in 1881. Early life and work On 23 December 1810, Blyth was born in London. His father, a cloth merchant, clothier, died in 1820 and his mother sent him to Dr. Fennell's school in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon. He took an interest in reading, but was often to be found spending time in the woods nearby. Leaving school in 1825, he went to study chemistry, at the suggestion of Dr. Fennell, in London under Dr. Keating at S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and other animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition for the other; humans, and many other animals, have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language and culinary usage, ''fruit'' normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet (or sour) and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term ''fruit'' als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Birds Of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka is home to 34 Endemism, endemic bird species. The number of bird species recorded in the island is 492 of which 219 are breeding residents. BirdLife International recognize Sri Lanka as one of the world's Endemic Bird Areas (EBAs). The number of endemic species has changed over the years. This is largely due to "Taxonomy (biology), close taxonomic revisions". The number of endemic species has fluctuated from 20 to 47. Since 1977 the number has settled at around 21. The figure was increased to 23 in 1990. Many authorities have accepted this figure since then. Wijesinghe published ''A Checklist of the Birds of Sri Lanka'' in 1994 which considered the addition of three more species, but this move did not receive widespread recognition because its rationale was not in keeping with rigorous taxonomic practice. Subsequent publications on the avifauna of Sri Lanka and the South Asia region have not listed these three as endemics. However, within some Sri Lankan circles considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gracula
''Gracula'' is a genus of mynas, tropical members of the starling family of birds found in southern Asia and introduced to Florida in the United States. Taxonomy The genus ''Gracula'' was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. The genus name is from Latin ''graculus'', an unknown bird sometimes identified as the western jackdaw. Of the seven species listed by Linnaeus, George Robert Gray, George Gray designated the common hill myna (''Gracula religiosa'') as the type species. Until recently only two species were recognised, ''G. religiosa'' and ''G. ptilogenys''. Previously, all ''Gracula'' were considered to belong to a very variable species commonly called the hill myna. Three additional subspecies of ''G. religiosa'' are increasingly being considered as distinct species. Formerly, the Sri Lanka hill myna was considered to be a subspecies of the common hill myna, but today al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
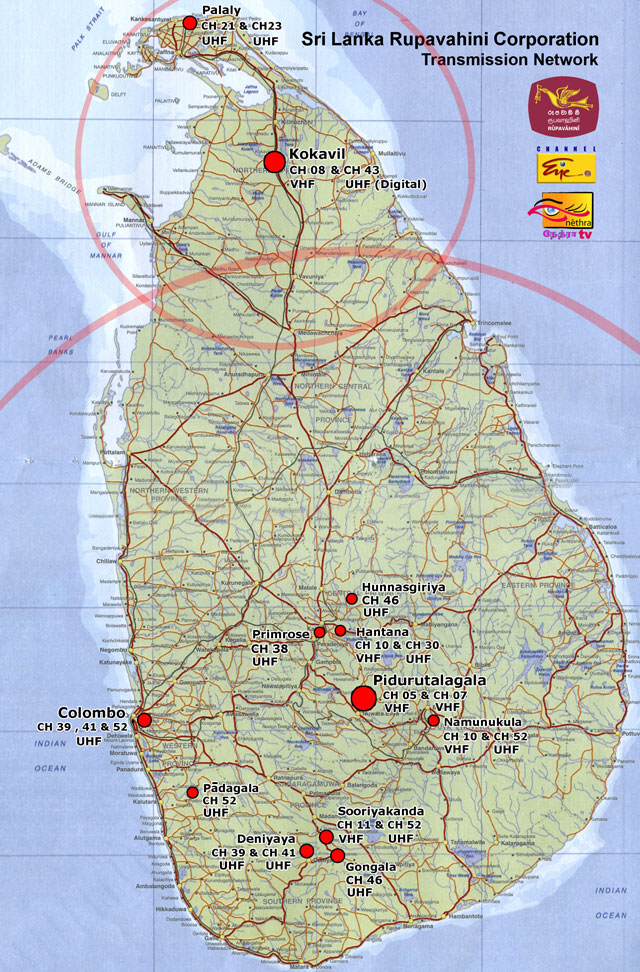
Sri Lanka Rupavahini Corporation
The Sri Lanka Rūpavāhinī Corporation (; ), also known as Jathika Rupavahini (lit. National Television) or simply as Rupavahini, is the national television network of Sri Lanka. The term Rupavahini literally means "purveyor of images" in the Sinhala language. Established by Parliament under Act No. 6 of 1982 for the provision of national television service, it produces and broadcasts programmes in three languages. Distinguished civil servant M.J Perera was the founder and chairman of Sri Lanka Rupavahini Corporation. SLRC is the largest television broadcaster in Sri Lanka and has an island-wide reception of its channels. SLRC broadcasts its channels in both VHF and UHF frequencies in Sri Lanka. Currently, all of the network's services are only available by Analog television, analog transmission. But there are plans to upgrade to digital broadcasting. From 2011 Kokavil transmission tower, Kokavil began to broadcast in DVB-T2 for the North area in Sri Lanka. There were plans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupee
Rupee (, ) is the common name for the currency, currencies of Indian rupee, India, Mauritian rupee, Mauritius, Nepalese rupee, Nepal, Pakistani rupee, Pakistan, Seychellois rupee, Seychelles, and Sri Lankan rupee, Sri Lanka, and of former currencies of Afghan rupee, Afghanistan, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, the United Arab Emirates (as the Gulf rupee), East African rupee, British East Africa, Burmese rupee, Burma, German East African rupie, German East Africa (as German East African rupie, Rupie/Rupien), and Historical money of Tibet, Tibet. In Indonesia and the Maldives, the unit of currency is known as ''rupiah'' and ''rufiyaa'' respectively, cognates of the word rupee. The Indian rupee and Pakistani rupee are subdivided into one hundred paisa, paise (singular ''paisa'') or pice. The Nepalese rupee (रू) subdivides into one hundred paisa (singular and plural) or four sukaas. The Mauritian rupee, Mauritian, Seychellois rupee, Seychellois, and Sri Lankan rupees subdivide into 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinhala Language
Sinhala ( ; Sinhala: , , ), sometimes called Sinhalese ( ), is an Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka, who make up the largest ethnic group on the island, numbering about 16 million. It is also the first language of about 2 million other Sri Lankans, as of 2001. It is written in the Sinhalese script, a Brahmic script closely related to the Grantha script of South India. The language has two main varieties, written and spoken, and is a notable example of the linguistic phenomenon known as diglossia. Sinhala is one of the official and national languages of Sri Lanka. Along with Pali, it played a major role in the development of Theravada Buddhist literature. Early forms of the Sinhalese language are attested to as early as the 3rd century BCE. The language of these inscriptions, still retaining long vowels and aspirated consonants, is a Prakrit similar to Magadhi, a regional associate of the Middle-Indian Prakrits that had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar
Nectar is a viscous, sugar-rich liquid produced by Plant, plants in glands called nectaries, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollination, pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal Mutualism (biology), mutualists, which in turn provide plant defense against herbivory#Indirect defenses, herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverfly, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterfly, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and Bat#Fruit and nectar, bats. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of predacious or Parasitoid wasp, parasitoid wasps (e.g., the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely on nectar as a primary food source. In turn, these wasps then hunt agricultural pest insects as food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms (Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myna
The mynas (; also spelled mynah) are a group of birds in the starling family (Sturnidae). This is a group of passerine birds which are native to Iran and Southern Asia, especially Afghanistan, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Several species have been introduced to areas like North America, Australia, South Africa, Fiji and New Zealand, especially the common myna, which is often regarded as an invasive species. It is often known as "Selarang" and "Teck Meng" in Malay and Chinese respectively in Singapore, due to their high population there. Mynas are not a natural group; instead, the term ''myna'' is used for any starling in the Indian subcontinent, regardless of their relationships. This range was colonized twice during the evolution of starlings, first by rather ancestral starlings related to the coleto and '' Aplonis'' lineages, and millions of years later by birds related to the common starling and wattled starling's ancestors. These two groups of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Hill Myna
The southern hill myna (''Gracula indica'') is a member of the starling family. It is a resident of the forested regions of south India and Sri Lanka. This species moves around in flocks in the forest, and members of a flock keep in contact with a wide range of vocalizations. Etymology The French word for the bird ''mainate'' is probably derived from the Indo-Portuguese mainato, from the name of a songbird living near water, and is probably a metaphor since it refers to a man whose job is to wash the clothes of others. Description The southern hill myna has a shiny black plumage. It generally measures about twenty centimeters. It can live between 15 and 30 years. The legs are yellow, the beak is bright orange at the base and yellow at the tip. It has white spots on the primary remiges. Like other species of hill myna, the southern hill myna has yellow wattles on the head. Habitats and behavior The southern hill myna is present in southwestern India and Sri Lanka. It inhab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |