|
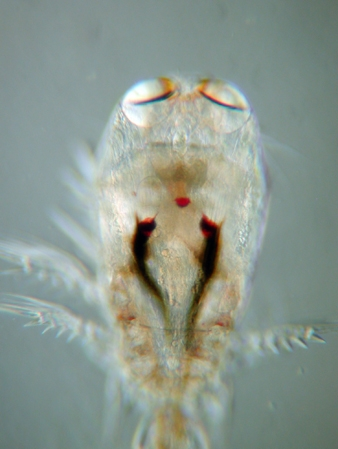
Speleophriidae
Speleophriidae is a family of copepods, comprising seven genera. All are restricted to anchialine caves, with the exception of '' Archimisophria'', which is found in the hyperbenthos of the depths of the Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the .... The genera are: References Copepods Taxa described in 2000 Copepod families {{copepod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sediments), several species have Parasitism, parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as Ecological indicator, biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a Crustacean larvae#Nauplius, nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchialine Cave
An anchialine system (, from Greek ''ankhialos'' 'near the sea') is a landlocked body of water with a subterranean connection to the ocean. Depending on its formation, these systems can exist in one of two primary forms: pools or caves. The primary differentiating characteristics between pools and caves is the availability of light; cave systems are generally aphotic while pools are euphotic. The difference in light availability has a large influence on the biology of a given system. Anchialine systems are a feature of coastal aquifers which are density stratified, with water near the surface being fresh or brackish, and saline water intruding from the coast at depth. Depending on the site, it is sometimes possible to access the deeper saline water directly in the anchialine pool, or sometimes it may be accessible by cave diving. Anchialine systems are extremely common worldwide especially along neotropical coastlines where the geology and aquifer systems are relatively young, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse colonization of North America, Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an Age of Discovery, age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceana
''Crustaceana'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal specialising in carcinology. It was established in 1960 and is published monthly by Brill Publishers. The journal is abstracted and indexed by BIOSIS Previews, the Science Citation Index, The Zoological Record, and GeoRef. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2011 impact factor of 0.464. The journal is edited by J.C. von Vaupel Klein. It charges an unspecified publication fee from authors of all regular papers, and an optional open access fee of USD 1830.CrustaceanaInstructions for Authors . Brill Publishers Brill Academic Publishers () is a Dutch international academic publisher of books, academic journals, and Bibliographic database, databases founded in 1683, making it one of the oldest publishing houses in the Netherlands. Founded in the South .... References External links * * Carcinology journals Academic journals established in 1960 Monthly journals Brill Publishers academi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepods
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthic (living on the sediments), several species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants ( phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult and then, after more molts, achieves adult development. The nauplius form is so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Described In 2000
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |