|
Split Sound System
Split sound is an old system in analog television transmitters. It has long been superseded, but transmitters working on this principle are still in use. In this system there are two almost independent transmitters, one for sound (aural) and one for picture (visual). The system requires more energy input relative to broadcast energy than the alternative system known as intercarrier system. Main stages of a transmitter All superheterodyne transmitters have the following stages: *Oscillators *Input stages : Buffer amplifiers, correction circuits etc. * IF modulator and IF amplifiers *Frequency mixer * RF power amplifiers * Antenna system Split sound TV transmitter In split sound TV broadcasting, two of each of the above stages (except the antenna system) are required, one for sound and one for video. At the output of the RF amplifiers both signals are combined by a high-power diplexer; the combined signal is transmitted. Split sound vs intercarrier system *In split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
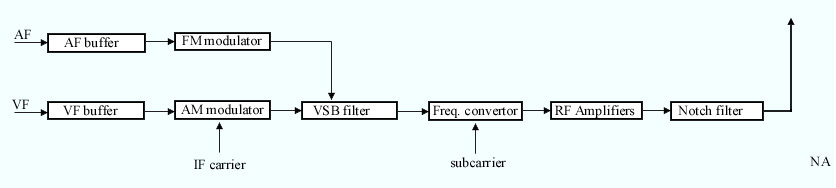 |
Television Transmitter
A television transmitter is a transmitter that is used for terrestrial television, terrestrial (over-the-air) television broadcasting. It is an electronic device that radiates radio waves that carry a video signal representing moving images, along with a synchronized audio signal, audio channel, which is received by television receivers ('televisions' or 'TVs') belonging to a public audience, which display the image on a screen. A television transmitter, together with the Television studio, broadcast studio which originates the content, is called a television station. Television transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to a certain frequency channel and power level. They transmit on frequency television channel frequencies, channels in the very high frequency, VHF and ultrahigh frequency, UHF bands. Since radio waves of these frequencies travel by line-of-sight propagation, line of sight, they are limited by the horizon to reception distances of 40–60 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Intercarrier Method
The intercarrier method is a system in television that reduces the cost of transmitters and receiver sets by processing audio and video signals together and minimizing the number of separate stages for audio and video signals. Transmission of audio and video signals In television, unlike monophonic radio, at least two signals should be transmitted; audio (AF) and video (VF) signals. Transmitting those signals by means of separate transmitters and antenna systems is a very costly solution, because every stage must be used twice, one for AF and one for VF. Two separate transmitters, a high power combiner and a common antenna system, known as the split sound system, is also quite costly. But if the signals are combined at an earlier stage, the number of costly outer stages is reduced. The same logic also applies to receiver sets. If the modulated signal is separated just before the picture tube the number of separate stages for AF and VF is minimized. This common signal proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Superheterodyne Transmitter
Superheterodyne transmitter is a radio or TV transmitter which uses an intermediate frequency signal in addition to radio frequency signal. Types of transmitters There are two types of transmitters. In some transmitters, the baseband information signal ( audio (AF), video (VF) etc.) modulates the radio frequency (RF) signal. These direct modulation transmitters are relatively simple. In the more complicated superheterodyne transmitter, the baseband signal modulates an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. After stages for correction, equalization and sometimes amplification, the IF signal is converted to an RF signal by a stage named frequency mixer or frequency converter. Superheterodyne transmitters are more complex than direct modulation transmitters. Mathematical approach Let : f (t) be the information signal :\omega_ be the angular RF, :\omega_ be the angular IF and :\omega_ be the angular subcarrier frequency. In direct modulation transmitter the information sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Oscillators
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Buffer Amplifier
In electronics, a buffer amplifier is a unity gain amplifier that copies a signal from one circuit to another while transforming its electrical impedance to provide a more ideal source (with a ''lower'' output impedance for a voltage buffer or a ''higher'' output impedance for a current buffer). This "buffers" the signal source in the first circuit against being affected by currents from the electrical load of the second circuit and may simply be called a buffer or follower when context is clear. Voltage buffer A voltage buffer amplifier is used to transform a voltage signal with high output impedance from a first circuit into an identical voltage with low impedance for a second circuit. The interposed buffer amplifier prevents the second circuit from loading the first circuit unacceptably and interfering with its desired operation, since without the voltage buffer, the voltage of the second circuit is influenced by output impedance of the first circuit (as it is larger than th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Intermediate Frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in Transmission (telecommunications), transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called heterodyning, resulting in a signal at the difference or beat frequency. Intermediate frequencies are used in Superheterodyne receiver, superheterodyne radio receivers, in which an incoming signal is shifted to an IF for Amplifier, amplification before final Detector (radio), detection is done. Conversion to an intermediate frequency is useful for several reasons. When several stages of filters are used, they can all be set to a fixed frequency, which makes them easier to build and to tune. Lower frequency transistors generally have higher gains so fewer stages are required. It's easier to make sharply selective filters at lower fixed frequencies. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information. The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message signal onto a carrier signal to be transmitted. For example, the message signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the message signal does. This is because it is impractical to transmit signals with low frequencies. Generally, receiving a radio wave requires a radio antenna with a length that is one-fourth of the wavelength of the transmitted wave. For low frequency radio waves, wavelength is on the scale of kilometers and building such a large antenna is not practical. Another purpose of modulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
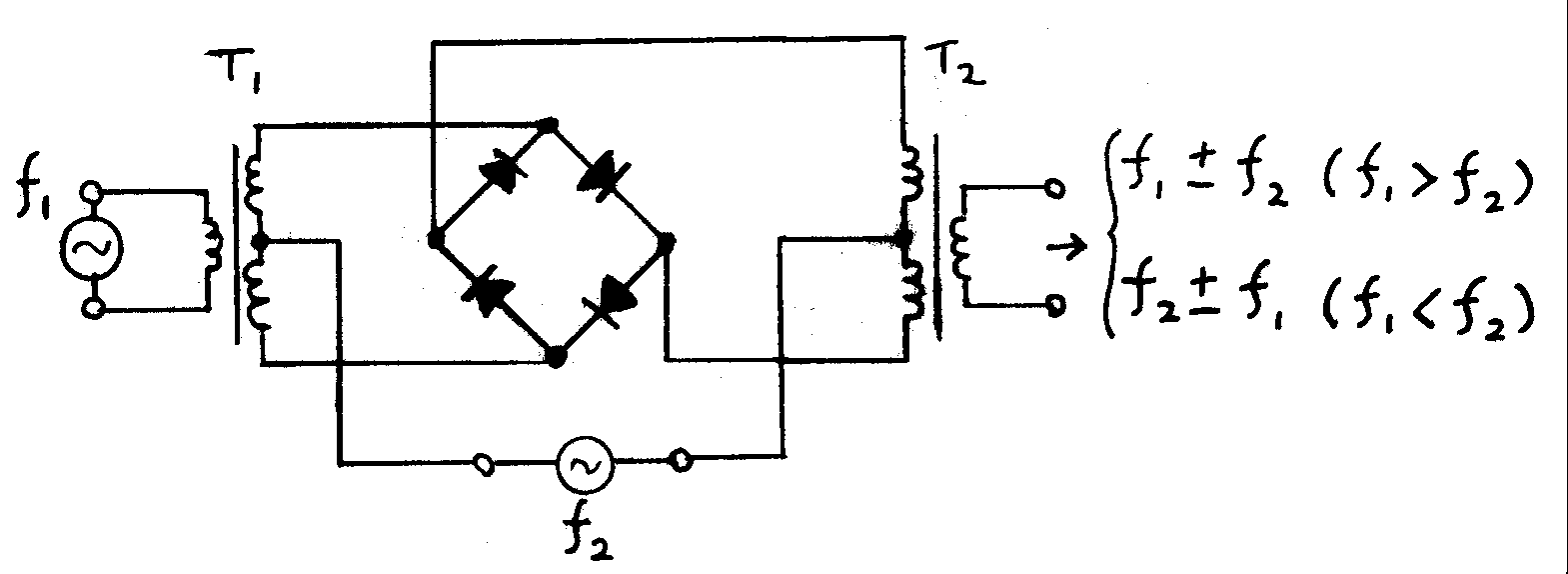 |
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulation, modulate a carrier signal in Transmitter, radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
RF Power Amplifier
A radio-frequency power amplifier (RF power amplifier) is a type of electronic amplifier that converts a low-power radio-frequency (RF) signal into a higher-power signal. Typically, RF power amplifiers are used in the final stage of a radio transmitter, their output driving the antenna. Design goals often include gain, power output, bandwidth, power efficiency, linearity (low signal compression at rated output), input and output impedance matching, and heat dissipation. Amplifier classes The operation of RF amplifier circuits is classified based on the proportion of the cycle of the sinusoidal radio signal the amplifier (transistor or vacuum tube) where current is conducting. Class-A, class-AB and class-B are considered the linear amplifier classes in which the active device is used as a controlled current source, while class-C is a nonlinear class in which the active device is used as a switch. The bias at the input of the active device determines the class of the ampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Antenna (radio)
In radio-frequency engineering, an antenna (American English) or aerial (British English) is an electronic device that converts an alternating current, alternating electric current into radio waves (transmitting), or radio waves into an electric current (receiving). It is the interface between radio waves Radio propagation, propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal Electrical conductor, conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver (radio), receiver. In transmission (telecommunications), transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's Terminal (electronics), terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In receiver (radio), reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplifier, amplified. Antennas are essential components ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Diplexer
A diplexer is a passive device that implements frequency-domain multiplexing. Two ports (e.g., L and H) are multiplexed onto a third port (e.g., S). The signals on ports L and H occupy disjoint frequency bands. Consequently, the signals on L and H can coexist on port S without interfering with each other. Typically, the signal on port L will occupy a single low frequency band and the signal on port H will occupy a higher frequency band. In that situation, the diplexer consists of a lowpass filter connecting ports L and S and high pass filter connecting ports H and S. Ideally, all the lowband signal power on port L is transferred to the S port and vice versa. All the highband signal power on port H is transferred to port S and vice versa. Ideally, the separation of the signals is complete. None of the low band signal is transferred from the L port to the H port. In the real world, some power will be lost, and some signal power will leak to the wrong port. The diplexer, being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |