|
Soyuz-TM
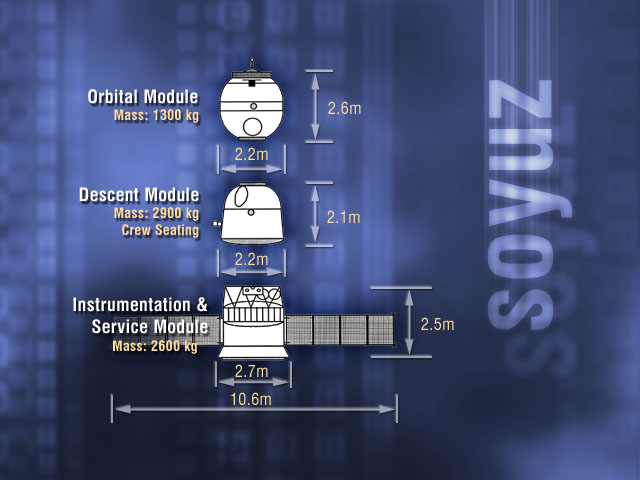
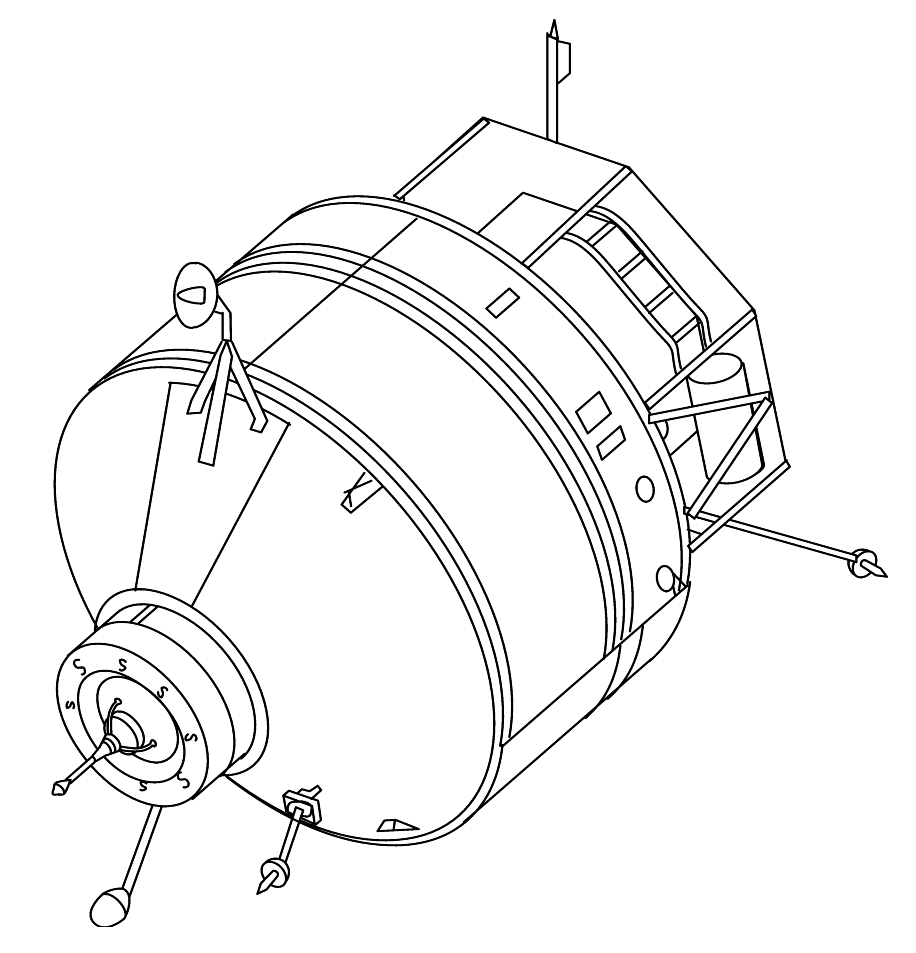
The Soyuz TM () were fourth generation (1986–2002) Soyuz spacecraft used for ferry flights to the Mir and International Space Station, ISS space stations. The Soyuz spacecraft consisted of four parts, the Orbital Module, the Descent Module and the Service Module. The first launch of the spacecraft was the uncrewed Soyuz TM-1 on May 21, 1986, where it docked with the Mir space station. The final flight was Soyuz TM-34, which docked with the International Space Station and landed November 10, 2002. Background After the Apollo–Soyuz, Apollo-Soyuz Test project in 1976, the Soyuz for crewed flights had the singular mission of supporting crewed space stations. The original Soyuz had a limited endurance when docked with a station, only about 60 to 90 days. There were two avenues for extending the duration of missions past this. The first avenue was to make upgrades to increase the Soyuz spacecraft's endurance. The Soyuz-T could last 120 days and the Soyuz-TM could last 180 d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched atop the similarly named Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Following the Soviet Union's dissolution, Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, continued to develop and utilize the Soyuz. Between the Space Shuttle's 2011 retirement and the SpaceX Crew Dragon's 2020 debut, Soyuz was the sole means of crewed transportation to and from the International Space Station, a role it continues to fulfill. The Soyuz design has also influenced other spacecraft, including China's Shenzhou and Russia's Progress cargo vehicle. The Soyuz is a single-use spacecraft composed of three main sections. The descent module is where cosmonauts are seated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz-TMA
The Soyuz-TMA () was a spacecraft built by Energia and used by Roscosmos for human spaceflight. It is a revision of the Soyuz spacecraft introduced in 2001 and was in use until 2012 after being superseded in 2010 by the Soyuz TMA-M. While it looks identical to the earlier Soyuz-TM on the outside, the spacecraft features several changes to accommodate requirements requested by NASA to better service the International Space Station. The most important difference are the anthropometric changes, primarily in the form of new adjustable crew couches that allowed shorter, taller, lighter and heavier passengers to ride in the spacecraft. The Soyuz also received improved parachute systems and a "glass cockpit," a first for an expendable vehicle. Design A Soyuz spacecraft consists of three parts (from front to back): * A spheroid orbital module * A small aerodynamic reentry module * A cylindrical service module with solar panels attached The first two portions are habitable livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KTDU-80
The KTDU-80 (Russian language, Russian: ) is the latest of a family of integrated propulsion system that KB KhIMMASH has implemented for the Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz since the Soyuz-T. It integrates main propulsion, Reaction control system, RCS and Spacecraft attitude control, attitude control in a single system Pressure-fed engine, pressure fed from a common dual string redundant pressurized propellant system. The common propellant is Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine, UDMH and Dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 and the main propulsion unit is the S5.80 main engine. It generates of thrust with a chamber pressure of and a nozzle expansion of 153.8 that enables it to achieve a specific impulse of . It is rated for 30 starts with a total firing time of 890 seconds. The integrated system without the pressurization or tanks weighs ; it is long with a diameter of . Description The KTDU-80 system integrates a dual string redundant propellant and pressurization system, a main propulsion system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-34
Soyuz TM-34 was the fourth Soyuz mission to the International Space Station (ISS). Soyuz TM-34 was launched by a Soyuz-U launch vehicle. Crew Docking with ISS *Docked to ISS: April 27, 2002, 07:55 UTC (to nadir port of Zarya) *Undocked from ISS: November 9, 2002, 20:44 UTC (from nadir port of Zarya) Mission highlights This was the 17th crewed mission to ISS. Soyuz TM-34 was a Russian Soyuz TM passenger transportation craft that was launched by a Soyuz-U rocket from Baikonur at 06:26 UT on 25 April 2002. It carried two cosmonauts and a South African tourist, Mark Shuttleworth, to the International Space Station (ISS). Shuttleworth performed some biology experiments, as he carried a live rat and sheep stem cells. All three returned on Soyuz TM-33 after an eight-day mission. Soyuz TM-34 was the final flight of the Soyuz-TM variant, due to its replacement by the upgraded Soyuz-TMA. It was also the last crewed vehicle to launch atop the Soyuz-U Soyuz-U ( GRAU index: 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-1
Soyuz TM-1 was an unmanned test flight of the Soyuz-TM spacecraft, intended for use in the Mir space station program. This was the maiden flight of the Soyuz-TM spacecraft, intended as the successor to the Soyuz-T spacecraft used in the Salyut program. It docked to Mir on 23 May 1986, and undocked on the 29th. It was the last uncrewed Soyuz Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Soviet Union, Union of Soviet Socialist Republi ... flight until Soyuz MS-14, in 2019. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz-7K-STM *Mass: 6450 kg *Crew: None *Launched: May 21, 1986 *Landed: May 30, 1986 References Further reading Mir Hardware Heritage - NASA report (PDF format)* Mir Hardware Heritage (wikisource) Soyuz uncrewed test flights Spacecraft launched in 1986 Spacecraft which reentered in 1986 {{USSR-spacec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energia (corporation)
S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation "Energia" () is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft and space station components. Its name is derived from the Russian word for energy and is also named for Sergei Korolev, Sergei Pavlovich Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau and the driving force behind early Soviet accomplishments in space exploration. Overview Energia is the largest company of the Russian space industry and one of its key players. It is responsible for all operations involving human spaceflight and is the lead developer of the Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz and Progress (spacecraft), Progress spacecraft, and the lead developer of the Russian end of the International Space Station (ISS). In the mid-2000s, the company employed 22,000–30,000 people. The enterprise has been awarded 4 Order of Lenin, Orders of Lenin, Order of the October Revolution and Russian Federation President's Message of Thanks. In addition, 14 cosmonauts employed by the company have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir EP-1
Mir EO-2 (also called Mir Principal Expedition 2) was the second long duration expedition to the Soviet space station Mir, and it lasted from February to December 1987. The mission was divided into two parts (sometimes called (a) and (b)), the division occurring when one of the two crew members, Aleksandr Laveykin, was replaced part way through the mission by Aleksandr Aleksandrov. Laveykin was replaced because ground-based doctors had diagnosed him with minor heart problems. Background The core module or Mir had been launched into orbit on 19 February 1986. It had been visited twice by the crew of Soyuz T-15, between March and July 1986, who transferred equipment from the previous Soviet space station Salyut 7. Prior to the arrival of EO-2, Mir was also visited by three Progress spacecraft, numbered 25, 26, and 27, as well as an uncrewed Soyuz-TM spacecraft, designated TM-1. From July 1986 to the arrival of EO-2 in February, Mir remained uncrewed. During this time an associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-2
Soyuz TM-2 was a crewed spaceflight to the Soviet space station Mir, which was uncrewed at the time. TM-2 was launched on February 5, 1987, and it was first crewed spaceflight of the Soyuz-TM spacecraft, and the second crewed spaceflight to Mir (the first being Soyuz T-15). The crew of the long duration expedition, Mir EO-2, who were launched by TM-2 consisted of Soviet cosmonauts Yuri Romanenko and Aleksandr Laveykin. The spacecraft remained docked to Mir, functioning as a lifeboat for the EO-2 crew, until July 1987 when it returned to Earth carrying Laveykin and the two man crew of Mir EP-1. Romanenko later returned to Earth in Soyuz TM-3 at the end of EO-2. Crew Mission parameters *Mass: 7100 kg *Perigee: 341 km *Apogee: 365 km *Inclination: 51.6° *Period: 91.6 minutes Mission highlights Early in the expedition EO-2, the module Kvant-1 Kvant-1 (; English: Quantum-I/1) (37KE) was the first module to be attached in 1987 to the Mir Core Module, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz-T
The Soyuz-T (, ''Union-T'') spacecraft was the third generation Soyuz spacecraft, in service for seven years from 1979 to 1986. The ''T'' stood for transport (, ). The revised spacecraft incorporated lessons learned from the Apollo Soyuz Test Project, Soyuz 7K-TM and Military Soyuz. The Soyuz-T was a major upgrade over previous Soyuz spacecraft, sporting solid-state electronics for the first time and a much more advanced onboard computer to help overcome the chronic docking problems that affected cosmonauts during space station missions. In addition, solar panels returned, allowing the Soyuz-T to fly up to 11 days independently as well as a redesigned propulsion system, the KTDU-426. Finally, it could carry three cosmonauts with pressure suits. Missions Between 1979 and 1986, a total of 18 Soyuz T spacecraft were launched into Low Earth Orbit, LEO, 13 of which carried cosmonauts to and from the space stations Salyut 6, Salyut 7, and Mir. References External links RSC Ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-3
Soyuz TM-3 was the third crewed spaceflight to visit the Soviet space station Mir, following Soyuz T-15 and Soyuz TM-2. It was launched in July 1987, during the long duration expedition Mir EO-2, and acted as a lifeboat for the second segment of that expedition. There were three people aboard the spacecraft at launch, including the two man crew of the week-long mission Mir EP-1, consisting of Soviet cosmonaut Aleksandr Viktorenko and Syrian Muhammed Faris. Faris was the first Syrian to travel to space, and as of June 2021, the only one. The third cosmonaut launched was Aleksandr Aleksandrov, who would replace one of the long duration crew members Aleksandr Laveykin of Mir EO-2. Laveykin had been diagnosed by ground-based doctors to have minor heart problems, so he returned to Earth with the EP-1 crew in Soyuz TM-2. Soyuz TM-3 landed near the end of December 1987, landing both members of the EO-2 crew, as well as potential Buran pilot Anatoli Levchenko, who had been lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federal Space Agency
The State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos (), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency,, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (). which was established on 25 February 1992 and restructured in 1999 and 2004 as the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (), established on 25 May 1999. and the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), (Роскосмос), ''Federalnoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo (Roskosmos)''. respectively. In 2015, the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) was merged with the United Rocket and Space Corporation, a government corporation, to re-nationalize the space industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |