|
Sputnik 7 (website)
Tyazhely Sputnik (, meaning ''Heavy Satellite''), also known by its development name as Venera 1VA No. 1, and in the West as Sputnik 7, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was intended to be the first spacecraft to explore Venus. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit. In order to avoid acknowledging the failure, the Soviet government instead announced that the entire spacecraft, including the upper stage, was a test of a "Heavy Satellite" which would serve as a launch platform for future missions. This resulted in the upper stage being considered a separate spacecraft, from which the probe was "launched", on several subsequent missions. Although Soviet program planners intended for missions to both Mars and Venus on the new 8K78 booster, the effort during 1960 was mainly spent on the former. The Mars 1MV bus could also be used for a Venus probe with some modifications such as heat-insulating foil to protect the probe from hot temperatures i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
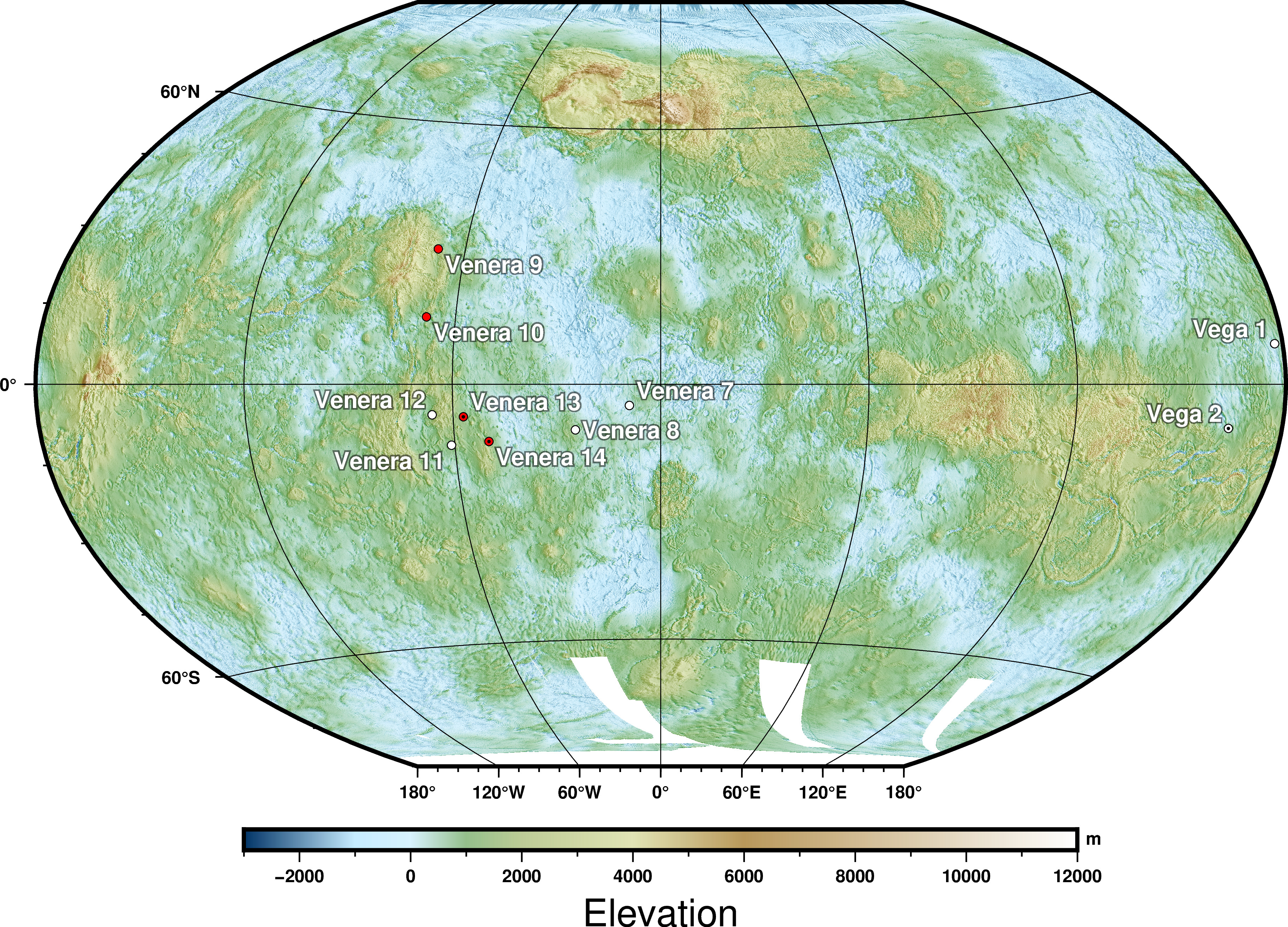
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker and denser than Earth and any other rocky body in the Solar System. Its atmosphere is composed of mostly carbon dioxide (), with a global sulfuric acid cloud cover and no liquid water. At the mean surface level the atmosphere reaches a temperature of and a pressure 92 times greater than Earth's at sea level, turning the lowest layer of the atmosphere into a supercritical fluid. Venus is the third brightest object in Earth's sky, after the Moon and the Sun, and, like Mercury, appears always relatively close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star", resulting from orbiting closer ( inferior) to the Sun than Earth. The orbits of Venus and Earth make the two planets approach each other in synodic periods of 1.6 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 1961
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather satellite, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, Planetary science, planetary exploration, and Space transport, transportation of Human spaceflight, humans and cargo spacecraft, cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Geocentric orbit, Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1961 In The Soviet Union
The following lists events that happened during 1961 in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. Incumbents *First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union - Nikita Khrushchev * Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union - Leonid Brezhnev *Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union - Nikita Khrushchev Births * 30 March - Sergei Nozikov, former Russian professional footballer * 1 June - Yevgeny Prigozhin, mercenary chief Deaths * 15 July - Nina Bari, Russian mathematician (b. 1901) * 4 October - Metropolitan Benjamin (Fedchenkov), Soviet Orthodox missionary and writer, Exarch of Russian Church in North America (b. 1880) Events * 1 September - first of the 1961 Soviet nuclear tests * 13 September - Exhibition of Leningrad artists * 5 November - 1961 Elbarusovo school fire killed 110 students and teachers. See also * 1961 in fine arts of the Soviet Union * List of Soviet films of 1961 References 1960s in the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera
The Venera (, 'Venus') program was a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere, including the two Venera-Halley probes. Ten of those successfully landed on the surface of the planet. Due to the extreme conditions, the probes could only survive for a short period on the surface, from 23 minutes to two hours. The ''Venera'' program established a number of precedents in space exploration, among them being the first human-made devices to enter the atmosphere of another planet ( Venera 3 on 1 March 1966), the first to make a soft landing on another planet ( Venera 7 on 15 December 1970), the first to return images from another planet's surface ( Venera 9 on 8 June 1975), the first to record sounds on another planet ( Venera 13 on 30 October 1981), and the first to perform high-resolution radar mapping scans ( Venera 15 on 2 June 1983). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missions To Venus
There have been 46 space missions to the planet Venus (including gravity-assist flybys). Missions to Venus constitute part of the exploration of Venus. The Soviet Union, followed by the United States, have soft landed probes on the surface. Venera 7 was the first lander overall and first for the Soviet Union, touching down on 15 December 1970. Pioneer Venus 2 contained the first spacecraft to land from the United States, the Day Probe. It soft landed on 9 December 1978. The most recent lander was part of the Vega 2 mission, which soft landed on 15 June 1985. List As of 2020, the Soviet Union, United States, European Space Agency and Japan have conducted missions to Venus. ;Mission Type Legend: Statistics Mission milestone by country ;Legend † First to achieve By organization Future missions Under development Proposed missions See also * Timeline of Solar System exploration ** List of missions to the Moon ** List of missions to Mars ** List of missions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Korolev
Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (14 January 1966) was the lead Soviet Aerospace engineering, rocket engineer and spacecraft designer during the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1950s and 1960s. He invented the R-7 Semyorka, R-7 Rocket, Sputnik 1, and was involved in the launching of Laika, Sputnik 3, the first luna 2, human-made object to make contact with another celestial body, Soviet space dogs#Belka and Strelka, Belka and Strelka, the first human being, Yuri Gagarin, into space, Voskhod 1, and the first person, Alexei Leonov, to conduct a Voskhod 2, spacewalk. Although Korolev trained as an aircraft designer, his greatest strengths proved to be in design integration, organization and strategic planning. Arrested on a false official charge as a "member of an anti-Soviet counter-revolutionary organization" (which would later be reduced to "saboteur of military technology"), he was imprisoned in 1938 for almost six years, including a few months in a K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Chertok
Boris Yevseyevich Chertok (; – 14 December 2011) was a Russian engineer in the former Soviet space program, mainly working in control systems, and later found employment in Roscosmos. Major responsibility under his guidance was primarily based on computerized control system of the Russian missiles and rocketry system, and authored the four-volume book ''Rockets and People''– the definitive source of information about the history of the Soviet space program. From 1974, he was the deputy chief designer of the Korolev design bureau, the space aircraft designer bureau which he started working for in 1946. He retired in 1992. Personal life Born in Łódź (modern Poland), his family moved to Moscow when he was aged 3. Starting from 1930, he worked as an electrician in a metropolitan suburb. Since 1934, he was already designing military aircraft in Bolkhovitinov design bureau. In 1946, he entered the rocket-pioneering NII-88 as a head of control systems department, working al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nedelin Catastrophe
The Nedelin catastrophe or Nedelin disaster, known in Russia as the Catastrophe at Baikonur Cosmodrome (), was a launch pad accident that occurred on 24 October 1960 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Soviet Kazakhstan. As a prototype of the R-16 intercontinental ballistic missile was being prepared for a test flight, an explosion occurred when the second stage engine ignited accidentally, killing an unknown number of military and technical personnel working on the preparations. Despite the magnitude of the disaster, information was suppressed for many years and the Soviet government did not acknowledge the event until 1989. With more than 54 recognized casualties, it is the deadliest disaster in space exploration history. The catastrophe is named for the Chief Marshal of Artillery Mitrofan Ivanovich Nedelin, who was the head of the R-16 development program and perished in the explosion. Launch preparations On 23 October 1960, the prototype R-16 intercontinental ballistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer 5
''Pioneer 5'' (also known as Pioneer P-2, and Able 4, and nicknamed the "Paddle-Wheel Satellite") was a spin-stabilized space probe in the NASA Pioneer program used to investigate interplanetary space between the orbits of Earth and Venus. It was launched on 11 March 1960 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 17A at 13:00:00 UTC with an on-orbit dry mass of . It was a diameter sphere with span across its four solar panels and achieved a solar orbit of 0.806 × 0.995 AU (121,000,000 by 149,000,000 km). Data was received until 30 April 1960. Among other accomplishments, the probe confirmed the existence of interplanetary magnetic fields. ''Pioneer 5'' was the most successful probe in the Pioneer/Able series. The original mission plan was for a launch in November 1959 where ''Pioneer 5'' would conduct a flyby of Venus, but technical issues prevented the launch from occurring until early 1960 by which time the Venus window for the year had closed. Since it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, peaking in number at an altitude around , while the farthest in LEO, before medium Earth orbit (MEO), have an altitude of 2,000 km, about one-third of the Earth radius, radius of Earth and near the beginning of the Van Allen radiation belt#Inner belt, inner Van Allen radiation belt. The term ''LEO region'' is used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. No human spaceflights other than the lunar missions of the Apollo program (1968-1972) have gone beyond L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |