|
Special Folder
On Microsoft Windows, a special folder is a folder that is presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept instead of an absolute folder path. (The synonymous term shell folder is sometimes used instead.) Special folders make it possible for any application to ask the operating system where an appropriate location for certain kinds of files can be found; independently of which version or user language of Windows is being used. In Windows Server 2003 and earlier, a folder like the "Start Menu" had a different name on non-English versions of Windows. For example, on German versions of Windows XP it is "Startmenü". However, starting with Windows Vista, all versions of Windows use the same English named folders and only display different names in the Windows Explorer. In Windows 10 the user can switch to another display language and the names of the special folders will change. Overview Windows uses the concept of special folders to present the contents of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry – Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a Server (computing), server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Windows is sold as either a consumer retail product or licensed to Original equipment manufacturer, third-party hardware manufacturers who sell products Software bundles, bundled with Windows. The first version of Windows, Windows 1.0, was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). The name "Windows" is a reference to the windowing system in GUIs. The 1990 release of Windows 3.0 catapulted its market success and led to various other product families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 2000
Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft, targeting the server and business markets. It is the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0, and was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999, and then to retail on February 17, 2000 for all versions, with Windows 2000 Datacenter Server being released to retail on September 26, 2000. Windows 2000 introduces NTFS 3.0, Encrypting File System, and basic and dynamic disk storage. Support for people with disabilities is improved over Windows NT 4.0 with a number of new Assistive technology, assistive technologies, and Microsoft increased support for different languages and Locale (computer software), locale information. The Windows 2000 Server family has additional features, most notably the introduction of Active Directory, which in the years following became a widely used directory service in business environments. Although not pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix Directory Structure
In Unix and operating systems inspired by it, the file system is considered a central component of the operating system. It was also one of the first parts of the system to be designed and implemented by Ken Thompson in the first experimental version of Unix, dated 1969. As in other operating systems, the filesystem provides information storage and retrieval, and one of several forms of interprocess communication, in that the many small programs that traditionally form a Unix system can store information in files so that other programs can read them, although pipes complemented it in this role starting with the Third Edition. Also, the filesystem provides access to other resources through so-called ''device files'' that are entry points to terminals, printers, and mice. The rest of this article uses ''Unix'' as a generic name to refer to both the original Unix operating system and its many workalikes. Principles The filesystem appears as one rooted tree of directories. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tweak UI
Tweak UI is a free Application software, application, released in 1996 by Microsoft for customizing the Microsoft Windows operating system's user interface. Tweak UI modifies the Windows Registry in the same way as a user could edit it manually with a program such as RegEdit, but provides a simple graphical user interface that does not need knowledge of the registry structure, is quicker and easier to use, and not susceptible to registry damage due to user error. Tweak UI was formerly downloadable free of charge from Microsoft's website. It is one of Microsoft's many non-supported ''Microsoft PowerToys, PowerToys''. History Tweak UI started as a Control panel (computer), control panel applet available for download on Microsoft's website, released shortly after the release of Windows 95. It was originally written by Raymond Chen and later included in Microsoft's PowerToys collection, a set of tools developed by Microsoft's Shell Development Team. An updated version of Tweak UI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folder Redirection
In computing, and specifically in the context of Microsoft Windows, folder redirection refers to automatically re-routing to or from standard folders to use storage elsewhere on a network. It is often used in an office network environment to ensure that users do not store data locally when a network device is the preferred storage location. Folder Redirection allows saving data regardless of storage location and separates user data from profile data decreasing the time required to log on. Other advantages include: * Data is stored on a server where it can be backed up * If the same redirection is applied to multiple users, all data is stored in the one location * Allows for sharing of data between users directly from the server rather than creating shares on individual workstations * Allows system administrators to spend less on workstation hard drives, and more on file server hard drives * If all user folders are redirected and caching is disabled, no files are stored on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Windows Platform Apps
Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps (formerly named Windows Store apps, Metro-style apps and Modern apps) are applications that can be used across all compatible Microsoft Windows devices. They are primarily purchased and downloaded via the Microsoft Store, Microsoft's digital application storefront. UWP was deprecated in October 2021. Nomenclature Starting with Windows 10, Microsoft initially used the term "Windows app" to describe Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps. These were applications that could be installed from the Microsoft Store, previously known as the Windows Store. Initially, these apps were called "Trusted Windows Store apps," and later they were referred to as "Trusted Microsoft Store apps." Traditional programs designed to run on desktop computers were referred to as " desktop apps." With the release of the Windows 10, version 1903, there was a shift in the terminology. Microsoft began using the term "Apps" to refer to both UWP apps and desktop apps in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Neighborhood
My Network Places (formerly Network Neighborhood) is the network browser feature in Windows Explorer. It was first introduced in Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 as Network Neighborhood, and was renamed My Network Places in Windows 2000 and later, before being replaced in Windows Vista. My Network Places maintains an automatically updated history of computers which the user has accessed before, by default placed in a folder called , found in the user's user profile. This default location can be changed by modifying the pair of registry entries found under the registry keys and . The feature also allows enumerating all computers on the local network that support the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol and are open to discovery. In a workgroup of fewer than 32 computers,Windows XP help file, "My Network Places overview" the list of network destinations in My Network Places is generated by one of the computers on the network, which has been designated "Browse Master" (sometimes called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
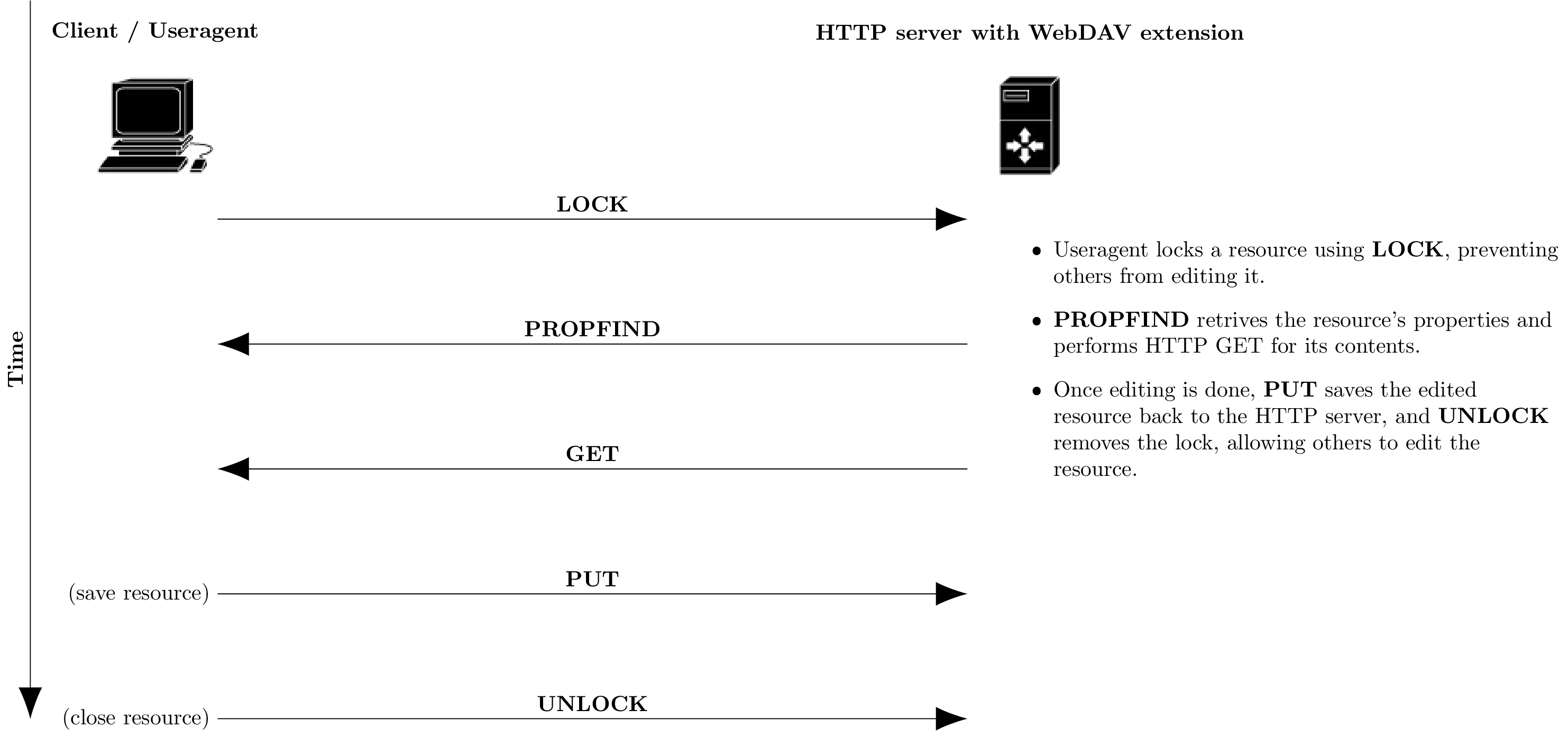
WebDAV
WebDAV (Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning) is a set of extensions to the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which allows user agents to collaboratively author contents ''directly'' in an HTTP web server by providing facilities for concurrency control and namespace operations, thus allowing the Web to be viewed as a ''writeable, collaborative medium'' and not just a read-only medium. WebDAV is defined in by a working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The WebDAV protocol provides a framework for users to create, change and move documents on a server. The most important features include the maintenance of properties about an author or modification date, namespace management, collections, and overwrite protection. Maintenance of properties includes such things as the creation, removal, and querying of file information. Namespace management deals with the ability to copy and move web pages within a server's namespace. Collections deal with the creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Panel (Windows)
Control Panel was a component of Microsoft Windows that provided the ability to view and change system settings. It consisted of a set of applets that included adding or removing hardware and software, controlling user accounts, changing accessibility options, and accessing networking settings. Additional applets were provided by third parties, such as audio and video drivers, VPN tools, input devices, and networking tools. Overview Control Panel had been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 1.0, with each successive version introducing new applets. Beginning with Windows 95, the Control Panel is implemented as a special folder (i.e. the folder does not physically exist), and as such only contains shortcuts to various applets such as ''Add or Remove Programs'' and ''Internet Options''. Physically, these applets are stored as ''.cpl'' files so that they can be shown on the Control Panel. For example, the ''Add or Remove Programs'' applet is stored under the name ''appw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Server Domain
A Windows domain is a form of a computer network in which all user accounts, computers, printers and other security principals, are registered with a central database located on one or more clusters of central computers known as domain controllers. Authentication takes place on domain controllers. Each person who uses computers within a domain receives a unique user account that can then be assigned access to resources within the domain. Starting with Windows Server 2000, Active Directory is the Windows component in charge of maintaining that central database.Northrup, Tony''Introducing Microsoft Windows 2000 Server'' Microsoft Press, 1999. The concept of Windows domain is in contrast with that of a workgroup in which each computer maintains its own database of security principals. Configuration Computers can connect to a domain via LAN, WAN or using a VPN connection. Users of a domain are able to use enhanced security for their VPN connection due to the support for a cert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SysWOW64
In computing on Microsoft platforms, WoW64 (Windows 32-bit on Windows 64-bit) is a subsystem of the Windows operating system capable of running 32-bit applications on 64-bit Windows. It is included in all 64-bit versions of Windows, except in Windows Server Server Core where it is an optional component, and Windows Nano Server where it is not included. WoW64 aims to take care of many of the differences between 32-bit Windows and 64-bit Windows, particularly involving structural changes to Windows itself. Translation libraries The WoW64 subsystem comprises a lightweight compatibility layer that has similar interfaces on all 64-bit versions of Windows. It aims to create a 32-bit environment that provides the interfaces required to run unmodified 32-bit Windows applications on a 64-bit system. WOW64 is implemented using several DLLs, some of which include: # Wow64.dll, the core interface to the Windows NT kernel that translates (thunks) between 32-bit and 64-bit calls, including po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |