|
Soviet 8th Guards Army
The 8th Guards Order of Lenin Combined Arms Army (abbreviated 8th GCAA) was an army of the Soviet Army, as a successor to the 62nd Army of the Soviet Union's Red Army, which was formed during World War II and was disbanded in 1998 after being downsized into a corps. The Soviet 8th Guards Army was formed from the 62nd Army in May 1943 and received Guards status in recognition of its actions in the Battle of Stalingrad. It went on to defend the right bank of the Donets and fight in the Donbass Strategic Offensive in August and September. It then fought in the Lower Dnepr Offensive, where it captured Zaporizhia. During winter and spring 1944 the army fought in the Dnieper–Carpathian Offensive. After the capture of Odessa, the army was transferred to the Kovel area and fought in the Lublin–Brest Offensive during the summer, capturing Lublin, crossing the Vistula and seizing the Magnuszew bridgehead. The army defended the bridgehead until January 1945, when it helped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combined Arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare that seeks to integrate different combat arms of a military to achieve mutually complementary effects—for example, using infantry and armoured warfare, armour in an Urban warfare, urban environment in which each supports the other. According to the strategist William S. Lind, combined arms can be distinguished from the concept of "supporting arms" as follows: Combined arms hits the enemy with two or more arms simultaneously in such a manner that the actions he must take to defend himself from one make him more vulnerable to another. In contrast, supporting arms is hitting the enemy with two or more arms in sequence, or if simultaneously, then in such combination that the actions the enemy must take to defend himself from one also defends himself from the other(s). Though the lower-military rank, echelon units of a combined arms team may be of similar types, a balanced mixture of such units are combined into an effective higher-echelon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Dnepr Strategic Offensive Operation
The Battle of the Dnieper was a military campaign that took place in 1943 on the Eastern Front of World War II. Being one of the largest operations of the war, it involved almost four million troops at one point and stretched over a front. Over four months, the eastern bank of the Dnieper was recovered from German forces by five of the Red Army's fronts, which conducted several assault river crossings to establish several lodgements on the western bank. Kiev was later liberated in the Second Battle of Kiev. 2,438 Red Army soldiers were awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union for their involvement. Strategic situation Following the Battle of Kursk, the Wehrmachts ''Heer'' and supporting ''Luftwaffe'' forces in the southern Soviet Union were on the defensive in southern Ukraine. By mid-August, Adolf Hitler understood that the forthcoming Soviet offensive could not be contained on the open steppe and ordered construction of a series of fortifications along the line of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nohra
Nohra () is a village and a former municipality in the Weimarer Land district of Thuringia, Germany. On 1 December 2007, the municipality of Utzberg was incorporated into Nohra. Nohra later became part of Grammetal municipality in December 2019. Nohra was the location of the first Nazi concentration camp, established on March 3, 1933. Prisoners were incarcerated in a school building. The former Luftwaffe airbase at Nohra was used by the Soviet Army for helicopter operations from 1945 until their withdrawal in 1992. The airfield had a short runway, a hangar and a radio beacon. Subsequently, the department for regional development largely demolished the complex, but a few elements were preserved because of their historic value, including a large stone statue of Lenin Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kostrzyn Nad Odrą
Kostrzyn nad Odrą (translated literally as Kostrzyn upon the Oder; ; ) is a town in Gorzów County, Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland, on the border with Germany. Geography The town is situated within the historic Lubusz Land (''Ziemia Lubuska'') region at the confluence of the Oder and Warta rivers, on the western rim of the extended Warta mires. The town centre is located about south of Szczecin. Until the end of World War II and the implementation of the Oder–Neisse line in 1945, the municipal area also comprised the Küstrin-Kietz suburb on the west bank of the Oder river, which today is part of the German Küstriner Vorland municipality. The former town centre, the Kostrzyn fortress located on the headland between the Oder and Warta rivers, was destroyed by the Red Army as an act of revenge weeks before the end of WW2 and not rebuilt. Today Kostrzyn's central area is located around Kostrzyn railway station east of the Warta's mouth. History Middle Ages Settled since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
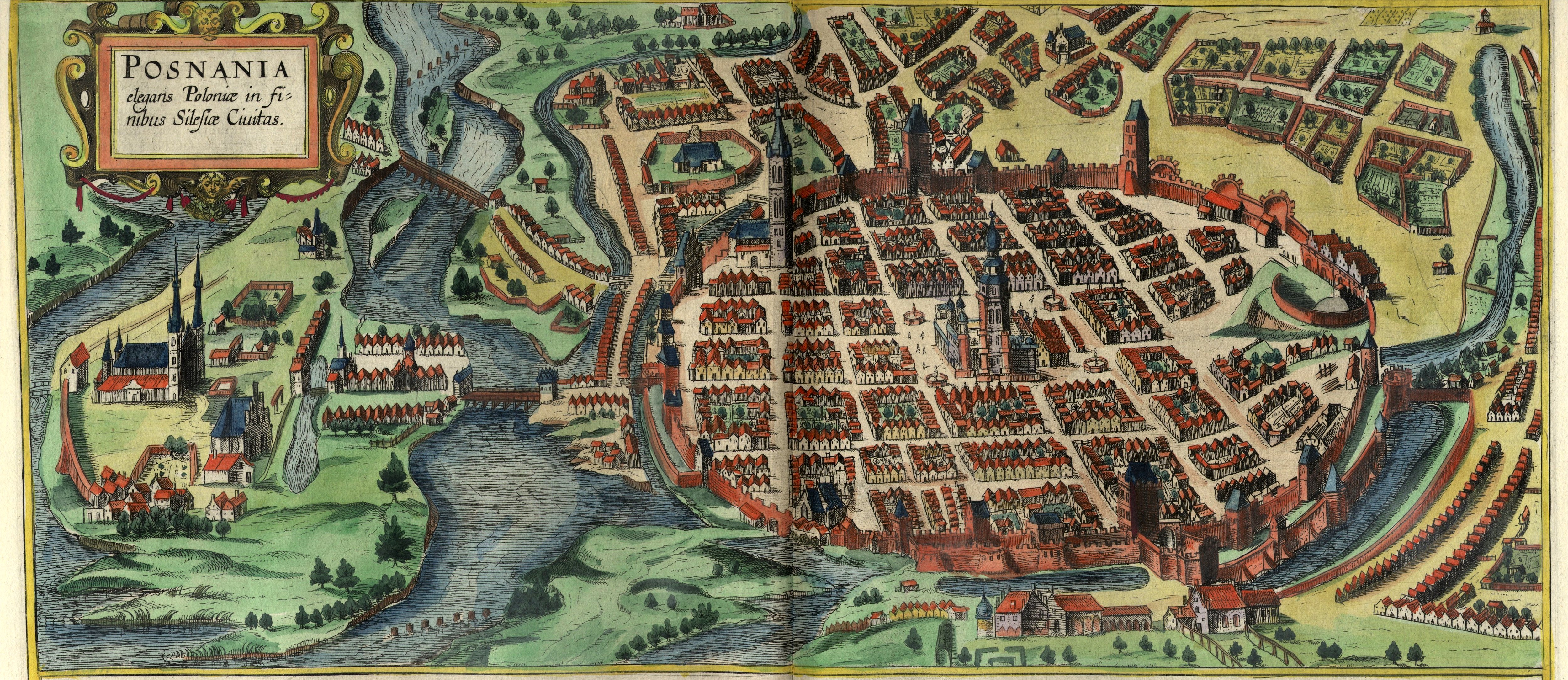
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Łódź
Łódź is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located south-west of Warsaw. Łódź has a population of 655,279, making it the country's List of cities and towns in Poland, fourth largest city. Łódź first appears in records in the 14th century. It was granted city rights, town rights in 1423 by the Polish King Władysław II Jagiełło and it remained a private town of the Kuyavian bishops and clergy until the late 18th century. In the Second Partition of Poland in 1793, Łódź was annexed to Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia before becoming part of the Napoleonic Duchy of Warsaw; the city joined Congress Poland, a Russian Empire, Russian client state, at the 1815 Congress of Vienna. The Second Industrial Revolution (from 1850) brought rapid growth in textile manufacturing and in population owing to the inflow of migrants, a sizable part of which were Jews and Germans. Ever since the industrialization of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnuszew
Magnuszew is a town in Kozienice County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Magnuszew. It located near the Vistula river and lies approximately north-west of Kozienice and south-east of Warsaw. In 2012 it had a population of 800 (2012). It was the site of a major battle in August 1944 during World War II, when the Soviet army established a strategic bridgehead in its vicinity, on the west bank of the Vistula. History The oldest settlement dates from the 12th century when the village, then called Magnussewo, was founded by one of the early Dukes of Masovia. In 1377, when the village was owned by Świętosław, it received Magdeburg town rights from Duke Siemowit IV. In 1576, as a result of war damage and fires that destroyed numerous wooden buildings, Magnuszew was demoted to the rank of a village. Later owners of Magnuszew were the Potocki family and - particularly powerful - the Zamoyski family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland. The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in the south of Poland, above sea level in the Silesian Beskids (western part of Carpathian Mountains), where it begins with the White Little Vistula (''Biała Wisełka'') and the Black Little Vistula (''Czarna Wisełka''). It flows through Poland's largest cities, including Kraków, Sandomierz, Warsaw, Płock, Włocławek, Toruń, Bydgoszcz, Świecie, Grudziądz, Tczew and Gdańsk. It empties into the Vistula Lagoon (''Zalew Wiślany'') or directly into the Gdańsk Bay of the Baltic Sea with a river delta, delta of six main branches (Leniwka, Przekop, Śmiała Wisła, Martwa Wisła, Nogat and Szkarpawa). The river has many associations with culture of Poland, Polish culture, history and national identity. It is Poland's most important wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lublin
Lublin is List of cities and towns in Poland, the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the centre of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of the Vistula River, located southeast of Warsaw. One of the events that greatly contributed to the city's development was the Union of Krewo, Polish–Lithuanian Union of Krewo in 1385. Lublin thrived as a centre of trade and commerce due to its strategic location on the route between Vilnius and Kraków; the inhabitants had the privilege of free trade in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The Lublin Sejm, Parliament session of 1569 led to the creation of a Union of Lublin, real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, thus creating the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Lublin witnessed the early stages of the Reformation in the 16th century. A Calvinist congregation wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kovel
Kovel (, ; ; ) is a city in Volyn Oblast, northwestern Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Kovel Raion within the oblast. Population: Kovel gives its name to one of the oldest runic inscriptions which were lost during World War II. The Kovel spearhead, unearthed near the town in 1858, contained text in Gothic. History The name Kovel comes from a Slavonic word for blacksmith hence the horseshoe on the town's coat of arms. The rune-inscribed Spearhead of Kovel was found near Kovel in 1858. It dates to the early 3rd century, when Gothic tribes lived in the area. Kovel (Kowel) was first mentioned in 1310. It received its town charter from the Polish King Sigismund I the Old in 1518. In 1547 the owner of Kowel became Bona Sforza, Polish queen. Since 1564 the starost of Kowel was Andrei Kurbski (d. 1584). From 1566 to 1795 it was part of the Volhynian Voivodeship. Kowel was a royal city of Poland. In 1792 the 3rd Polish Vanguard Regiment was garrisoned in Kowel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |