|
Southwest Temple
The Southwest Temple is the modern name for a tetrastyle prostyle Doric temple located in the southwest part of the Ancient Agora of Athens. Fragments from the temple found throughout the Agora enable a full, if tentative, reconstruction of the temple's appearance. These fragments originally belonged to several Hellenistic structures and a fifth-century BC stoa at Thorikos in southeastern Attica, but they were spoliated to build the temple in the Agora in the age of Augustus. It is unknown which god or hero the temple was dedicated to. It was spoliated to build the post-Herulian fortification wall after the Herulian sack of Athens in 267 AD. Description The temple is located in the southwestern part of the Athenian Agora, to the west of the Odeon of Agrippa. To the south is a small stoa linked to the Civic Offices and then the Middle Stoa, with all of which it is aligned. It faces west, towards the Tholos. Foundations The foundations consisted of conglomerate blocks on top of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plan Agora Of Athens Roman Colored
A plan is typically any diagram or list of steps with details of timing and resources, used to achieve an Goal, objective to do something. It is commonly understood as a modal logic, temporal set (mathematics), set of intended actions through which one expects to achieve a goal. For space, spatial or Plane (geometry), planar topology, topologic or topography, topographic sets see map. Plans can be formal or informal: * Structured and formal plans, used by multiple people, are more likely to occur in projects, diplomacy, careers, economic development, military campaigns, combat, sports, games, or in the conduct of other business. In most cases, the absence of a well-laid plan can have adverse effects: for example, a non-robust project plan can cost the organization time and money. * Informal or ad hoc plans are created by individuals in all of their pursuits. The most popular ways to describe plans are by their breadth, time frame, and specificity; however, these planning clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
In Classical architecture, a or naos () is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings: of a hermit's or monk's cell, and (since the 17th century) of a biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek and Roman temples, the ''cella'' was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the ''cella'' might contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings, such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the ''cella'', as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and temporary altars for other deities were built next to it. The accumulated offerings made Greek and Roman temples virtual treasuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Stoa, Thorikos
Double, The Double or Dubble may refer to: Mathematics and computing * Multiplication by 2 * Double precision, a floating-point representation of numbers that is typically 64 bits in length * A double number of the form x+yj, where j^2=+1 * A 2-tuple, or ordered list of two elements, commonly called an ordered pair, denoted (a,b) * Double (manifold), in topology Food and drink * A drink order of two shots of hard liquor in one glass * A "double decker", a hamburger with two patties in a single bun Games * Double, action in games whereby a competitor raises the stakes ** , in contract bridge ** Doubling cube, in backgammon ** Double, doubling a blackjack bet in a favorable situation ** Double, a bet offered by UK bookmakers which combines two selections * Double, villain in the video game ''Mega Man X4'' * A kart racing game '' Mario Kart: Double Dash'' * An arcade action game ''Double Dragon'' Sports * Double (association football), the act of a winning a division and primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mason's Mark
A mason's mark is an engraved symbol often found on dressed Rock (geology), stone in buildings and other public structures. In stonemasonry Regulations issued in Scotland in 1598 by James VI and I, James VI's Master of Works, William Schaw, stated that on admission to the guild, every Masonry, mason had to enter his name and his mark in a register. There are three types of marks used by Stonemasonry, stonemasons. *Banker marks were made on stones before they were sent to be used by the walling masons. These marks served to identify the banker mason who had prepared the stones for their paymaster. This system was employed only when the stone was paid for by measure, rather than by time worked. For example, the 1306 contract between Richard of Stow, mason, and the Dean and Chapter of Lincoln Cathedral, specified that the plain walling would be paid for by measure, and indeed banker marks are found on the blocks of walling in this cathedral. Conversely, the masons responsible for wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anta (architecture)
An anta (pl. antæ, antae, or antas; Latin, possibly from ''ante'', "before" or "in front of"), or sometimes parastas (pl. parastades), is a term in classical architecture describing the posts or pillars on either side of a doorway or entrance of a Greek temple – the slightly projecting piers which terminate the side walls (of the naos). Antae are formed either by thickening the walls or by attaching a separate strip and can serve to reinforce brick walls, as in the Heraeum of Olympia (c. 600 BCE). Antae differ from the pilaster, which is purely decorative, and does not have the structural support function of the anta. Anta In contrast to columns or pillars, antae are directly connected with the walls of a temple. They owe their origin to the vertical posts of timber employed in the early, more primitive palaces or temples of Greece, as at Tiryns and in the Temple of Hera at Olympia. They were used as load-bearing structures to carry the roof timbers, as no reliance cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metope
A metope (; ) is a rectangular architectural element of the Doric order, filling the space between triglyphs in a frieze , a decorative band above an architrave. In earlier wooden buildings the spaces between triglyphs were first open, and later the free spaces in between triglyphs were closed with metopes; however, metopes are not load-bearing part of a building. Earlier metopes are plain, but later metopes were painted or ornamented with reliefs. The painting on most metopes has been lost, but sufficient traces remain to allow a close idea of their original appearance. In terms of structure, metopes were made out of clay or stone. A stone metope may be carved from a single block with a triglyph (or triglyphs), or they may be cut separately and slide into slots in the triglyph blocks as at the Temple of Aphaea. Sometimes the metopes and friezes were cut from different stone, so as to provide color contrast. Although they tend to be close to square in shape, some metopes ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
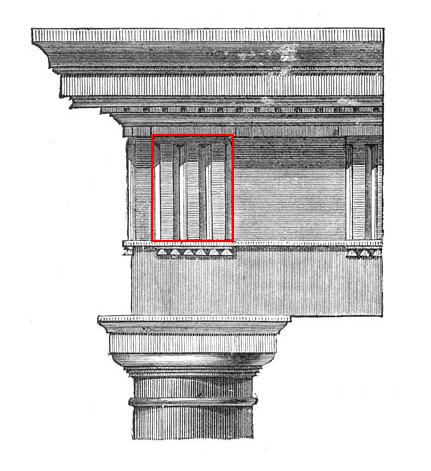
Triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (Layered intrusion, layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. The extraction of marble is performed by quarrying. Marble production is dominated by four countries: China, Italy, India and Spain, which account for almost half of world production of marble and decorative stone. Because of its high hardness and strong wear resistance, and because it will not be deformed by temperature, marble is often used in Marble sculpture, sculpture and construction. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeast Temple
The Southeast Temple is the modern name for an Ionic order, Ionic octastyle prostyle temple located in the southeast corner of the Ancient Agora of Athens. Architectural fragments from the temple enable a full, if tentative, reconstruction of its appearance.These fragments originally belonged to the Temple of Athena, Sounion, Temple of Athena at Sounion at the southern tip of Attica, but they were spoliated to build the temple in the Agora in the first half of the second century AD. It was thus the last of several "itinerant temples," relocated from the Attic countryside to the Athenian Agora in the Imperial period. It is unknown which god or hero it was dedicated to. It was heavily damaged during the Herulian Sack of Athens in 267 AD and then spoliated to build the post-Herulian fortification wall. Description The temple is located in the southeastern corner of the Athenian Agora, at the foot of the Acropolis' north slope, on the west side of the Panathenaic Way, just past the Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sounion
Cape Sounion (Modern Greek: Aκρωτήριο Σούνιο ''Akrotírio Soúnio'' ; ''Άkron Soúnion'', latinized ''Sunium''; Venetian: ''Capo Colonne'' "Cape of Columns") is the promontory at the southernmost tip of the Attica peninsula, south of the town of Lavrio (ancient Thoricus), and 69.5 km (43.1 miles) southeast of Athens in the Athens Riviera. It is part of Lavreotiki municipality, East Attica, Greece. Cape Sounion is noted for its Temple of Poseidon, one of the major monuments of the Golden Age of Athens. Its remains are perched on the headland, surrounded on three sides by the Aegean sea. Climate Cape Sounio has a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification: ''BSh''). Cape Sounio experiences hot, dry summers and mild, wetter winters. History The earliest literary reference to Sounion is in Homer's ''Odyssey'' (III. 278–285). The story recounts that as the various Greek commanders sailed back from Troy, the helmsman of the ship of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Athena, Sounion
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in English, while those of other religions are not, even though they fulfill very similar functions. The religions for which the terms are used include the great majority of ancient religions that are now extinct, such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. Among religions still active: Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir or Kovil), Buddhism (whose temples are called Vihar), Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baháʼí Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baháʼí House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are often called Jinja), Confucian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |