|
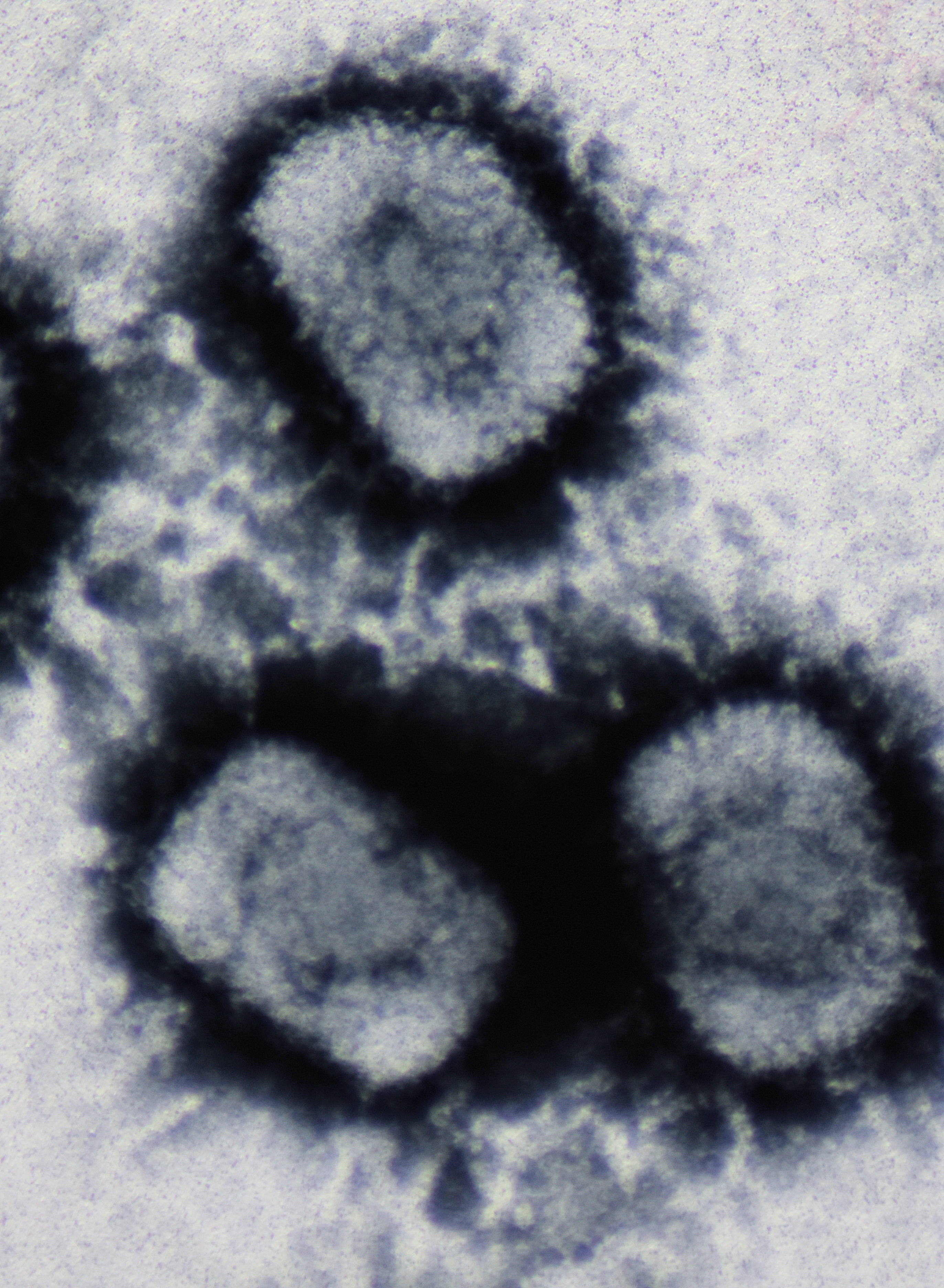
Sputnik (virus)
Sputnik virophage (from Russian "satellite") is a subviral agent that reproduces in amoeba cells that are already infected by a certain helper virus; Sputnik uses the helper virus's machinery for reproduction and inhibits replication of the helper virus. It is known as a virophage, in analogy to the term ''bacteriophage''. Viruses like Sputnik that depend on co-infection of the host cell by helper viruses are known as satellite viruses. At its discovery in a Paris water-cooling tower in 2008, Sputnik was the first known satellite virus that inhibited replication of its helper virus and thus acted as a parasite of that virus. In analogy, it was called a ''virophage''. Sputnik virophages were found infecting giant viruses of ''Mimiviridae'' group A. However, they are able to grow in amoebae infected by ''Mimiviridae'' of any of the groups A, B, and C. Virology Sputnik was first isolated in 2008 from a sample obtained from humans; it was harvested from the contact lens fluid o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Mimivirus With Satellite Sputnik Virophages
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''wiktionary:gigas, gigas'', cognate wiktionary:giga-, giga-) are beings of humanoid appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''giant'' is first attested in 1297 from Robert of Gloucester (historian), Robert of Gloucester's chronicle. It is derived from the ''Giants (Greek mythology), Gigantes'' () of Greek mythology. Fairy tales such as ''Jack the Giant Killer'' have formed the modern perception of giants as dimwitted and violent Ogre, ogres, sometimes said to eat humans, while other giants tend to eat livestock. In more recent portrayals, like those of Jonathan Swift and Roald Dahl, some giants are both intelligent and friendly. Literary and cultural analysis Giants appear many times in folklore and myths. Representing the human body enlarged to the point of being monstrous, giants evoke terror and remind humans of their body's frailty and mortality. They are ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom '' Pararnavirae'' in the realm ''Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher-order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various mechanisms of HGT such as transformation, transduction and conjugation, subsequently armin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Ocean Sampling Expedition
The Global Ocean Sampling Expedition (GOS) is an ocean exploration genome project whose goal is to assess genetic diversity in marine microbial communities and to understand their role in nature's fundamental processes. The two-year journey, which used Craig Venter's personal yacht, originated in Halifax, Canada, circumnavigated the globe and terminated in the U.S. in January 2006. The expedition sampled water from Halifax, Nova Scotia to the Eastern Tropical Pacific Ocean. During 2007, sampling continued along the west coast of North America. Data analysis The GOS datasets were submitted to both NCBIGlobal Ocean Sampling Expedition project at the J. Craig Venter Institute, Project ID 13694 |
DNA-binding Subunit
DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional groups that identify a base pair. Examples DNA-binding proteins include transcription factors which modulate the process of transcription, various polymerases, nucleases which cleave DNA molecules, and histones which are involved in chromosome packaging and transcription in the cell nucleus. DNA-binding proteins can incorporate such domains as the zinc finger, the helix-turn-helix, and the leucine zipper (among many others) that facilitate binding to nucleic acid. There are also more unusual examples such as transcription activator like effectors. Non-specific DNA-protein interactions Structural proteins that bind DNA are well-understood examples of non-specific DNA-protein interactions. Within chromosomes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, ATP hydrolase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or the inverse reaction. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme (in most cases) harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life. Some such enzymes are integral membrane proteins (anchored within biological membranes), and move solutes across the membrane, typically against their concentration gradient. These are called transmembrane ATPases. Functions Transmembrane ATPases import metabolites necessary for cell metabolism and export toxins, wastes, and solutes that can hinder cellular processes. An important example is the sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ATPase) that maintains the cell membrane potential. Another example is the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Genetics
The ''Annual Review of Genetics'' is an annual peer-reviewed scientific review journal published by Annual Reviews. It was established in 1967 and covers all topics related to the genetics of viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals, including humans. The current editor is Tatjana Piotrowski. As of 2024, ''Journal Citation Reports'' gives the journal a 2023 impact factor of 8.7, ranking it eleventh out of 191 journals in the category "Genetics & Heredity". As of 2023, it is being published as open access, under the Subscribe to Open model. History In 1965, the nonprofit publisher Annual Reviews surveyed geneticists to determine if there was a need for an annual journal that published review articles about recent developments in the field of genetics. Responses to the survey were favorable, with the first volume of the ''Annual Review of Genetics'' published two years later in 1967. Its inaugural editor was Herschel L. Roman. As of 2020, it was published both in print and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairpin Loop
Stem-loops are nucleic acid secondary structural elements which form via intramolecular base pairing in single-stranded DNA or RNA. They are also referred to as hairpins or hairpin loops. A stem-loop occurs when two regions of the same nucleic acid strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in a loop of unpaired nucleotides. Stem-loops are most commonly found in RNA, and are a key building block of many RNA secondary structures. Stem-loops can direct RNA folding, protect structural stability for messenger RNA (mRNA), provide recognition sites for RNA binding proteins, and serve as a substrate for enzymatic reactions. Formation and stability The formation of a stem-loop is dependent on the stability of the helix and loop regions. The first prerequisite is the presence of a sequence that can fold back on itself to form a paired double helix. The stability of this helix is determined by its length, the number of mismatche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AT-content
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out of an implied four total bases, also including adenine and thymine in DNA and adenine and uracil in RNA. GC-content may be given for a certain fragment of DNA or RNA or for an entire genome. When it refers to a fragment, it may denote the GC-content of an individual gene or section of a gene (domain), a group of genes or gene clusters, a non-coding region, or a synthetic oligonucleotide such as a primer. Structure Qualitatively, guanine (G) and cytosine (C) undergo a specific hydrogen bonding with each other, whereas adenine (A) bonds specifically with thymine (T) in DNA and with uracil (U) in RNA. Quantitatively, each GC base pair is held together by three hydrogen bonds, while AT and AU base pairs are held together by two hydrogen bonds. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Gene
Orphan genes, ORFans, or taxonomically restricted genes (TRGs) are genes that lack a detectable homologue outside of a given species or lineage. Most genes have known homologues. Two genes are homologous when they share an evolutionary history, and the study of groups of homologous genes allows for an understanding of their evolutionary history and divergence. Common mechanisms that have been uncovered as sources for new genes through studies of homologues include gene duplication, exon shuffling, gene fusion and fission, etc. Studying the origins of a gene becomes more difficult when there is no evident homologue. The discovery that about 10% or more of the genes of the average microbial species is constituted by orphan genes raises questions about the evolutionary origins of different species as well as how to study and uncover the evolutionary origins of orphan genes. In some cases, a gene can be classified as an orphan gene due to undersampling of the existing genome space. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |