|
Spondyloarthropathy
Spondyloarthritis (SpA), also known as spondyloarthropathy, is a collection of syndromes connected by genetic predisposition and clinical symptoms. The best-known subtypes are enteropathic arthritis (EA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and reactive arthritis (ReA). Symptoms of spondyloarthritis include back pain, arthritis, and enthesitis, inflammation at bone-adhering ligaments, tendons, or joint capsules. Spondyloarthritis is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is associated with intestinal inflammation, with a connection between Crohn's disease and ankylosing spondylitis. Reactive arthritis is primarily caused by gastrointestinal, genitourinary, respiratory infections, and genetic factors. Spondyloarthritis is diagnosed based on symptoms and imaging. Early diagnosis criteria use genetic testing and more advanced forms of medical imaging. Spondyloarthritis is categorized into two groups based on the Assessment of Spondylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteropathic Arthropathy
Enteropathic arthropathy, commonly referred to as enteropathic arthritis, is a type of arthritis linked to Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. Along with reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis, this type of arthritis is categorized as a seronegative spondyloarthropathy. Other gastrointestinal disorders like Whipple's disease, celiac disease, and intestinal bypass surgery for severe obesity can also cause joint involvement. The pathogenesis of arthritis in these conditions is likely influenced by immunologic, genetic, and abnormal bowel permeability factors, though the precise mechanisms are still unknown. Signs and symptoms Historically, there have been two main patterns of joint involvement with enteropathic arthritis: axial involvement, which includes sacroiliitis with or without spondylitis resembling idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis, and peripheral arthritis. Additional conditions that may ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
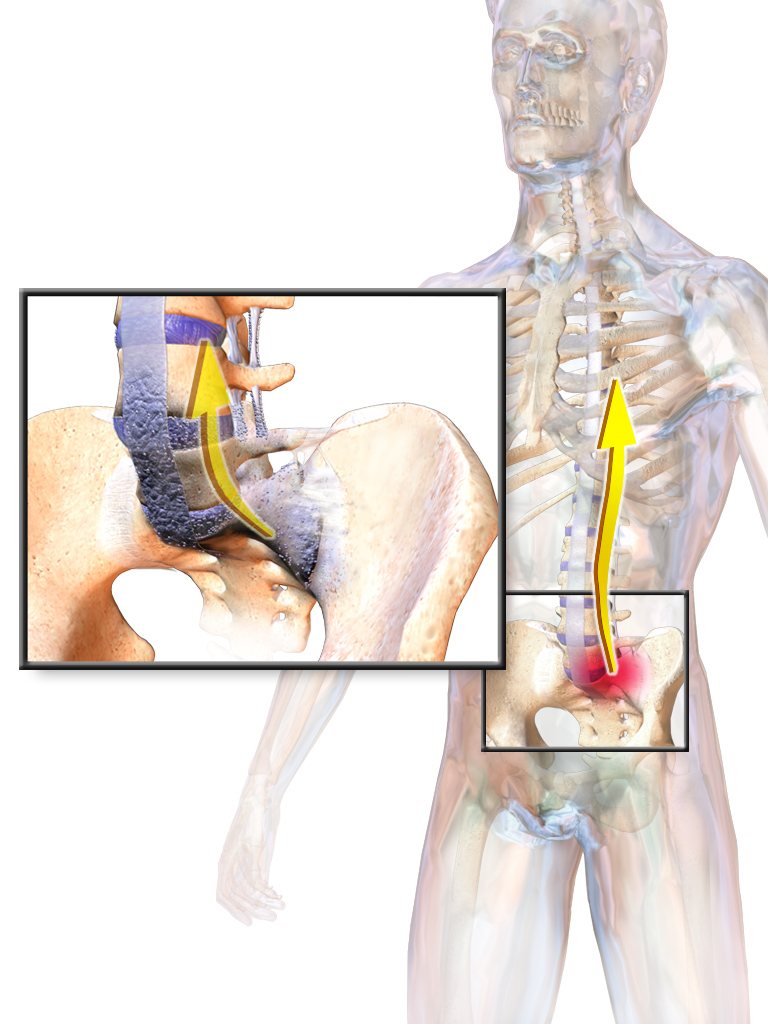
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis from the disease spectrum of axial spondyloarthritis. It is characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine, typically where the spine joins the pelvis. With AS, eye and bowel problems—as well as back pain—may occur. Joint mobility in the affected areas sometimes worsens over time. Ankylosing spondylitis is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. More than 90% of people affected in the UK have a specific human leukocyte antigen known as the HLA-B27 antigen. The underlying mechanism is believed to be autoimmune or autoinflammatory. Diagnosis is based on symptoms with support from medical imaging and blood tests. AS is a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy, meaning that tests show no presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) antibodies. There is no cure for AS. Treatments may include medication, physical therapy, and surgery. Medication therapy focuses on relieving the pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis, previously known as Reiter's syndrome, is a form of inflammatory arthritis that develops in response to an infection in another part of the body (cross-reactivity). Coming into contact with bacteria and developing an infection can trigger the disease. By the time a person presents with symptoms, the "trigger" infection has often been cured or is in remission in chronic cases, thus making determination of the initial cause difficult. The manifestations of reactive arthritis include the following triad of symptoms: inflammatory arthritis of large joints, inflammation of the eyes in the form of conjunctivitis or uveitis, and urethritis in men or cervicitis in women. Arthritis occurring alone following sexual exposure or enteric infection is also known as reactive arthritis. Affected people may present with mucocutaneous lesions, as well as psoriasis-like skin lesions such as circinate balanitis, and keratoderma blennorrhagicum. Enthesitis can involve the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Scintigraphy
A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique used to help diagnose and assess different bone diseases. These include cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures (that may not be visible in traditional X-ray images), and bone infection (osteomyelitis). Nuclear medicine provides functional imaging and allows visualisation of bone metabolism or bone remodeling, which most other imaging techniques (such as X-ray computed tomography, CT) cannot. Bone scintigraphy competes with positron emission tomography (PET) for imaging of abnormal metabolism in bones, but is considerably less expensive. Bone scintigraphy has higher sensitivity but lower specificity than CT or MRI for diagnosis of scaphoid fractures following negative plain radiography. History Some of the earliest investigations into skeletal metabolism were carried out by George de Hevesy in the 1930s, using phosphorus-32 and by Charles Pecher in the 1940s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distal Interphalangeal Joint
Distal interphalangeal joints are the articulations between the phalanges of the hand or foot. This term therefore includes: * Interphalangeal joints of the hand * Interphalangeal joints of the foot The interphalangeal joints of the foot are the joints between the phalanx bones of the toes in the feet. Since the great toe only has two phalanx bones ( proximal and distal phalanges), it only has one interphalangeal joint, which is often ab ... {{Set index article Joints ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
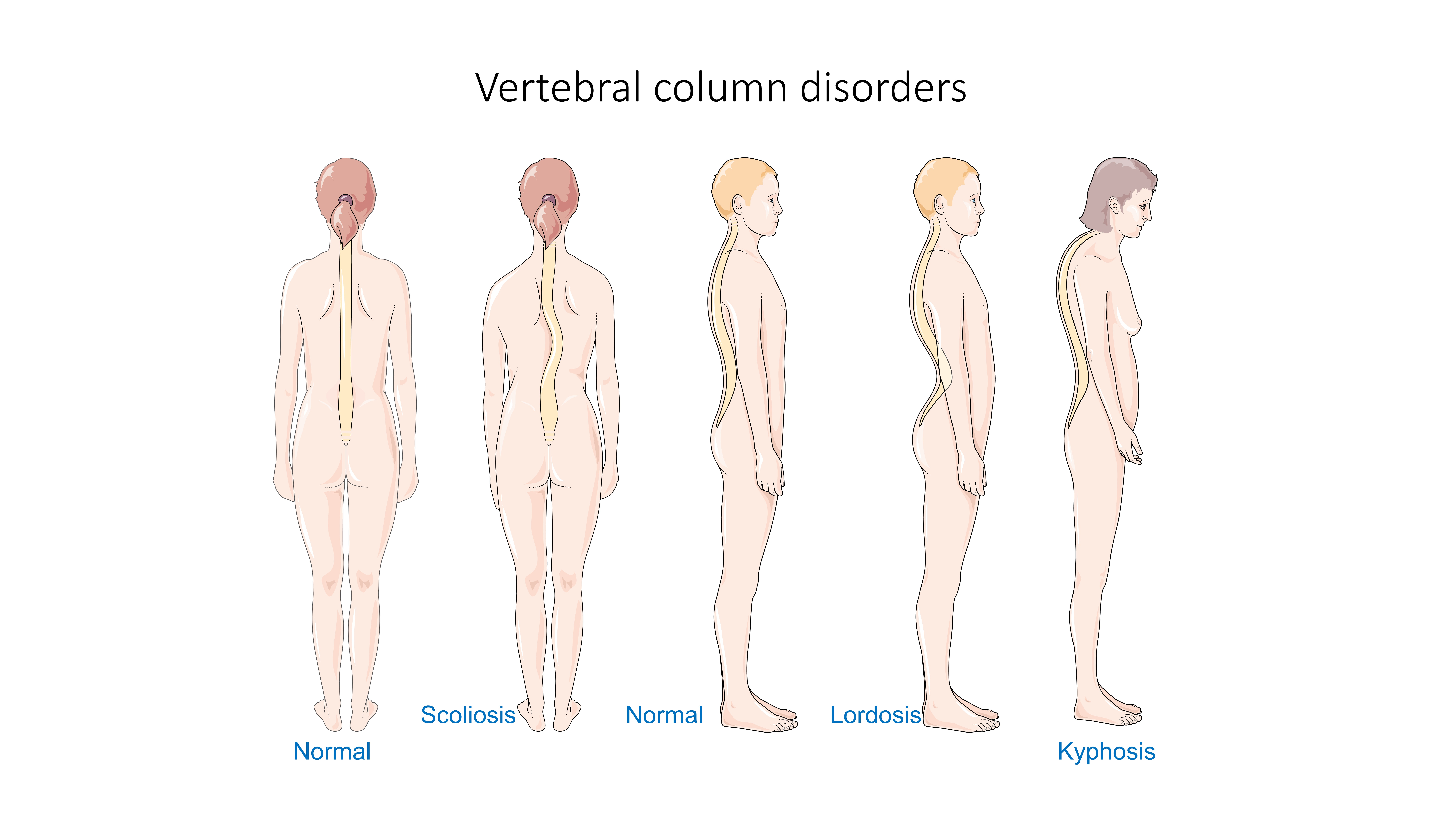
Thoracic Kyphosis
Kyphosis () is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the spine as it occurs in the thoracic and sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; Copenhagen disease, osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma. A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st thoracic to the 12th thoracic vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial and is seen more frequently in males than females. In the sense of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dactylitis
Dactylitis or sausage digit is inflammation of an entire digit (a finger or toe), and can be painful. The word ''dactyl'' comes from the Greek word ''daktylos'' 'finger'. As a medical term, it refers to both the fingers and the toes. __TOC__ Associated conditions Dactylitis can occur in seronegative arthropathies, such as psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, and in sickle-cell disease as result of a vasoocclusive crisis with bone infarcts, and in infectious conditions including tuberculosis, syphilis, and leprosy. In reactive arthritis, sausage fingers occur due to synovitis. Dactylitis may also be seen with sarcoidosis. In sickle-cell disease it typically occurs after 6 months of age (as in infants protective fetal hemoglobin Fetal hemoglobin, or foetal haemoglobin (also hemoglobin F, HbF, or α2γ2) is the main oxygen carrier protein in the human fetus. HemoglobinF is found in fetal red blood cells, and is involved in transporting oxygen from the mother's bloodstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that may occur in some people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic features of psoriatic arthritis include dactylitis (sausage-like swelling of the fingers), skin lesions, and nail lesions. Lesions of the nails may include small depressions in the nail (pitting), thickening of the nails, and detachment of the nail from the nailbed. Skin lesions consistent with psoriasis (e.g., red, scaly, and itchy plaques) frequently occur before the onset of psoriatic arthritis but psoriatic arthritis can precede the rash in 15% of affected individuals. It is classified as a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy. Genetics are thought to be strongly involved in the development of psoriatic arthritis. Obesity and certain forms of psoriasis are thought to increase the risk. Psoriatic arthritis affects up to 30% of people with psoriasis. It occurs in both children and adults. Some people with Ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas UC primarily affects the colon and the rectum. Signs and symptoms In spite of Crohn's and UC being very different diseases, both may present with any of the following symptoms: abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, severe internal cramps/muscle spasms in the region of the pelvis and weight loss. Anemia is the most prevalent extraintestinal complication of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Associated complaints or diseases include arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and non-thyroidal illness syndrome (NTIS). Associations with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) have also been reported. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis Mutilans
Arthritis mutilans is a rare medical condition involving severe inflammation damaging the joints of the hands and feet, and resulting in deformation and problems with moving the affected areas; it can also affect the spine. As an uncommon arthropathy, arthritis mutilans was originally described as affecting the hands, feet, fingers, and/or toes, but can refer in general to severe derangement of any joint damaged by arthropathy. First described in modern medical literature by Marie and Leri in 1913, in the hands, arthritis mutilans is also known as opera glass hand (''la main en lorgnette'' in French), or chronic absorptive arthritis. Sometimes there is foot involvement in which toes shorten and on which painful calluses develop in a condition known as opera glass foot, or ''pied en lorgnette''. Signs and symptoms For a person with arthritis mutilans in the hands, the fingers become shortened by arthritis, and the shortening may become severe enough that the hand looks paw-like, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spondylitis
Spondylitis is an inflammation of the vertebrae. It is a form of spondylopathy. In many cases, spondylitis involves one or more vertebral joints, as well, which itself is called spondylarthritis. __TOC__ Types Pott disease is a tuberculous disease of the vertebrae marked by stiffness of the vertebral column The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ..., pain on motion, tenderness on pressure, prominence of certain vertebral spines, and occasionally abdominal pain, abscess formation, and paralysis. Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, although other joints can become involved. It causes inflammation of the spinal joints (vertebrae) that can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort. In more advanced cases this inflammation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |