|
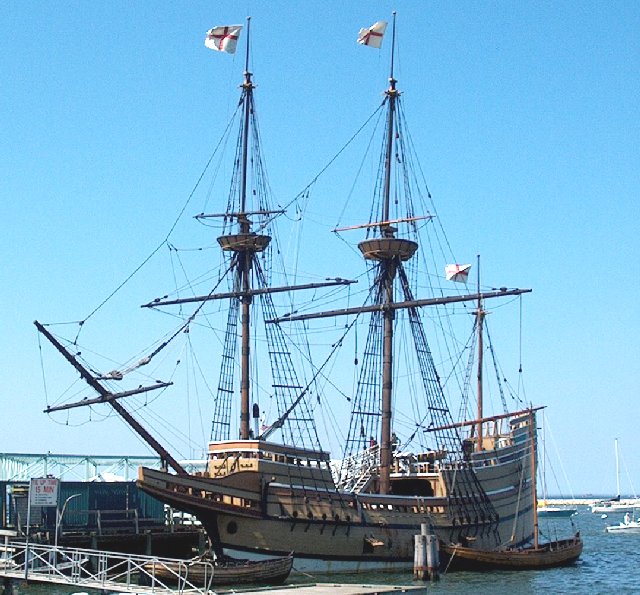
Sparrow Hawk (pinnace)
The ''Sparrow-Hawk'' was a 'small pinnace' similar to the full-rigged pinnace ''Virginia'' that sailed for the English Colonies in June 1626. She is the earliest ship to participate in the first decades of English settlement in the New World to have survived to the present day. A rough, six-week voyage ended in a storm off Orleans, Massachusetts on Cape Cod when the heavily loaded ''Sparrow-Hawk'' was driven onto the isolated Nauset Beach. All aboard survived and were removed to the nearby Plymouth Colony. Storms and shifting sand buried the wrecked pinnace within several weeks. ''Sparrow-Hawk'' remained buried until storms in May 1863 uncovered the hull, which was soon salvaged. Keel, planks, rudder and other hull elements from the ''Sparrow-Hawk'' were found in good condition, removed from the beach and carefully reconstructed for subsequent exhibition. Several of the best naval architects of the 1860s in Boston collaborated on the reconstruction of ''Sparrow-Hawk'', which rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparrow Hawk Ship
Sparrow may refer to: Birds * Old World sparrows, family Passeridae * New World sparrows, family Passerellidae * two species in the Passerine family Estrildidae: ** Java sparrow ** Timor sparrow * Hedge sparrow, also known as the dunnock or hedge accentor in the family Prunellidae People * Sparrow (surname) * Sparrow (American poet) (born 1953), American poet, activist, musician, and rabble-rouser * Alex Sparrow, also known as Alexey Vorobyov (born 1988), Russian singer and actor * Robert Brown (footballer, born 1856), Scottish footballer known by the nickname 'Sparrow' * The Little Sparrow (La Môme Piaf), the nickname of French singer Édith Piaf (1915 –1963) Media Films * ''The Sparrow'' (1914 film), a 1914 French silent film * ''Sparrows'' (1916 film), a Dutch film * ''Sparrows'' (1926 film), starring Mary Pickford * ''The Sparrow'' (1972 film), Arabic title ''Al Asfour'', a 1972 Egyptian film by director Youssef Chahine * ''Sparrow'' (1993 film), a 1993 Italian dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth are shaped by the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Chesapeake Bay, which provide habitat for much of its flora and fauna. The capital of the Commonwealth is Richmond, Virginia, Richmond; Virginia Beach, Virginia, Virginia Beach is the most-populous city, and Fairfax County, Virginia, Fairfax County is the most-populous political subdivision. The Commonwealth's population was over 8.65million, with 36% of them living in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The area's history begins with Native American tribes in Virginia, several indigenous groups, including the Powhatan. In 1607, the London Company established the Colony of Virginia as the first permanent English overseas posse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
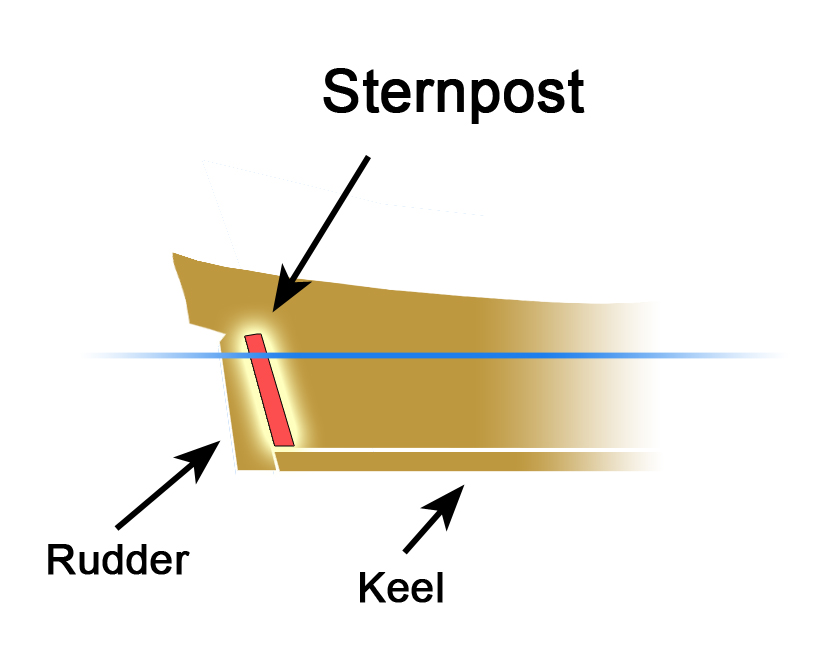
Sternpost
A sternpost is the upright structural member or post at the stern of a (generally wooden) ship or a boat, to which are attached the transoms and the rearmost left corner part of the stern. The sternpost may either be completely vertical or may be tilted or "raked" slightly aft. It rests on or "fays to" the ship's keel. See also * Boat building * Shipbuilding Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other Watercraft, floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roo ... References Watercraft components {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparrow Hawk Hull
Sparrow may refer to: Birds * Old World sparrows, family Passeridae * New World sparrows, family Passerellidae * two species in the Passerine family Estrildidae: ** Java sparrow ** Timor sparrow * Hedge sparrow, also known as the dunnock or hedge accentor in the family Prunellidae People * Sparrow (surname) * Sparrow (American poet) (born 1953), American poet, activist, musician, and rabble-rouser * Alex Sparrow, also known as Alexey Vorobyov (born 1988), Russian singer and actor * Robert Brown (footballer, born 1856), Scottish footballer known by the nickname 'Sparrow' * The Little Sparrow (La Môme Piaf), the nickname of French singer Édith Piaf (1915 –1963) Media Films * ''The Sparrow'' (1914 film), a 1914 French silent film * ''Sparrows'' (1916 film), a Dutch film * ''Sparrows'' (1926 film), starring Mary Pickford * ''The Sparrow'' (1972 film), Arabic title ''Al Asfour'', a 1972 Egyptian film by director Youssef Chahine * ''Sparrow'' (1993 film), a 1993 Italian dram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rye, East Sussex
is a small town and civil parish in the Rother district of East Sussex, England, two miles from the sea at the confluence of three rivers: the Rother, the Tillingham and the Brede. An important member of the mediaeval Cinque Ports confederation, it was at the head of an embayment of the English Channel, and almost entirely surrounded by the sea. At the 2011 census, Rye had a population of 4,773. Its historical association with the sea has included providing ships for the service of the Crown in time of war, and being involved in smuggling. The notorious Hawkhurst Gang used its ancient inns The Mermaid Inn and The Olde Bell Inn, which are said to be connected to each other by a secret passageway. Those historic roots and its charm make it a tourist destination, with hotels, guest houses, B&Bs, tea rooms, and restaurants. Rye has a small fishing fleet, and Rye Harbour has facilities for yachts and other vessels. History The name of Rye is believed to come from the West S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheer (ship)
The sheer is a measure of longitudinal main deck curvature, in naval architecture. The sheer forward is usually twice that of sheer aft. Increases in the rise of the sheer forward and aft build volume into the hull, and in turn increase its buoyancy forward and aft, thereby keeping the ends from diving into an oncoming wave and slowing the ship. In the early days of sail, one discussed a hull's sheer in terms of how much "hang" it had. William Sutherland's ''The Ship-builders Assistant'' (1711) covers this information in more detail. The practice of building sheer into a ship dates back to the era of small sailing ship A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships ...s. These vessels were built with the decks curving upwards at the bow and stern in order to increase stability by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Colonies
The New England Colonies of British America included Connecticut Colony, the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Massachusetts Bay Colony, Plymouth Colony, and the Province of New Hampshire, as well as a few smaller short-lived colonies. The New England colonies were part of the Thirteen Colonies and eventually became five of the six states in New England, with Plymouth Colony absorbed into Massachusetts and Maine separating from it. Captain John Smith's 1616 work '' A Description of New England'' first applied the term "New England" to the coastal lands from Long Island Sound to Newfoundland. Arriving in America England, France, and the Netherlands made several attempts to colonize New England early in the 17th century, and those nations were often in contention over lands in the New World. French nobleman Pierre Dugua Sieur de Monts established a settlement on Saint Croix Island, Maine in June 1604 under the authority of the King of France. Nearly half the settlers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Water
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see ''Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. Tides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnacles
A barnacle is a type of arthropod constituting the subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in erosive settings. They are sessile (nonmobile) and most are suspension feeders, but those in infraclass Rhizocephala are highly specialized parasites on crustaceans. They have four nektonic (active swimming) larval stages. Around 1,000 barnacle species are currently known. The name is Latin, meaning "curl-footed". The study of barnacles is called cirripedology. Description Barnacles are encrusters, attaching themselves temporarily to a hard substrate or a symbiont such as a whale ( whale barnacles), a sea snake ('' Platylepas ophiophila''), or another crustacean, like a crab or a lobster ( Rhizocephala). The most common among them, "acorn barnacles" ( Sessilia), are sessile where they grow their shells directly onto the substrate. Pedu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plimouth Plantation
Plimoth Patuxet is a complex of living history museums in Plymouth, Massachusetts, founded in 1947. Formerly Plimoth Plantation, it replicates the original settlement of the Plymouth Colony established in the 17th century by the English colonists who became known as the Pilgrims, as well as that of the Patuxet people upon whose land the Pilgrims settled. They were among the first people who immigrated to America to seek religious separation from the Church of England. It is a not-for-profit museum supported by administrations, contributions, grants and volunteers. The recreations are based upon a wide variety of first-hand and second-hand records, accounts, articles and period paintings and artifacts, and the museum conducts ongoing research and scholarship, including historical archaeological excavation and curation locally and abroad. In the English Village section of the museum, trained first-person ("historical") interpreters speak, act and dress appropriately for the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bradford (Plymouth Governor)
William Bradford ( 19 March 15909 May 1657) was an English Puritan Separatism, separatist originally from the West Riding of Yorkshire in Northern England. He moved to Leiden in Holland in order to escape persecution from James VI and I, King James I of England, and then emigrated to the Plymouth Colony on the ''Mayflower'' in 1620. He was a signatory to the Mayflower Compact and went on to serve as Governor of the Plymouth Colony intermittently for about 30 years between 1621 and 1657. His journal ''Of Plymouth Plantation'' covered the years from 1620 to 1646 in Plymouth. ''The fast and thanksgiving days of New England'' by William Deloss Love, Houghton, Mifflin and Co., Cambridge, 1895. Early life [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |