|
Springfield Science Museum
The Springfield Science Museum is located in Springfield, Massachusetts, in the United States. Founded in 1859, the museum has operated in its current building since 1899. The building has undergone two expansions, in 1934 and 1970. It is also home to the country's oldest operating projection planetarium, Seymour Planetarium. History The Springfield Science Museum was founded in December 1859 at Springfield's City Hall, originally as a natural history museum and curiosities collection. It was moved to the City Library in 1871, when the library gained its own building separate from City Hall. Early exhibits included geological displays of rocks and minerals, and Revolutionary War relics. In the early 1890s the museum was moved once again, this time to the Art museum. The museum's collections began being moved to its own building in February 1899, and it opened as the Springfield Ethnological and Natural History Museum on October 16, 1899. In 1928, the museum received Miss Oita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springfield, Massachusetts
Springfield is the most populous city in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States, and its county seat. Springfield sits on the eastern bank of the Connecticut River near its confluence with three rivers: the western Westfield River, the eastern Chicopee River, and the eastern Mill River (Springfield, Massachusetts), Mill River. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city's population was 155,929, making it the List of municipalities in Massachusetts, third most populous city in the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the fourth most populous city in New England after Boston, Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester, and Providence, Rhode Island, Providence. Springfield metropolitan area, Massachusetts, Metropolitan Springfield, as one of two metropolitan areas in Massachusetts (the other being Greater Boston), had a population of 699,162 in 2020. Springfield was founded in 1636, the first Springfield (toponym), Springfield in the New World. In the late 1700s, during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
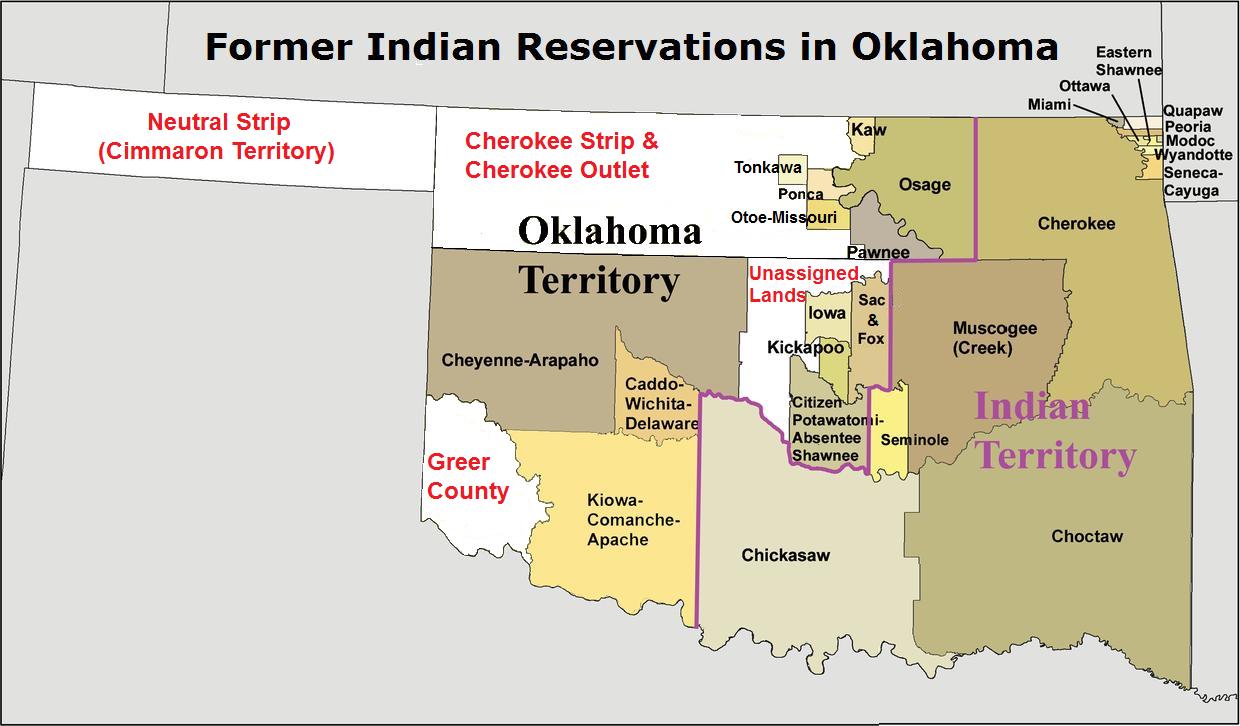
Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northeast, Arkansas to the east, New Mexico to the west, and Colorado to the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "The Sooner State", in reference to the Sooners, American pioneer, American settlers who staked their claims in formerly American Indian-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seneca People
The Seneca ( ; ) are a group of Indigenous Iroquoian-speaking people who historically lived south of Lake Ontario, one of the five Great Lakes in North America. Their nation was the farthest to the west within the Six Nations or Iroquois League ( Haudenosaunee) in New York before the American Revolution. For this reason, they are called “The Keepers of the Western Door.” In the 21st century, more than 10,000 Seneca live in the United States, which has three federally recognized Seneca tribes. Two of them are centered in New York: the Seneca Nation of Indians, with five territories in western New York near Buffalo; and the Tonawanda Seneca Nation. The Seneca-Cayuga Nation is in Oklahoma, where their ancestors were relocated from Ohio during the Indian Removal. Approximately 1,000 Seneca live in Canada, near Brantford, Ontario, at the Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation. They are descendants of Seneca who resettled there after the American Revolution, as they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repatriation (cultural Property)
Repatriation is the return of the cultural property, often referring to ancient or looted art, to their country of origin or former owners (or their heirs). The disputed cultural property items are physical artifacts of a group or society taken by another group, usually in the act of looting, whether in the context of imperialism, colonialism, or war. The contested objects vary widely and include sculptures, paintings, monuments, objects such as tools or weapons for purposes of anthropology, anthropological study, and Repatriation and reburial of human remains, human remains. The looting of defeated peoples' cultural heritage by war has been common practice since ancient times. In the modern era, the Napoleonic looting of art was confiscations of artworks and precious objects by the French army or officials. After Napoleon's defeat, some List of art looted by Napoleonic armies, looted artworks were returned to their country of origin, according the Treaty of Paris (1815), Treaty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luman Andrews House
The Luman Andrews House is a historic house at 469 Andrews Street in Southington, Connecticut. Built in 1745, it is one of the oldest houses in Southington. Its property was also the site of the early manufacture of hydraulic cement. The property was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989. Description and history The Luman Andrews House stands in a rural area of central eastern Southington, on the east side of Andrews Street just south of its junction with Woodruff Street. It is a -story wood-frame structure, with a side-gable roof, central chimney, and clapboarded exterior. Its main facade is five bays wide, with a center entrance topped by a four-light transom window and framed by a Greek Revival surround with pilasters and a corniced entablature. The side gable ends have also been fully pedimented in another Greek Revival alteration. The property also includes the remains of a 19th-century lime kiln. and A quarry on the site was the source of vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southington, Connecticut
Southington ( ) is a town in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Capitol Planning Region. As of the 2020 United States census, it had a population of 43,501. Southington contains the villages of Marion, Milldale, and Plantsville. History Although Southington was formally established as a town in 1779, its roots go back to a much earlier time. Samuel Woodruff, Southington's first white settler, moved from Farmington to the area then known as "Panthorne" that was settled in 1698. The land was formerly occupied by the Tunxis or Sepores Indians. The settlement grew, prospered, and came to be known as "South Farmington" and then later, the shortened version, Southington. The town's most important early visitor was General George Washington, who passed through the town in 1770 on his way to Wethersfield. The Marion section of Southington is one of the most historic places in the town. It is the site of an encampment by the great French gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. The term ''observatoire'' has been used in French since at least 1976 to denote any institution that compiles and presents data on a particular subject (such as public health observatory) or for a particular geographic area (European Audiovisual Observatory). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space observatory, space-based, airborne observatory, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Historically, ground-based observatories were as simple as containing a mural instrument (for measuring the angle between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum
A museum is an institution dedicated to displaying or Preservation (library and archive), preserving culturally or scientifically significant objects. Many museums have exhibitions of these objects on public display, and some have private collections that are used by researchers and specialists. Museums host a much wider range of objects than a library, and they usually focus on a specific theme, such as the art museums, arts, science museums, science, natural history museums, natural history or Local museum, local history. Public museums that host exhibitions and interactive demonstrations are often tourist attractions, and many draw large numbers of visitors from outside of their host country, with the List of most-visited museums, most visited museums in the world attracting millions of visitors annually. Since the establishment of Ennigaldi-Nanna's museum, the earliest known museum in ancient history, ancient times, museums have been associated with academia and the preserva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetarium
A planetarium (: planetariums or planetaria) is a theatre built primarily for presenting educational and entertaining shows about astronomy and the night sky, or for training in celestial navigation. A dominant feature of most planetariums is the large dome-shaped projection screen onto which scenes of stars, planets, and other celestial objects can be made to appear and move realistically to simulate their motion. The projection can be created in various ways, such as a star ball, slide projector, video, fulldome projector systems, and lasers. Typical systems can be set to simulate the sky at any point in time, past or present, and often to depict the night sky as it would appear from any point of latitude on Earth. Planetaria range in size from the 37 meter dome in St. Petersburg, Russia (called "Planetarium No 1") to three-meter inflatable portable domes where attendees sit on the floor. The largest planetarium in the Western Hemisphere is the Jennifer Chalsty Planetariu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederic Brewster Loomis
Frederic Brewster Loomis (November 22, 1873 – July 28, 1937) was an American paleontologist. Educated at Amherst College and the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, he spent his entire professional career at Amherst. His specialty was vertebrate paleontology. Many fossils he uncovered during his extensive field work are still exhibited at Amherst's Beneski Museum of Natural History. He was a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, a fellow of the Geological Society of America, and president of the Paleontological Society. Early life and education Loomis was born November 22, 1873, in Brooklyn, New York, to Julie R. Loomis (''née'' Brewster) and Nathaniel H. Loomis, a businessman who ran produce warehouses in New York City. Walter Granger. Memorial to Frederick Brewster Loomis. ''Proceedings of the Geological Society of America for 1937'', Jun. 1938, pp. 173–82. In March 1877 his father died of rabies contracted from a dog bite. The family later moved to Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amherst College
Amherst College ( ) is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Amherst, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1821 as an attempt to relocate Williams College by its then-president Zephaniah Swift Moore, Amherst is the third oldest institution of higher education in List of colleges and universities in Massachusetts, Massachusetts. The institution was named after the town, which in turn had been named after Jeffery Amherst, 1st Baron Amherst, Jeffery, Lord Amherst, Commander-in-Chief of British forces of North America during the French and Indian War. Originally established as a Men's colleges, men's college, Amherst became Mixed-sex education, coeducational in 1975. Amherst is an exclusively undergraduate four-year institution; 1,971 students were enrolled in fall 2021. Admissions are highly selective. Students choose courses from 42 major programs in an Curriculum#Open curriculum, open curriculum and are not required to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosauridae
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to fifteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera is controversial, with some experts recognizing as few as three. All of these animals lived near the end of the Cretaceous Period and their fossils have been found only in North America and Asia. Although descended from smaller ancestors, tyrannosaurids were almost always the largest predators in their respective ecosystems, putting them at the apex of the food chain. The largest species was ''Tyrannosaurus rex'', the most massive known terrestrial predator, which measured over in length and according to most modern estimates up to in weight. Tyrannosaurids were bipedal carnivores with massive skulls filled with large teeth. Despite their large size, their legs were long and proportioned for fast movement. In contrast, their arms were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |