|
Spartan Constitution
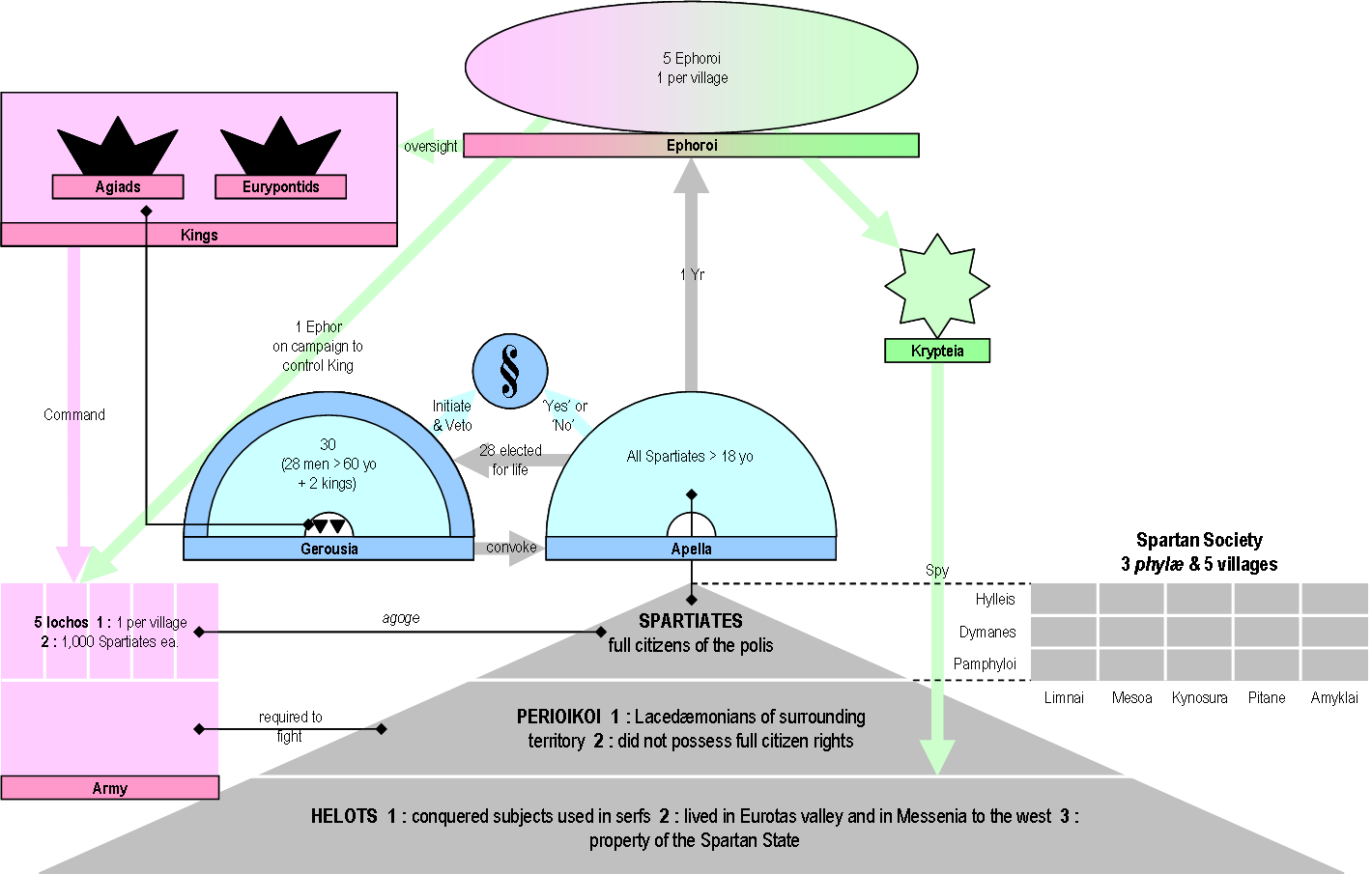
The Spartan Constitution (or Spartan politeia) are the government and laws of the Classical Greece, classical Greek city-state of Sparta. All classical Greek city-states had a politeia; the politeia of Sparta however, was noted by many classical authors for its unique features, which supported a rigidly layered social system and a strong hoplite army. The Spartans had no historical records, literature, or written laws, which were, according to tradition, prohibited. Attributed to the mythical figure of Lycurgus of Sparta, Lycurgus, the legendary law-giver, the Spartan system of government is known mostly from the ''Constitution of the Lacedaemonians'', a treatise attributed to the ancient Greek historian Xenophon, describing the institutions, customs, and practices of the ancient Spartans. The act of the foundation Great Rhetra According to Plutarch, Lycurgus of Sparta, Lycurgus (to whom is attributed the establishment of the severe reforms for which Sparta has become renown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politeia
''Politeia'' ( πολιτεία) is an ancient Greek word used in Greek political thought, especially that of Plato and Aristotle. Derived from the word '' polis'' ("city-state"), it has a range of meanings from " the rights of citizens" to a " form of government". English translations of the Greek word According to Liddell and Scott's '' Greek-English Lexicon'' a meaning of ''politeia'' is "the conditions and rights of the citizen, or citizenship", analogous to the Latin '' civitas''. ''Politeia'', in Greek means the community of citizens in a city / state. It should not be confused with "regime" that is meant by ''politeuma'' or "Status quo" that is meant by '' kathestos''. ''Politeuma'' is the word describing the political situation of the community of citizens in a city/state, and ''kathestos'' means also the general situation of an object, an agreement, or something else. ''Politeia'' is derived from both the root word '' polis'' meaning "city" or "state", and from the ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartiates
A Spartiate (, ''Spartiátēs'') or ''Homoios'' (pl. ''Homoioi'', , "alike") was an elite full-citizen men of the ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. Spartiate-class men (including boys) were a small minority: estimates are that they made up between 1/10 and 1/32 of the population, with the proportion decreasing over time; the vast majority of the people of Sparta were helots (slaves). Spartan citizenship was restricted to adult men without metic ancestry, as in most Greek poleis. Spartiate-class women could not hold citizenship but were eligible to marry Spartiates, and their sons could become Spartiates. After the First Messenian War, the mass enslavement of the Messenian population created a slave society (60-79% slaves; by contrast, US slave states generally had 30-65%). This society was recognized as unusual by both modern historians and contemporary non-Spartans. Spartiate-class people came to be barred from work by law and strong social norms and were supported by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partheniae
In ancient Greece, the Partheniae or Parthenians (in Greek /'' hoi Partheníai,'' literally “sons of virgins”, i.e. unmarried young girls) were a lower ranking Spartiate population which, according to tradition, left Laconia to go to Magna Graecia and founded Taras, modern Taranto, in the current region of Apulia, in southern Italy. Origins of the Parthenians At least three distinct traditions carry the origins of the Parthenians. The oldest is that of Antiochus of Syracuse (a contemporary of Thucydides quoted by Strabo, VI, 3, 2), according to which the Spartiates, during the first Messenian war (end of the 8th century BC), had rejected like cowards those who had not fought, along with their descendants: Antiochus says that, during the Messenian war, those Lacedemonians which did not take part with the mission shall be declared as slaves and called Helots; as for the children born during the mission, we shall call them Parthenians and deny them of all legal rights. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epeunacti
Epeunacti () or Epeunactae (ἐπευνακταί), were a class of citizens in ancient Sparta. They were Helots who either slept with the widows of Spartans when Sparta had manpower shortage because of war casualties, or outright replaced the fallen Spartans as soldiers. During a war with the Messenians, the Lacedaemonians lost many men. Being afraid that their enemies will become aware of their situation, they "put Helots into the beds of those who were dead" (that's why the name, from ἐπὶ (into) and εὐνὴ (bed)). Afterwards, they made those men citizens. In Sicyon, there were people who were called Catonacophori (κατωνακοφόροι) who were very similar to the Epeunacti. Numa Denis Fustel de Coulanges Numa Denis Fustel de Coulanges (; 18 March 1830 – 12 September 1889) was a French historian. Biography Coulanges was born in Paris; he was of Breton descent. After studying at the École Normale Supérieure, he attended the French School at ... mentions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodamodes
The neodamodes (, ''neodamōdeis'') were helots freed after passing a time of service as hoplites in the Spartan army. The date of their first apparition is uncertain. Thucydides does not explain the origin of this special category. Jean Ducat, in his book ''Les Hoplites'' (1990), concludes that their statute "was largely inspired by the measures dictated concerning the Brasidians", i.e. the helots freed after taking part in the expedition of Brasidas in 424 BC. Their existence is attested from 420 to 369 BC. They were part of Sparta's army and 2,000 of them are recorded taking part, for example, in Agesilaus II's campaign in Ionia between 396 and 394 BC. The name comes from the words νέος ''neos'', meaning "new", and ''dêmos'', meaning "''deme'' or territory". Differently from what is written by Hesychius of Alexandria, who brings together the neodamodes and the Athenian '' demotes'' (citizens of a deme), they never acquired full citizenship. The suffix -ωδης ''- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mothax
Mothax (, ''mothax'', pl.: μόθακες, ''mothakes'') is a Doric Greek word meaning "stepbrother". The term was used for a sociopolitical class in ancient Sparta, particularly during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC). The mothakes were primarily either offspring of Spartiate fathers and helot mothers or children of impoverished Spartiates. Mothakes were not able to contribute to the syssitia, the core civic daily institution for citizens, and thus were not allowed to maintain an "equal" status. They were, however, permitted to fight as troops along with perioeci The Perioeci or Perioikoi (, ) were the second-tier citizens of the ''polis'' of Sparta until 200 BC. They lived in several dozen cities within Spartan territories (mostly Laconia and Messenia), which were dependent on Sparta. The ''perioeci'' .... Though free, they were not Spartan citizens but were brought up alongside Spartan boys as their foster brothers. Due to the expenses of providing extra mess contrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypomeion
A Spartiate (, ''Spartiátēs'') or ''Homoios'' (pl. ''Homoioi'', , "alike") was an elite full-citizen men of the ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. Spartiate-class men (including boys) were a small minority: estimates are that they made up between 1/10 and 1/32 of the population, with the proportion decreasing over time; the vast majority of the people of Sparta were helots (slaves). Spartan citizenship was restricted to adult men without metic ancestry, as in most Greek poleis. Spartiate-class women could not hold citizenship but were eligible to marry Spartiates, and their sons could become Spartiates. After the First Messenian War, the mass enslavement of the Messenian population created a slave society (60-79% slaves; by contrast, US slave states generally had 30-65%). This society was recognized as unusual by both modern historians and contemporary non-Spartans. Spartiate-class people came to be barred from work by law and strong social norms and were supported by the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciritae
The Sciritae or Skiritai or Skioreitai or Skioritai (Greek: ) were a people subject to Sparta, whose status is comparable to that of the Perioeci. Deriving their name from the town of Skiritis, a mountainous region located in northern Laconia on the border with Arcadia, between the Oenus and the Eurotas rivers. According to Stephanus of Byzantium and Hesychius of Alexandria, the Sciritae were of Arcadian origin. Their way of life was essentially rural: they mostly lived in villages, of which the biggest were Oion and Caryai. Their territory was inhospitable, but was of strategic importance for Sparta since it controlled the road to Tegea, which explains why it rapidly fell in Spartan hands. Their status was similar to that of the Perioeci, but Xenophon distinguished between them writing: "To meet the case of a hostile approach at night, he assigned the duty of acting as sentries outside the lines to the Sciritae. In these days the duty is shared by foreigners, if any happen to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helots
The helots (; , ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their exact characteristics, such as whether they constituted an Ancient Greek tribe, a social class, or both. For example, Critias described helots as "slaves to the utmost", whereas according to Pollux, they occupied a status "between free men and slaves". Tied to the land, they primarily worked in agriculture as a majority and economically supported the Spartan citizens. The proportion of helots in relation to Spartan citizens varied throughout the history of the Spartan state; according to Herodotus, there were seven helots for each of the 5,000 Spartan soldiers at the time of the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC. Thus the need to keep the helot population in check and to prevent rebellion were major concerns of the Spartans. Helots were ritually mistreated and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
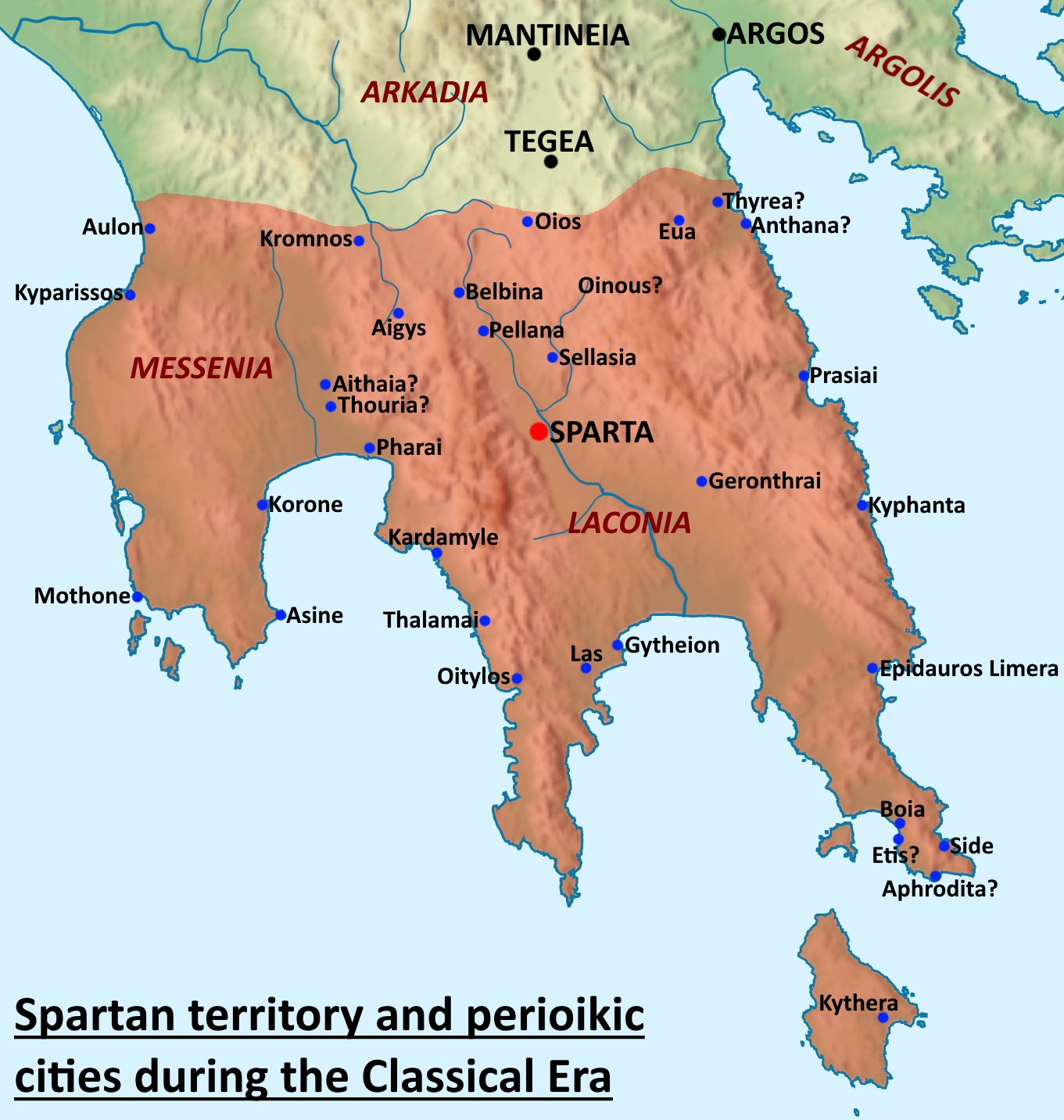
Perioeci
The Perioeci or Perioikoi (, ) were the second-tier citizens of the ''polis'' of Sparta until 200 BC. They lived in several dozen cities within Spartan territories (mostly Laconia and Messenia), which were dependent on Sparta. The ''perioeci'' only had political rights in their own city, while the course of the Spartan state exclusively belonged to Spartan citizens, or Spartiates. The name ''perioeci'' roughly means "those dwelling around/nearby", deriving from , ''peri'', "around", and , ''oîkos'', "dwelling, house". ''Perioeci'' and Spartans were collectively called the ''Lakedaimonians''. They had a central role in the Spartan economy, controlling commerce and business, as well as being responsible for crafts and manufacturing, including producing the weapons and armour of the Spartan army, as the higher-ranking Spartan citizens considered all commercial and money-making activities to be unworthy of them. The ''perioeci'' were also the only people allowed to freely travel o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcmaeonid
The Alcmaeonidae (; , ; Attic: , ) or Alcmaeonids () were a wealthy and powerful noble family of ancient Athens, a branch of the Neleides who claimed descent from the mythological Alcmaeon, the great-grandson of Nestor. In the 7th to late 5th centuries BC, the Alcmaeonidae played a significant role in the developments and events that occurred in Athens. Such developments included overthrowing an Athenian tyrant, helping to lay the foundations of Athenian democracy, and having generals for Athens during the Peloponnesian War. The Alcmaeonidae were mentioned frequently throughout Herodotus' '' The Histories'', and many played a key role in shaping Athens. The first prominent Alcmaeonid was Megacles, who was exiled from the city and given a curse on him and his family. Furthermore, there was Cleisthenes, who became known as "the father of Athenian democracy" by numerous scholars and historians. Another famous Alcmaeonid was Pericles, whom Thucydides would later call "the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcibiades
Alcibiades (; 450–404 BC) was an Athenian statesman and general. The last of the Alcmaeonidae, he played a major role in the second half of the Peloponnesian War as a strategic advisor, military commander, and politician, but subsequently fell from prominence. During the course of the Peloponnesian War, Alcibiades changed his political allegiance several times. In his native Athens in the early 410s BC, he advocated an aggressive foreign policy and was a prominent proponent of the Sicilian Expedition. After his political enemies brought charges of sacrilege against him, he fled to Sparta, where he served as a strategic adviser, proposing or supervising several major campaigns against Athens. However, Alcibiades made powerful enemies in Sparta too, and defected to Persia. There he served as an adviser to the satrap Tissaphernes until Athenian political allies brought about his recall. He served as an Athenian general (strategos) for several years, but enemies eventually suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |