|
Soymovirus
''Soymovirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Caulimoviridae'' order ''Ortervirales ''Ortervirales'' is an order that contains all accepted species of single-stranded RNA viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate (Group VI) and all accepted species of double-stranded DNA viruses (except ''Hepadnaviridae'') that replicat ...''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: *'' Blueberry red ringspot virus'' *'' Cestrum yellow leaf curling virus'' *'' Peanut chlorotic streak virus'' *'' Soybean chlorotic mottle virus'' Structure Viruses in ''Soymovirus'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral geometries, and T=7 symmetry. The diameter is around 50 nm. Genomes are circular. The genome codes for 8 proteins. Life cycle Viral replication is nuclear/cytoplasmic. Replication follows the dsDNA(RT) replication model. The method of transcription is dsDNA(RT) transcription. The virus exits the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caulimoviridae
''Caulimoviridae'' is a family of viruses infecting plants. There are 94 species in this family, assigned to 11 genera. Viruses belonging to the family ''Caulimoviridae'' are termed double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) reverse-transcribing viruses (or pararetroviruses) i.e. viruses that contain a reverse transcription stage in their replication cycle. This family contains all plant viruses with a dsDNA genome that have a reverse transcribing phase in their lifecycle. Taxonomy The following genera are recognized: *'' Badnavirus'' *'' Caulimovirus'' *'' Cavemovirus'' *'' Dioscovirus'' *''Petuvirus'' *'' Rosadnavirus'' *'' Ruflodivirus'' *''Solendovirus'' *''Soymovirus'' *'' Tungrovirus'' *'' Vaccinivirus'' Virus particle structure All viruses of this family are non-enveloped. Virus particles are either bacilliform or isometric. The type of nucleocapsid incorporated into the virus structure determines the size of the viral particles. Bacilliform particles are approximately 35–50 nm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ... of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ortervirales
''Ortervirales'' is an order that contains all accepted species of single-stranded RNA viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate (Group VI) and all accepted species of double-stranded DNA viruses (except ''Hepadnaviridae'') that replicate through an RNA intermediate (Group VII). The name is derived from the reverse of retro. All reverse-transcribing viruses possess significant similarities to each other. Their reverse transcriptase proteins share a common origin. Moreover, belpaoviruses, metaviruses, pseudoviruses, and retroviruses have other features in common. Their polymerase proteins are similar in structure and include aspartic protease (retroviral aspartyl protease) and an integrase belonging to the DDE recombinase superfamily (see Recombination-activating gene tructure. They also share similar capsid and nucleocapsid proteins/domains. Caulimoviruses also share some features with belpaoviruses, metaviruses, pseudoviruses, and retroviruses such as a homologous as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
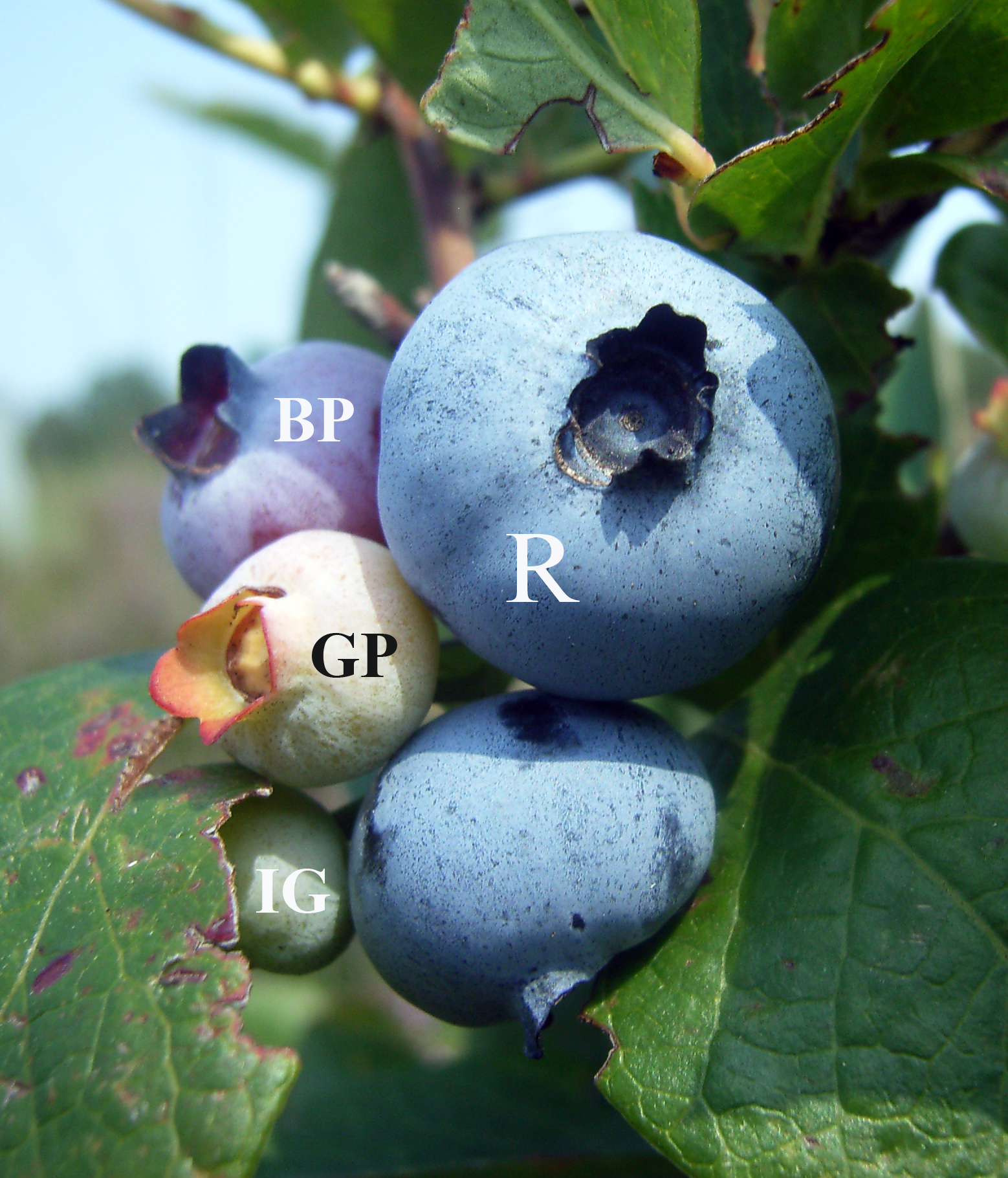
Blueberry Red Ringspot Virus
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus '' Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world supply of highbush blueberries. Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cestrum Yellow Leaf Curling Virus
''Cestrum'' is a genus of — depending on authority — 150-250 species of flowering plants in the family Solanaceae. They are native to warm temperate to tropical regions of the Americas, from the southernmost United States (Florida, Texas: day-blooming cestrum, '' C. diurnum'') south to the Bío-Bío Region in central Chile ( green cestrum, ''C. parqui''). They are colloquially known as cestrums or jessamines (from "jasmine", due to their fragrant flowers). They are shrubs growing to tall. Most are evergreen; a few are deciduous. All parts of the plants are toxic, causing severe gastroenteritis if eaten. Uses and ecology Several species are grown as ornamental plants for their strongly scented flowers. Numerous cultivars have been produced for garden use, of which ‘Newellii’ has gained the Royal Horticultural Society’s Award of Garden Merit. (confirmed 2017). Some are invasive species. Especially notorious is green cestrum (''C. parqui'') in Australia, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peanut Chlorotic Streak Virus
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small and large commercial producers. It is classified as both a grain legume and, due to its high oil content, an oil crop. World annual production of shelled peanuts was 44 million tonnes in 2016, led by China with 38% of the world total. Atypically among legume crop plants, peanut pods develop underground ( geocarpy) rather than above ground. With this characteristic in mind, the botanist Carl Linnaeus gave peanuts the specific epithet ''hypogaea'', which means "under the earth." The peanut belongs to the botanical family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), commonly known as the legume, bean, or pea family. Like most other legumes, peanuts harbor symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria in root nodules. The capacity to fix nitrogen means peanuts require les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybean Chlorotic Mottle Virus
''Soybean chlorotic mottle virus'' (SbCMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family '' Caulimoviridae'', genus ''Soymovirus''. See also * List of soybean diseases References External linksICTVdB – The Universal Virus Database: Soybean chlorotic mottle virus Caulimoviridae Viral plant pathogens and diseases Soybean diseases {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |