|
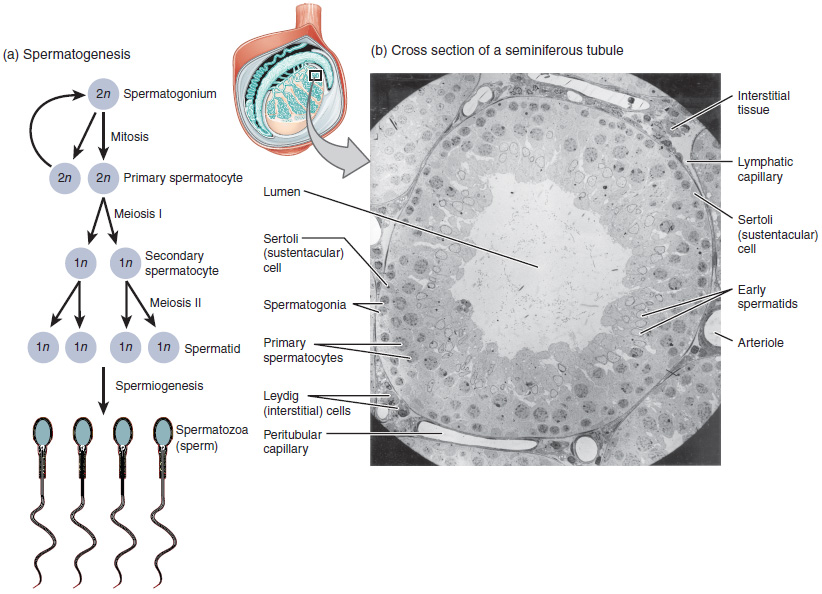
Spermatids
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte. Spermatids are connected by cytoplasmic material and have superfluous cytoplasmic material around their nuclei. When formed, ''early round spermatids'' must undergo further maturational events to develop into spermatozoa, a process termed spermiogenesis (also termed ''spermeteliosis''). The spermatids begin to grow a living thread, develop a thickened mid-piece where the mitochondria become localised, and form an acrosome. Spermatid DNA also undergoes packaging, becoming highly condensed. The DNA is packaged firstly with specific nuclear basic proteins, which are subsequently replaced with protamines during spermatid elongation. The resultant tightly packed chromatin is transcriptionally inactive. In 2016 scientists at Nanjing Medical University claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in humans: Type A (dark) cells, with dark nuclei. These cells are reserve spermatogonial stem cells which do not usually undergo active mitosis. Type A (pale) cells, with pale nuclei. These are the spermatogonial stem cells that undergo active mitosis. These cells divide to produce Type B cells. Type B cells, which undergo growth and become primary spermatocytes. Types of spermatogonia Spermatogonia are often classified into different types depending on their stage in the differentiation process. In humans and most mammals, spermatogonia are divided into two types, A and B, but this can differ for other organisms. There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in humans: *Type A (dark) cells, with dark nuclei. These cells are reserve spermatogonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatocyte
Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and secondary spermatocytes. Primary and secondary spermatocytes are formed through the process of spermatocytogenesis. Primary spermatocytes are diploid (2N) cells. After meiosis I, two secondary spermatocytes are formed. Secondary spermatocytes are haploid (N) cells that contain half the number of chromosomes. In all animals, Male, males produce spermatocytes, even hermaphrodites such as Caenorhabditis elegans, ''C. elegans'', which exist as a male or hermaphrodite. In hermaphrodite ''C. elegans'', sperm production occurs first and is then stored in the spermatheca. Once the egg cell, eggs are formed, they are able to self-fertilize and produce up to 350 offspring, progeny. Development At puberty, spermatogonia located along the walls of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm. Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes (reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia, which Cellular differentiation, differentiate into spermatocytes. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis, reducing their Ploidy, chromosome number by half, which produces spermatids. The sper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Cell
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they undergo meiosis, followed by cellular differentiation into mature gametes, either eggs or sperm. Unlike animals, plants do not have germ cells designated in early development. Instead, germ cells can arise from somatic cells in the adult, such as the floral meristem of flowering plants. Introduction Multicellular eukaryotes are made of two fundamental cell types: germ and somatic cells. Germ cells produce gametes and are the only cells that can undergo meiosis as well as mitosis. Somatic cells are all the other cells that form the building blocks of the body and they only divide by mitosis. The lineage of germ cells is called the germline. Germ cell specification begins during cleavage in many animals or in the epiblast during gastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, primarily testosterone. The release of testosterone is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Sperm production is controlled by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland and by testosterone produced within the gonads. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and compari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sertoli Cell
Sertoli cells are a type of sustentacular "nurse" cell found in human testes which contribute to the process of spermatogenesis (the production of sperm) as a structural component of the seminiferous tubules. They are activated by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secreted by the adenohypophysis and express FSH receptor on their membranes. History Sertoli cells are named after Enrico Sertoli, an Italian physiologist who discovered them while studying medicine at the University of Pavia, Italy. He published a description of his eponymous cell in 1865. The cell was discovered by Sertoli with a Belthle microscope which had been purchased in 1862. In the 1865 publication, his first description used the terms "tree-like cell" or "stringy cell"; most importantly, he referred to these as "mother cells". Other scientists later used Enrico's family name to label these cells in publications, beginning in 1888. As of 2006, two textbooks that are devoted specifically to the Sertoli cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in Cell (biology), cells, by internal metabolism, metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for Transcription (biology), transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. The sexual fusion of haploid cells is called karyogamy, the result of which is the formation of a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, diploid cell called the zygote or zygospore. History German zoologists Oscar Hertwig, Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. In multicellular organisms The zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other Anisogamy, anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm, sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. The formation of a cell potency, totipotent zygote with the potential to produce a whole organism depends on epigenetics, epigenetic reprogramming. DNA demethyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50 to 150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Damage (naturally Occurring)
Natural DNA damage is an alteration in the chemical structure of DNA, such as a break in a strand of DNA, a nucleobase missing from the backbone of DNA, or a chemically changed base such as 8-OHdG. DNA damage can occur naturally or via environmental factors, but is distinctly different from mutation, although both are types of error in DNA. DNA damage is an abnormal chemical structure in DNA, while a mutation is a change in the sequence of base pairs. DNA damages cause changes in the structure of the genetic material and prevents the replication mechanism from functioning and performing properly. The DNA damage response (DDR) is a complex signal transduction pathway which recognizes when DNA is damaged and initiates the cellular response to the damage. DNA damage and mutation have different biological consequences. While most DNA damages can undergo DNA repair, such repair is not 100% efficient. Un-repaired DNA damages accumulate in non-replicating cells, such as cells in the brai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovum
The egg cell or ovum (: ova) is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is not capable of movement (non- motile). If the male gamete (sperm) is capable of movement, the type of sexual reproduction is also classified as oogamous. A nonmotile female gamete formed in the oogonium of some algae, fungi, oomycetes, or bryophytes is an oosphere. When fertilized, the oosphere becomes the oospore. When egg and sperm fuse together during fertilisation, a diploid cell (the zygote) is formed, which rapidly grows into a new organism. History While the non-mammalian animal egg was obvious, the doctrine ''ex ovo omne vivum'' ("every living nimal comes froman egg"), associated with William Harvey (1578–1657), was a rejection of spontaneous generation and preformationism as well as a bold assumption that mammals also reproduced v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |