|
Space Pharmacology
Space pharmacology is the application of biomedical engineering that studies the use and dynamics of drugs or pharmaceuticals in space environments. Falling in the realm of space medicine, outer space drug delivery is the practical application of using Medical treatment during spaceflight, drugs to treat disorders that may arise due to space's extreme conditions, such as Micro-g environment, microgravity, radiation, and other physiological and psychological risks. The physical conditions and Astronautical hygiene, hazards posed by outer space conditions can result in Bioastronautics, space-related disorders to the human body, posing a necessity to manufacture, modify, and test drugs to work in outer space. History of space medicine and drug delivery Concerns about aviation drug delivery started as early as 1924 when orthostatic stress was found to be the reason for a pilot's inability to digest chocolate during a flight. In addition, studies on the effect of digitalis on altitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
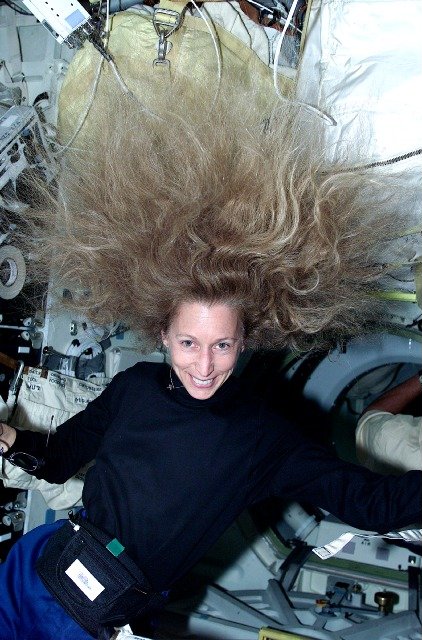
STS-31 MS Sullivan, MS McCandless, DSO 462 Medical Device On OV-103 Middeck
STS-31 was the 35th mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program and the tenth flight of the Space Shuttle Space Shuttle Discovery, ''Discovery''. The primary purpose of this mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) into low Earth orbit. ''Discovery'' lifted off from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39B, Launch Complex 39B on April 24, 1990, from Kennedy Space Center, Florida. Following the Challenger accident clarification was required on mission numbering. As STS-51-L was also designated STS-33, future flights with the previous STS-26 through STS-33 designators would require the R in their documentation to avoid conflicts in tracking data from one mission to another. ''Discovery''s crew deployed the Hubble Space Telescope on April 25, 1990, and then spent the rest of the mission tending to various scientific experiments in the Shuttle's payload bay as well as operating a set of IMAX cameras to record the mission. ''Discovery''s launch marked the first tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effect Of Spaceflight On The Human Body
The effects of spaceflight on the human body are complex and largely harmful over both short and long term. Significant adverse effects of long-term weightlessness include muscle atrophy and deterioration of the skeleton ( spaceflight osteopenia). Other significant effects include a slowing of cardiovascular system functions, decreased production of red blood cells (space anemia), balance disorders, eyesight disorders and changes in the immune system. Additional symptoms include fluid redistribution (causing the " moon-face" appearance typical in pictures of astronauts experiencing weightlessness), loss of body mass, nasal congestion, sleep disturbance, and excess flatulence. A 2024 assessment noted that "well-known problems include bone loss, heightened cancer risk, vision impairment, weakened immune systems, and mental health issues... t what’s going on at a molecular level hasn’t always been clear", arousing concerns especially vis a vis private and commercial space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degenerative Disease
Degenerative disease is the result of a continuous process based on degenerative cell changes, affecting tissues or organs, which will increasingly deteriorate over time. In neurodegenerative diseases, cells of the central nervous system stop working or die via neurodegeneration. An example of this is Alzheimer's disease. The other two common groups of degenerative diseases are those that affect circulatory system (e.g. coronary artery disease) and neoplastic diseases (e.g. cancers). Many degenerative diseases exist and some are related to aging. Normal bodily wear or lifestyle choices (such as exercise or eating habits) may worsen degenerative diseases, depending on the specific condition. Sometimes the main or partial cause behind such diseases is genetic. Thus some are clearly hereditary like Huntington's disease. Other causes include viruses, poisons or chemical exposures, while sometimes, the underlying cause remains unknown. Some degenerative diseases can be cured. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cell (biology), cells are malignant transformation, transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, Genetics, genetic, and Epigenetics, epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all Tissue (biology), tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and Organ (anatomy), organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and Epigenetics, epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
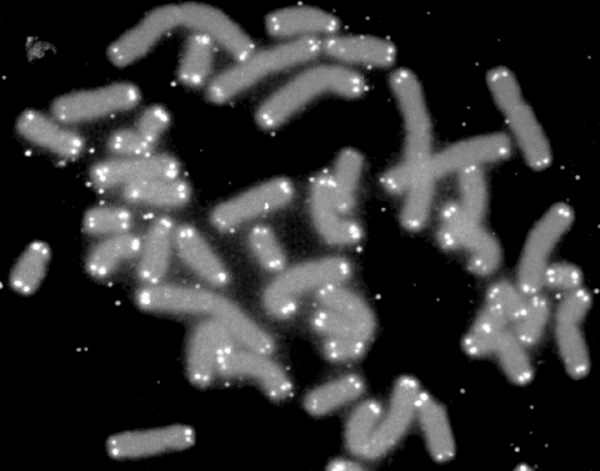
Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of DNA, chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery The existence of a special structure at the ends of chromosomes was independently proposed in 1938 by Hermann Joseph Muller, studying the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', and in 1939 by Barbara McClintock, working with maize. Muller observed that the ends of irradiated fruit fly chromosomes did not present alterations such as deletions or inversions. He hypothesized the presence of a protective cap, which he coined "telomeres", from the Greek ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen#Compounds, hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and biology. In biological systems, methylation is Catalysis, catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of Protein#Functions, protein function, and RNA processing. ''In vitro'' methylation of tissue samples is also a way to reduce some histology#Histological Artifacts, histological staining artifacts. The reverse of methylation is demethylation. In biology In biological systems, methylation is accomplished by enzymes. Methylation can modify heavy metals and can regulate gene expression, RNA processing, and protein function. It is a key pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-stranded Break
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in cells, by internal metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair processes fail, including apoptosis, irreparable DNA damage may occur, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |