|
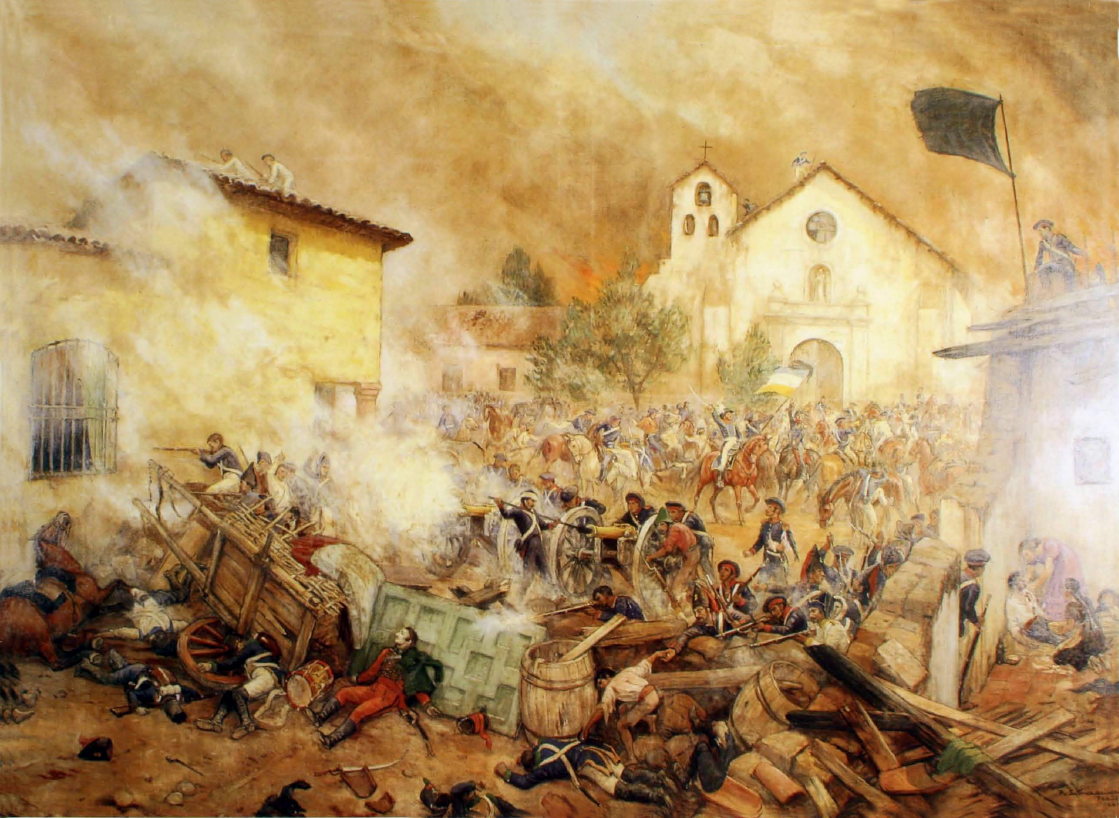
Spanish Conquest Of Oran (1509)
The conquest of Oran by the Spanish Empire took place on May 1509, when an army led by Pedro Navarro on behalf of the Cardinal Cisneros seized the North African city, which was controlled by the Kingdom of Tlemcen (Zayyanid dynasty). Background In 1505, the Spanish captured the city of Mers-El-Kébir after a successful expedition against the Zayyanids. In 1507, the Zayyanids ambushed the city of Mers-el-Kébir, with about 11,000 cavalry, gaining a decisive victory against the Spanish forces. Siege Preparations for the expedition began in September 1508. The Crown invested 39.6 million maravedis in the expedition. In comparison, the armada to Castilla del Oro in 1514 would cost 14 million and the armada of Maluco led by Hernando de Magallanes cost 8.35 million. A fleet left port from Cartagena on 16 May and sailed towards Mers el-Kebir, a city located near Oran and already (since 1505) under Spanish control. The fleet had 80 ''naos'' and 10 galleys, plus additional sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Borgoña
Juan de Borgoña (c. 1470–1536), was a Spanish Renaissance, High Renaissance painter who was born in the Duchy of Burgundy, probably just before it ceased to exist as an independent state, and was active in Spain from about 1495 to 1536. His earliest documented work was painted in 1495 for the cloister of the Cathedral of Toledo. Borgoña’s compositions are well balanced with finely drawn figures in elegant, tranquil poses. They are set either against open spaces leading on to craggy landscapes or against gold embroidered drapery. There were a number of foreign painters active in Spain in this period, including Juan de Flandes. He brought the Quattrocento form of paintings into Castile. He is not to be confused with another painter Joan de Burgunya or Borgunya who was active in Catalonia between 1510 and 1525. Borgoña’s students include Pedro de Cisneros the Elder (died 1546), Antonio de Comontes (ca. 1500-1519), Juan Correa de Vivar (ca. 1510-1566) and Borgoña’s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
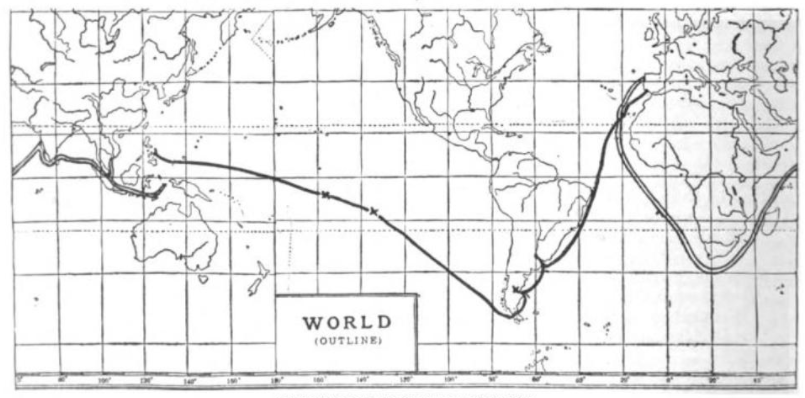
Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies. During this expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fleet to pass from the Atlantic into the Pacific Ocean and perform the first European navigation to Asia via the Pacific. Magellan was killed in battle in the Philippines and his crew, commanded by the Spanish Juan Sebastián Elcano, completed the return trip to Spain in 1522 achieving the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. Born around 1480 into a family of minor Portuguese nobility, Magellan became a skilled sailor and naval officer in service of the Portuguese Crown in Asia. King Manuel I refused to support Magellan's plan to reach the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, by sailing westwards around the American continent. Magellan then proposed the same plan to King Charles I of Spain, who approved it. In Seville, he married, fathere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sieges Of Oran
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender (military), surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment (military), investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (military), mining (also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1509
Conflict may refer to: Social sciences * Conflict (process), the general pattern of groups dealing with disparate ideas * Conflict continuum from cooperation (low intensity), to contest, to higher intensity (violence and war) * Conflict of interest, involvement in multiple interests which could possibly corrupt the motivation or decision-making * Cultural conflict, a type of conflict that occurs when different cultural values and beliefs clash * Ethnic conflict, a conflict between two or more contending ethnic groups * Group conflict, conflict between groups * Intragroup conflict, conflict within groups * Organizational conflict, discord caused by opposition of needs, values, and interests between people working together * Role conflict, incompatible demands placed upon a person such that compliance with both would be difficult * Social conflict, the struggle for agency or power in something * Work–family conflict, incompatible demands between the work and family roles of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Zayyanid Dynasty
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1790 Oran Earthquake
The 1790 Oran earthquake occurred on 10 October, striking near the coastal city of Oran in Algeria. The earthquake had an evaluated maximum seismic intensity of VIII–X on the European macroseismic scale (EMS-98). An estimated 3,000 people died during the earthquake and accompanying tsunami. The Seismic magnitude scales, magnitude of this earthquake has been disputed among members of the paleoseismology field, with estimates ranging from 7.5 to even as small as 5.5. Impact Beginning on 8 October, the Spanish conquest of Oran (1732), Spanish-conquered city was rocked by a earthquake swarm, series of strong earthquakes which were felt as far as Spain and Malta. The earthquakes were felt by residents in Granada, Cartagena, Spain, Cartagena, Málaga, and Santa Fe, Granada, Santa Fe. Violent shaking was felt at Oran until 25 October. Major damage occurred in Oran, with much of the historic city destroyed. Reports of damage also came from Carthage, Tunisia, and Spain across the Medite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between supporters of the French House of Bourbon, Bourbons and the Austrian House of Habsburg, Habsburgs. Charles had named as his heir Philip V of Spain, Philip of Anjou, a grandson of Louis XIV of France, whose claim was backed by Kingdom of France, France and most of Habsburg Spain, Spain. His Habsburg rival, Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Archduke Charles, was supported by the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance, whose primary members included Habsburg monarchy, Austria, the Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain. Significant related conflicts include the Great Northern War (1700–1721) and Queen Anne's War (1702–1713). Although by 1701 Spain was no longer the predominant European power, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mers El-Kebir
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a viral respiratory infection caused by ''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV). Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe depending on age and risk level. Typical symptoms include fever, cough, diarrhea, and shortness of breath. The disease is typically more severe in those with other health problems. The first case was identified in June 2012 by Egyptian physician Ali Mohamed Zaki at the Dr. Soliman Fakeeh Hospital in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, and most cases have occurred in the Arabian Peninsula. Over 2,600 cases have been reported as of January 2021, including 45 cases in the year 2020. About 35% of those who are diagnosed with the disease die from it. Larger outbreaks have occurred in South Korea in 2015 and in Saudi Arabia in 2018. MERS-CoV is a virus in the coronavirus family believed to be originally from bats. However, humans are typically infected from camels, either during direct con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartagena, Spain
Cartagena () is a Spanish city belonging to the Region of Murcia. As of January 2018, it has a population of 218,943 inhabitants. The city lies in a natural harbor of the Mediterranean coastline of the southeast of the Iberian Peninsula. Cartagena is the region's second-largest municipality. The wider urban or metropolitan area of Cartagena, known as Campo de Cartagena, has a population of 409,586 inhabitants. Cartagena has been inhabited for over two millennia, being founded around 227 BC by the Carthaginians, Carthaginian military leader Hasdrubal the Fair, Hasdrubal. The city reached its peak under the Hispania, Roman Empire, when it was known as , capital of the province of . Cartagena was temporarily held over by the Byzantine Empire in late antiquity, before being raided by Visigoths circa 620–625. The Islamic city rebuilt around the Concepción Hill, mentioned as , was noted by the 11th century as a great harbor. Unsubmissive to the terms of the Treaty of Alcaraz, Carta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castilla De Oro
Castilla de Oro or del Oro () was the name given by the Spaniards, Spanish settlers at the beginning of the 16th century to the Central American territories from the Gulf of Urabá, near today's Colombian-Panamanian Colombia–Panama border, border, to the Belén River. Beyond that river, the region was known as Veragua, and was disputed by the Spanish crown along with the Christopher Columbus, Columbus family. The name "Castilla de Oro" was made official in May 1513 by King Ferdinand II of Aragon, then regent of the Crown of Castile. After Vasco Núñez de Balboa's discovery of the Pacific Ocean, Castilla de Oro's jurisdiction was broadened to include the Pacific coasts of Panama, Costa Rica, and Nicaragua. With the creation, in 1527, of the Province of Nicaragua, which included today's Nicaragua as well as the Nicoya Peninsula, Castilla de Oro's jurisdiction was reduced. In 1537, once the conflict between the crown and the Columbus family was settled, Castilla de Oro was split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oran
Oran () is a major coastal city located in the northwest of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria, after the capital, Algiers, because of its population and commercial, industrial and cultural importance. It is west-southwest from Algiers. The total population of the city was 803,329 in 2008, while the metropolitan area has a population of approximately 1,500,000, making it the second-largest city in Algeria. Etymology The word ''Wahran'' comes from the Berber expression ''wa - iharan'' (place of lions). A locally popular legend tells that in the period around AD 900, there were sightings of Barbary lions in the area. The last two lions were killed on a mountain near Oran, and it became known as ''la montagne des lions'' ("The Mountain of Lions"). Two giant lion statues stand in front of Oran's city hall, symbolizing the city. History Overview During the Roman Empire, a small settlement called ''Unica Colonia'' existed in the area of the current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |