|
Southern Eastern Rift
The Southern Eastern Rift is a freshwater ecoregion in Kenya and Tanzania. It occupies the southern end of the Gregory Rift, Eastern Rift Valley, or Gregory Rift, and includes a number of closed or endorheic basins which drain into central lakes with no outlet to the sea. The Southern Eastern Rift extends 700 km, from central Kenya to Central Tanzania. The Eastern Rift Valley is 50 to 100 km wide for most of its length, but widens out at its southern end. The lake basins are, from north to south, Lake Baringo, Lake Bogoria, Lake Nakuru, Lake Naivasha, Lake Elementaita, and Lake Magadi in Kenya, and Lake Natron, Lake Manyara, Lake Burungi, Lake Eyasi, Lake Kitangiri, Lake Balangida, Lake Singida, and Lake Sulunga in Tanzania."Southern Eastern Rift" "Freshwater Ecoregions of the World". Accessed 19 September 2019/ref> In the Kenyan portion of the Southern Eastern Rift, Northern Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets occupies the rift valley floor, with East African mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Ecoregions are also known as "ecozones" ("ecological zones"), although that term may also refer to biogeographic realms. Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic frame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Singida
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions of oceans or large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Hanang
Mount Hanang is a mountain in northern Tanzania. The peak has an elevation of 3,420 m above sea level. Hanang is located in Manyara Region's Hanang District. It is (after Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Meru and Mount Loolmalasin) the fourth-highest mountain in Tanzania, if the three peaks of Kilimanjaro are counted as one mountain. The principal path to the summit starts in the town of Katesh. The climb can be done in one day (10 hours), but it is also common for climbers to spend one night in a tented camp on the mountain and reach the summit on the second day. Hanang Forest Reserve Mount Hanang Nature Forest Reserve has an area of 58.66 km², protecting an enclave of evergreen montane forest on the mountain's higher slopes. Between 2000 and 2700 meters elevation, evergreen montane forests cover the mountain's wetter eastern and southern slopes, while the drier western and northern slopes are home to dry montane evergreen forests with bushland and grassland on the ridges. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mbulu Highlands
The Mbulu Highlands is a plateau in north-central Tanzania. Geography The Mbulu Highlands lie between the basins of Lake Eyasi to the west and Lake Manyara to the east. The plateau ranges from 1500 to 2300 meters in elevation. The highlands extend northeast-southwest. A steep northeast-southwest-running escarpment bounds the highlands on the east, overlooking the basins of Lake Manyara, and further south, Lake Balangida. The plateau descends less steeply in a series of ridges and valleys to Lake Eyasi to the west and the Yaeda Valley to the southwest. To the north lies the volcanic Ngorongoro Highlands. The volcanic peak of Mount Hanang rises south of Lake Balangida. The highlands lie mostly in Mbulu District of Manyara Region, extending northwards into Karatu District of Arusha Region. The principal town on the plateau is Mbulu. Tanzania's B141 highway crosses the highlands, running through Mbulu on its way from Madukani east of the highlands to Singida in the southwest. Clima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wembere River
The Wembere River is a river located in north western Singida Region, Tanzania. The river is part of the water basin of Lake Eyasi. The Wembere River originates in hilly country in central Tanzania at 6.0º south, and flows northwards through a branch of the Eastern Rift Valley. Its tributary the Nyahua River forms a seasonal floodplain 60 miles long and 1-5 km wide, covering 11,000 ha. After the Nyahua joins the Wembere from the northwest, the Wembere widens into a larger floodplain 105 km long and up to 20 km wide, and covering 140,000 ha. (4º12'-5º01' S/33º47'-34º11' E). Other tributaries are the Wamba, which joins from the northeast, the Mwaru, which joins from the east, and the Mapiringa, which joins from the west. The floodplain consists of flooded grasslands, inundated during the wet season and laced with drainage channels. Stands of the trees '' Vachellia seyal'' and '' Vachellia drepanolobium'' edge the seasonally-flooded portion of the plain. Above the floodplain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Zambezian Miombo Woodlands
The Central Zambezian miombo woodlands ecoregion spans southern central Africa. Miombo woodland is the predominant plant community. It is one of the largest ecoregions on the continent, and home to a great variety of wildlife, including many large mammals. Location and description The region covers a large area stretching northeast from Angola, including the southeast section of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the northern half of Zambia, a large section of western Tanzania, southern Burundi, and northern and western Malawi. In the Congo the ecoregion is almost conterminous with Katanga Province. In Zambia it covers the northern half of the country above Lusaka, including the eastern and western "ears" and the Copperbelt. In Tanzania it covers the western inland provinces between Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika and Lake Malawi. The area is mostly flat plateau, and the soils are poor. There is a tropical climate with a long dry season, up to seven months, which leaves the fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarangire River
— River mouth The Tarangire River is a perennial river located in central Manyara Region in the eastern branch of the East African Rift Valley, within northern Tanzania. Course The headwaters of the Tarangire River are in the highlands and escarpments of Babati District of the Manyara Region and Kondoa District of the Dodoma Region, primarily the Irangi Hills and Irangi Escarpment in Kondoa District. The river rises in the Wasi Highlands, falls down the eastern Kondoa Escarpment. It flows east to Chubi where it then turns north to flow through Tarangire National Park. It then turns west and then south, before terminating at its river mouth on Lake Burunge. Ecology Much of the Tarangire River headwaters in the Irangi Hills headwaters area is forested with Miombo woodland habitat trees and lower plants, that are designated for protection within the Salanka, Bereko, and Isabe Forest Reserves. Deforestation for agriculture and degradation of forests in the Irangi Hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Acacia–Commiphora Bushlands And Thickets
The Southern ''Acacia''–''Commiphora'' bushlands and thickets is a tropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in Tanzania and Kenya. It includes portions of Serengeti National Park and Ngorongoro Conservation Area, which are designated World Heritage Sites and biosphere reserves for their outstanding wildlife and landscapes. It is one of three Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets ecoregions in eastern Africa. Geography The Southern ''Acacia''–''Commiphora'' bushlands and thickets consist of two continuous blocks. The southern block lies west of the Eastern Arc Mountains in Tanzania, in the drier rain shadow of the mountains. It extends northeast-southwest, from the southern slope of Mount Kilimanjaro to the Usangu Plain at the edge of the Southern Highlands. Tarangire and Ruaha national parks are in the southern block. A belt of miombo woodland, Serengeti volcanic grasslands, and East African montane forests separate the northern and southern blocks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Kilimanjaro
Mount Kilimanjaro () is a dormant volcano in Tanzania. It is the highest mountain in Africa and the highest free-standing mountain above sea level in the world, at above sea level and above its plateau base. It is also the highest volcano in the Eastern Hemisphere and the fourth most topographically prominent peak on Earth. Kilimanjaro's southern and eastern slopes served as the home of the Chagga Kingdoms until their abolition in 1963 by Julius Nyerere. The origin and meaning of the name Kilimanjaro is unknown, but may mean "mountain of greatness" or "unclimbable". Although described in classical sources, German missionary Johannes Rebmann is credited as the first European to report the mountain's existence, in 1848. After several European attempts, Hans Meyer reached Kilimanjaro's highest summit in 1889. The mountain was incorporated into Kilimanjaro National Park in 1973. As one of the Seven Summits, Kilimanjaro is a major hiking and climbing destination. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Meru, Tanzania
__NOTOC__ Mount Meru is a dormant stratovolcano located west of Kilimanjaro in southeast Arusha Region, Tanzania. At a height of , it is visible from Mount Kilimanjaro on a clear day, and is the fifth-highest of the highest mountain peaks of Africa, dependent on definition. Mount Meru is located just north of the city of Arusha, in the Arusha Region of Tanzania. It is the second-highest mountain in Tanzania, after Mount Kilimanjaro, and the highest mountain in Arusha Region. The Momella route – which starts at Momella gate, on the eastern side of the mountain – is the most common route for climbers to reach the peak. Mount Meru's lavas are alkaline in character and include nephelinite. Much of the mountain's height was lost about 7,800 years ago due to a summit collapse. Mount Meru most recently had a minor eruption in 1910. The several small cones and craters seen in the vicinity probably reflect numerous episodes of volcanic activity. Mount Meru's caldera is wide. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
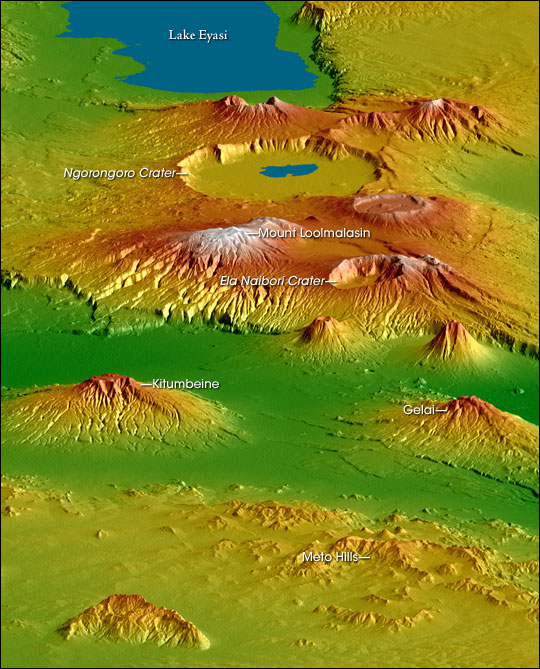
Ngorongoro Highlands
The Crater Highlands or Ngorongoro Volcanic Highlands (''Milima kasoko ya Ngorongoro '', in Swahili) are a geological region along the East African Rift in the Arusha Region and parts of northern Manyara Region in north Tanzania. The Crater Highlands are made up of several large volcanic complexes, including the 2.4-2.2 Ma Lemagarut and 2.25-2.0 Ma Ngorongoro basalt-trachybasalt- trachyandesite volcanoes (Ngorongoro also contains trachydacite) and the 1.6-1.5 Ma Oldeani basalt-trachyandesite volcano.Zaitsev, A., Marks, M., Wenzel, T., Spratt, J., Sharygin, V., Strekopytov, S., & Markl, G. (2012). Mineralogy, geochemistry and petrology of the phonolitic to nephelinitic Sadiman volcano, Crater Highlands, Tanzania. Lithos, 152, 66-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2012.03.001 Geology The highlands are located in a spreading zone at the intersection of branches of two tectonic plates, the African Plate and Somali Plate, resulting in distinctive and prominent landforms. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serengeti Volcanic Grasslands
The Serengeti volcanic grasslands is a tropical grassland ecoregion of Tanzania. The Serengeti volcanic grasslands are distinctive grasslands growing on deposits of volcanic ash in northern Tanzania. It includes the eastern portion of Serengeti National Park and areas south and east of the Ngorongoro Highlands. Topography The Serengeti volcanic grasslands are an edaphic plant community that grows on soils derived from volcanic ash. The eruption of the now-extinct Kerimasi volcano 150,000 years ago deposited huge amounts of fine whitish-grey ash. More recent eruptions of the Ol Doinyo Lengai volcano deepened the ash deposits. These ash deposits hardened with time, creating layers of calcareous tuff and calcitic hard-pan soil. The flat or slightly undulating plains are interrupted here and there by rocky kopjes, outcrops of the underlying Precambrian rocks. The terrain lies at a mean altitude of , rising to a maximum of . Climate The climate of the ecoregion is '' Oceanic cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |