|
Spatharokandidatos
(), Latinized as , was a mid-ranking Byzantine court dignity used in the 7th–11th centuries. History The title was created as a portmanteau of the titles and , both of which were types of palace guards in the 4th–6th centuries.. The earliest references to the title occur in the ''History'' of Sebeos and in a letter by Pope Gregory II to Emperor Leo III the Isaurian (). John B. Bury accepted a creation in the early 7th century, but the title is clearly attested only from the early 9th century on. In the 9th-century lists of precedence ('' Taktika''), the dignity ranks below that of and above that of among the dignities intended for 'bearded men' (i.e. non-eunuchs). Its distinctive insigne () was a golden chain () worn around the chest. The dignity was not given to eunuchs, for whom the corresponding dignity was that of . Judging from sigillographic Sigillography, also known by its Greek-derived name, sphragistics, is the scholarly discipline that studies the Sealin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
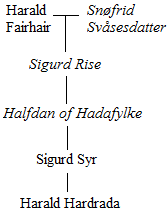
Harald Hardrada
Harald Sigurdsson (; – 25 September 1066), also known as Harald III of Norway and given the epithet ''Hardrada'' in the sagas, was List of Norwegian monarchs, King of Norway from 1046 to 1066. He unsuccessfully claimed the Monarchy of Denmark, Danish throne until 1064 and the List of English monarchs, English throne in 1066. Before becoming king, Harald spent 15 years in exile as a mercenary and military commander in Kievan Rus' and chief of the Varangian Guard in the Byzantine Empire. In his Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum, chronicle, Adam of Bremen called him the "''Thunderbolt of the North''". In 1030, the fifteen-year-old Harald fought in the Battle of Stiklestad along-side his half-brother Saint Olaf, Olaf Haraldsson. Olaf sought to reclaim the Norwegian throne, which he had lost to Danish king Cnut two years previously. Olaf and Harald were defeated by forces loyal to Cnut, and Harald was forced into exile to Kievan Rus'. Thereafter, he was in the army of Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
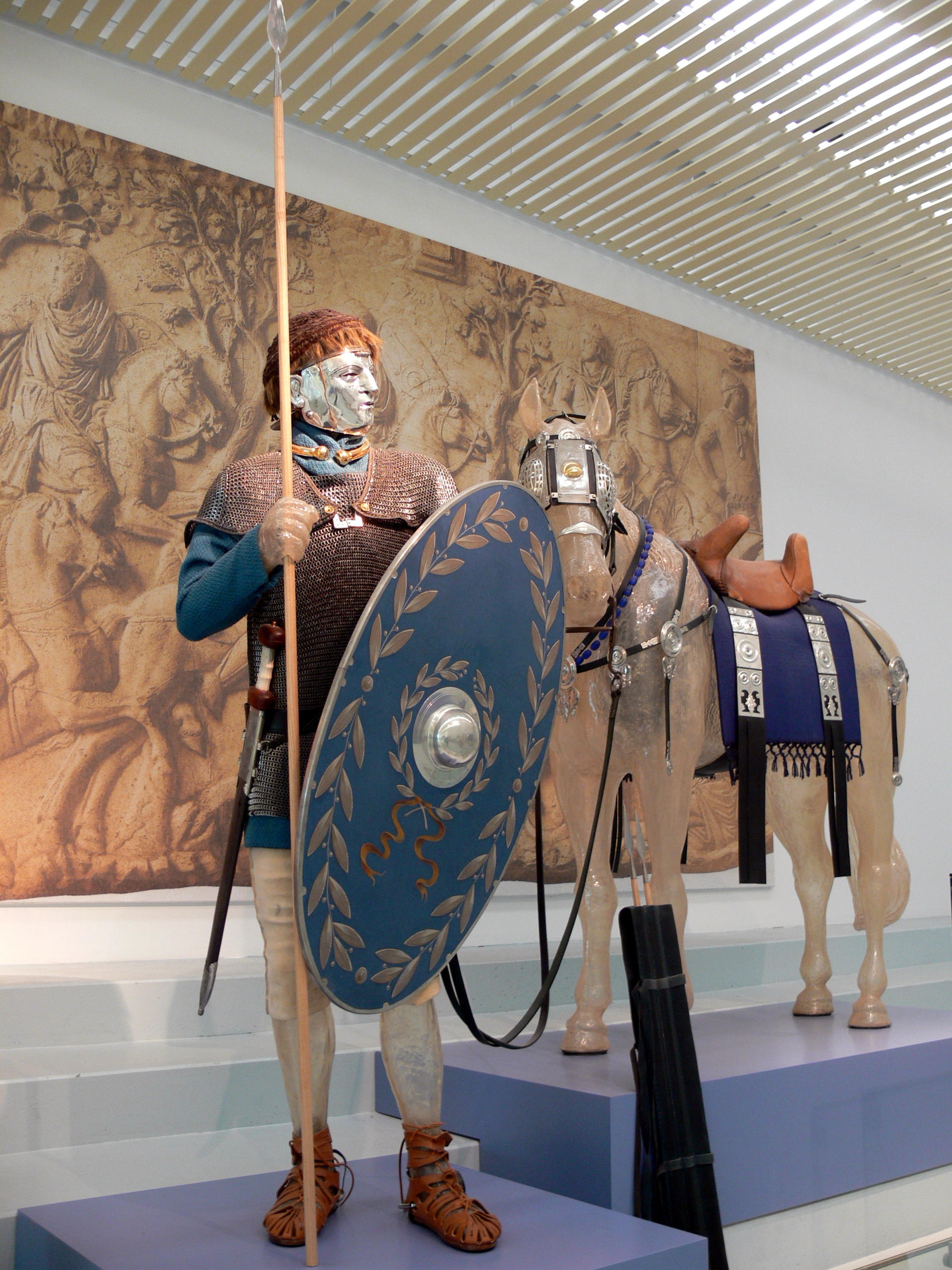
Spatharios
The ''spatharii'' or ''spatharioi'' (singular: ; , literally " spatha-bearer") were a class of Late Roman imperial bodyguards in the court in Constantinople in the 5th–6th centuries, later becoming a purely honorary dignity in the Byzantine Empire. History Originally, the term was probably applied to both private and imperial bodyguards.. The original imperial ''spatharioi'' were probably or later became also the eunuch '' cubicularii'' (Greek: ''koubikoularioi''), members of the ''sacrum cubiculum'' (the imperial "sacred chamber") charged with military duties. They are attested from the reign of Emperor Theodosius II (r. 408–450), where the eunuch Chrysaphius held the post. The existence of the specific title of ''spatharokoubikoularios'' for eunuchs in 532 probably suggests the existence by then of other, non-eunuch, ''spatharioi'' in imperial service. The various generals and provincial governors also maintained military attendants called ''spatharioi'', whilst those of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourmarches
A ''turma'' (; plural ''turmae''; ) was a cavalry unit in the Roman army of the Republic and Empire. In the Byzantine Empire, it became applied to the larger, regiment-sized military-administrative divisions of a '' thema''. The word is often translated as " squadron" but so is the term '' ala'', a unit that was made up of several ''turmae''. Roman army Republic In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, the time of the Punic Wars and Rome's expansion into Spain and Greece, the core of the Roman army was formed by citizens, augmented by contingents from Rome's allies (''socii''). The organization of the Roman legion of the period is described by the Greek historian Polybius (cf. the so-called " Polybian army"), who writes that each 4,200-strong infantry legion was accompanied by 300 citizen cavalry (''equites''). This contingent was divided into ten ''turmae''.. According to Polybius, the squadron members would elect as their officers three '' decuriones'' ("leaders of 10 men"), of whom the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dishypatos
, Latinized as (), was a Byzantine honorary dignity (, ) in the 9th–11th centuries, intended for "bearded men" (i.e. non-eunuchs). From then on, and especially during the Palaiologan period, it is attested as a family name. The title is relatively rarely mentioned in literary sources, and few seals of have been found. Likely created in the 8th century, it is first attested in the early 9th century, when a certain Thomas, addressee of Theodore the Studite, held the title.. Nevertheless, in the ''Kletorologion'', compiled in 899 by Byzantine court official Philotheos, it ranks quite high, being placed below the and above the . The ''Kletorologion'' also mentions that its characteristic insigne of the rank (, ) was a diploma. The title seems to have disappeared in Byzantium itself by the late 11th century, but it is still attested during the 12th century in Byzantine-influenced southern Italy. In the same period, 'Dishypatos' begins to appear as a surname, becoming more common a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Of Niketas, Spatharokandidatos And Chartoularios Of The Cibyrrhaeots (Schlumberger, 1889)
Seal may refer to any of the following: Common uses * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** Earless seal, also called "true seal" ** Fur seal ** Eared seal * Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of authentication, on paper, wax, clay or another medium (the impression is also called a seal) * Seal (mechanical), a device which helps prevent leakage, contain pressure, or exclude contamination where two systems join ** Hermetic seal, an airtight mechanical seal * Security seals such as labels, tapes, bands, or ties affixed onto a container in order to prevent and detect tampering Arts, entertainment and media * ''Seal'' (1991 album), by Seal * ''Seal'' (1994 album), sometimes referred to as ''Seal II'', by Seal * '' Seal IV'', a 2003 album by Seal * ''Seal Online'', a 2003 massively multiplayer online role-playing game Law * Seal (contract law), a legal formality for contracts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guards Units Of The Byzantine Empire
Guard or guards may refer to: Professional occupations * Bodyguard, who protects an individual from personal assault * Crossing guard, who stops traffic so pedestrians can cross the street * Lifeguard, who rescues people from drowning * Prison guard, who supervises prisoners in a prison or jail * Security guard, who protects property, assets, or people * Conductor (rail) § Train guard, in the UK, Australia, New Zealand, and India Computing and telecommunications * Guard (computer science), in programming language, an expression that directs program execution * Guard (information security), a device for controlling communication between computer networks * Guard interval, intervals in transmission, used in telecommunications * Aircraft emergency frequency, commonly referred to as "guard" Governmental and military * Border guard, a state security agency * Coast guard, responsible for coastal defence and offshore rescue * Colour guard, a detachment of soldiers assigned to the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Court Titles
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, experienced recurring cycles of decline and recovery. It reached its greatest extent un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florian Munteanu
Florian Munteanu (; born 13 October 1990) is a German actor. He is known for playing the boxer Viktor Drago in ''Creed II'' (2018) and ''Creed III'' (2023), and Razor Fist in ''Shang-Chi and the Legend of the Ten Rings'' (2021). Early life Munteanu was born in Germany to Romanian parents in 1990. His mother is a lawyer, while his father was a dermatologist and former boxer. Munteanu grew up in Bogen, and later moved to Munich to study at the university of applied science Hochschule Mittweida. In 2014 he defended his Bachelor of Arts thesis on the "Structure and organization of the sport of boxing in Germany: associations, boxing promotion companies, federations, management and marketing in general, with a comparison to the structures implemented in the USA". He has competed in boxing in Germany under the ring name "Big Nasty". Career Munteanu had his first film role in ''Bogat'', a 2016 German-Romanian film shot in Munich. His breakthrough in acting came in 2018, when Sylvester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Suter
Leo Suter (born 26 September 1993) is an English actor. His credits include '' Bad Education'' (2012), ''Victoria'' (2017), ''Ransom'' (2017), ''Clique'' (2018), '' Beecham House'' (2019), ''Sanditon'' (2019), ''Intelligence'' (2020), '' The Liberator'' (2020). However, he is most notable for playing the main role of Harald Sigurdsson in the Netflix series '' Vikings: Valhalla'' (2022–2024). Early life and education Suter was born in London, son of media executive Tim Suter and businesswoman Dame Helen Alexander, chair of UBM plc and chancellor of the University of Southampton from 2011 to 2017. He was educated at Colet Court, St Paul's School, and New College, Oxford, where he read Human Sciences. Career He began acting while studying in school at the age of eleven. He signed his first professional acting contract after playing in his school final play. His theatre roles included Patsy in ''The Winterling'' by Oxford Playhouse, Subtle in ''The Alchemist'' by Arcola Theatre, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Maniakes
George Maniakes (; ; died 1043) was a prominent general of the Byzantine Empire during the 11th century. He was the catepan of Italy in 1042. He is known as Gyrgir in Scandinavian sagas. He is popularly said to have been extremely tall and well built, almost a giant. Biography Maniakes was a Greek general of the Byzantine Empire, who first came to prominence during a campaign in 1030–1031 when the Byzantine army was defeated at Aleppo, but went on to capture Edessa from the Arabs. His greatest achievement was the partial reconquest of Sicily from the Arabs beginning in 1038. He was aided by the Varangian Guard, then led by Harald Hardrada, who later became King of Norway. Also with him were Norman mercenaries under William de Hauteville, who earned his nickname ''Iron Arm'' by defeating the Emir of Syracuse in single combat. However, he soon ostracized his admiral, Stephen, whose wife was the sister of John the Eunuch, the highest-ranking man at court. He then publicly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valhalla
In Norse mythology, Valhalla ( , ; , )Orchard (1997:171–172) is described as a majestic hall located in Asgard and presided over by the god Odin. There were five possible realms the soul could travel to after death. The first was Fólkvangr, ruled by the goddess Freyja. The second was Hel, ruled by Hel, Loki's daughter. The third was that of the goddess Rán. The fourth was the Burial Mound where the dead could live. The fifth and last realm was Valhalla, ruled by Odin and was called the Hall of Heroes. The masses of those killed in combat (known as the einherjar), along with various legendary Germanic heroes and kings, live in Valhalla until Ragnarök, when they will march out of its many doors to fight in aid of Odin against the jötnar. Valhalla was idealized in Viking culture and gave the Scandinavians a widespread cultural belief that there is nothing more glorious than death in battle. The belief in a Viking paradise and eternal life in Valhalla with Odin may have g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |