|
Spy (ship)
Several vessels have been named ''Spy'': * After the Royal Navy sold in 1773, between 1773 and 1780 she became the transport ''Spy''. * was launched in Liverpool in 1777. She traded locally until 1781 when her owners renamed her ''Spy'' and placed her in the slave trade. The French Navy captured her in 1782 in the West Indies as she was arriving to deliver her cargo of enslaved people. * was built in France in 1780, almost surely under another name, and taken in prize. The British East India Company (EIC) purchased her in 1781 and used her for almost two years as a fast packet vessel and cruiser based in St Helena. It then sold her and she became a London-based slave ship, making two voyages carrying enslaved people in the triangular trade, in the Middle Passage from West Africa to the West Indies. next, she became a whaler, making seven whaling voyages between 1786 and 1795. She was probably wrecked in August 1795 on a voyage as a government transport. * was a 16-gun French private ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perform some form of work while also having their location or residence dictated by the enslaver. Many historical cases of enslavement occurred as a result of breaking the law, becoming indebted, or suffering a military defeat; other forms of slavery were instituted along demographic lines such as race. Slaves may be kept in bondage for life or for a fixed period of time, after which they would be granted freedom. Although slavery is usually involuntary and involves coercion, there are also cases where people voluntarily enter into slavery to pay a debt or earn money due to poverty. In the course of human history, slavery was a typical feature of civilization, and was legal in most societies, but it is now outlawed in most countries of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet Trade
Generally, packet trade is any regularly scheduled cargo, passenger and mail trade conducted by ship. The ships are called " packet boats" as their original function was to carry mail. A "packet ship" was originally a vessel employed to carry post office mail packets to and from British embassies, colonies and outposts. In sea transport, a packet service is a regular, scheduled service, carrying freight and passengers. The ships used for this service are called packet ships or packet boats. The seamen are called packetmen, and the business is called packet trade. "Packet" can mean a small parcel but, originally meant a parcel of important correspondence or valuable items, for urgent delivery.Oxford English Dictionary - ''Packet'': "A small pack, package, or parcel. In later use freq.: the container or wrapping in which goods are sold; packaging; a bag or envelope for packing something in. Also: the contents of a packet. In early use chiefly used of a parcel of letters or dispatch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Helena
Saint Helena () is a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote volcanic tropical island west of the coast of south-western Africa, and east of Rio de Janeiro in South America. It is one of three constituent parts of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. Saint Helena measures about and has a population of 4,439 per the 2021 census. It was named after Helena, mother of Constantine I. It is one of the most remote islands in the world and was uninhabited when discovered by the Portuguese enroute to the Indian subcontinent in 1502. For about four centuries the island was an important stopover for ships from Europe to Asia and back, while sailing around the African continent, until the opening of the Suez canal. St Helena is the United Kingdom's second-oldest overseas territory after Bermuda. Saint Helena is known for being the site of Napoleon's second exile, following his final defeat in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
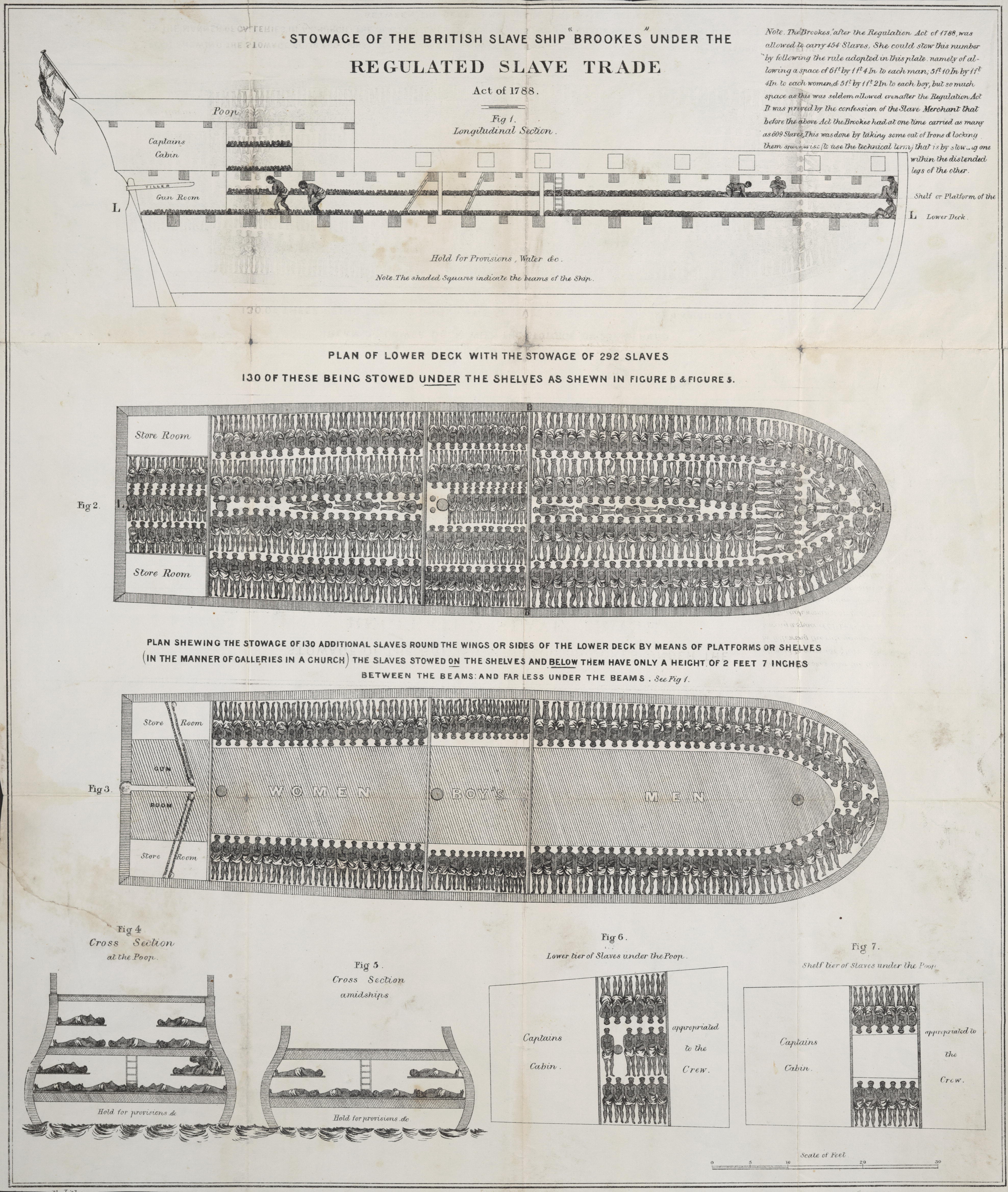
Slave Ship
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangular Trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset trade imbalances between different regions. The Atlantic slave trade used a system of three-way trans-Atlantic exchanges – known historically as the triangular trade – which operated between Europe, Africa and the Americas from the 16th to 19th centuries. A classic example is the colonial molasses trade, which involved the circuitous trading of slaves, sugar (often in liquid form, as molasses), and rum between West Africa, the West Indies and the northern colonies of British North America in the 17th and 18th centuries. The slaves grew the sugar that was used to brew rum, which in turn was traded for more slaves. In this circuit, the sea lane west from Africa to the West Indies (and later, also to Brazil) was known as the Middle Pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Passage
The Middle Passage was the stage of the Atlantic slave trade in which millions of enslaved Africans were transported to the Americas as part of the triangular slave trade. Ships departed Europe for African markets with manufactured goods (first side of the triangle), which were then traded for slaves with rulers of African states and other African slave traders. Slave ships (also known as Guineamen) transported the slaves across the Atlantic (second side of the triangle). The proceeds from selling slaves was then used to buy products such as hides, tobacco, sugar, rum, and raw materials, which would be transported back to northern Europe (third side of the triangle) to complete the triangle. The First Passage was the forced march of African slaves from their inland homes, where they had often been captured by other tribes or by other members of their own tribe, to African ports where they were imprisoned until they were sold and loaded onto a ship. The Final Passage was the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales. Terminology The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japan, still dedicates a single factory ship for the industry. The vessels used by aboriginal whaling communities are much smaller and are used for various purposes over the course of the year. The ''whale catcher'' was developed during the age of steam, and then driven by diesel engines throughout much of the twentieth century. It was designed with a harpoon gun mounted at its bow and was fast enough to chase and catch rorquals such as the fin whale. At first, whale catchers either brought the whales they killed to a whaling station, a settlement ashore where the carcasses could be processed, or to its factory ship anchored in a sheltered bay or inlet. With the later development of the slipway at the ship's stern, whale catchers were abl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize (law), prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nantes
Nantes (, , ; Gallo: or ; ) is a city in Loire-Atlantique on the Loire, from the Atlantic coast. The city is the sixth largest in France, with a population of 314,138 in Nantes proper and a metropolitan area of nearly 1 million inhabitants (2018). With Saint-Nazaire, a seaport on the Loire estuary, Nantes forms one of the main north-western French metropolitan agglomerations. It is the administrative seat of the Loire-Atlantique department and the Pays de la Loire region, one of 18 regions of France. Nantes belongs historically and culturally to Brittany, a former duchy and province, and its omission from the modern administrative region of Brittany is controversial. Nantes was identified during classical antiquity as a port on the Loire. It was the seat of a bishopric at the end of the Roman era before it was conquered by the Bretons in 851. Although Nantes was the primary residence of the 15th-century dukes of Brittany, Rennes became the provincial capital aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |