|
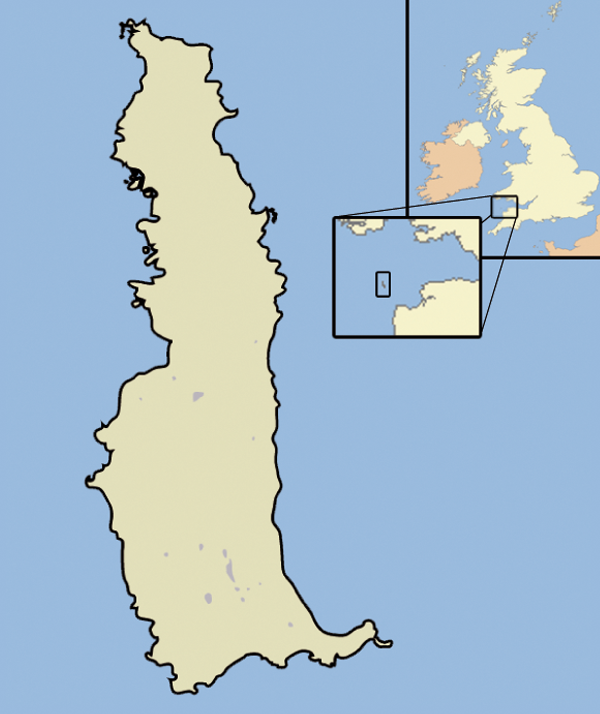
South West Deeps (East) MPA
South-West Deeps (East), along with the adjoining the South-West Deeps (West), is an offshore Marine Conservation Zone (MCZ), approximately 190 km off Land's End, Cornwall. It was designated on 31 May 2019 by the Marine and Coastal Access Act 2009 and is a predominantly sandy area of the continental shelf, supporting molluscs and crustaceans living on and in mixed and coarse sediments. Geography South-West Deeps (East) covers an area of in the Western Channel and Celtic Sea, and has a maximum depth of . The eastern boundary is off the Land's End peninsula. Subtidal sand with areas of subtidal coarse sediment dominate the seabed and there is an area of deep-sea bed in the south. A geological feature is the Celtic Sea Relict Sandbanks, which are among the largest and deepest shelf sand ridges in UK waters and is one of two MPAs to protect deep-sea bed habitats outside of Scotland. The MCZ protects various species including clams, cockles, burrowing marine worms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Conservation Zone
A Marine Conservation Zone (MCZ) is a type of marine nature reserve in UK waters. They were established under the Marine and Coastal Access Act (2009) and are areas designated with the aim to protect nationally important, rare or threatened habitats and species. Approximately 20% of UK waters now have some protection although some conservation, fisherman and wildlife groups are concerned that there are no management plans for each zone. Following Brexit, legislation was introduced into Parliament in January 2020 which would give new powers to the Marine Management Organisation in English waters. No Take Zones MCZs generally do not provide "no-take" protection banning fishing. However, Lundy Island MCZ includes a preexisting "no-take zone", which was established in 2003. Two more no-take zones were established in UK waters by 2010 (bringing the total area protected to five square kilometres):, and an additional one in 2016 * Lamlash Bay (2008), subsequently included within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockle (bivalve)
A cockle is an edible marine bivalve mollusc. Although many small edible bivalves are loosely called cockles, true cockles are species in the family Cardiidae. MolluscaBase eds. (2022). MolluscaBase. Cardiidae Lamarck, 1809. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=229 on 2022-02-09 True cockles live in sandy, sheltered beaches throughout the world. The distinctive rounded shells are bilaterally symmetrical, and are heart-shaped when viewed from the end. Numerous radial, evenly spaced ribs are a feature of the shell in most but not all genera (for an exception, see the genus '' Laevicardium'', the egg cockles, which have very smooth shells). The shell of a cockle is able to close completely (i.e., there is no "gap" at any point around the edge). Though the shell of a cockle may superficially resemble that of a scallop because of the ribs, cockles can be distinguished from scallops morphologically in that coc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 Establishments In The United Kingdom
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album '' 63/19'' by Kool A.D. * '' Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Protected Area
Marine protected areas (MPA) are protected areas of seas, oceans, estuaries or in the US, the Great Lakes. These marine areas can come in many forms ranging from wildlife refuges to research facilities. MPAs restrict human activity for a conservation purpose, typically to protect natural or cultural resources. Such marine resources are protected by local, state, territorial, native, regional, national, or international authorities and differ substantially among and between nations. This variation includes different limitations on development, fishing practices, fishing seasons and catch limits, moorings and bans on removing or disrupting marine life. In some situations (such as with the Phoenix Islands Protected Area), MPAs also provide revenue for countries, potentially equal to the income that they would have if they were to grant companies permissions to fish. The value of MPA to mobile species is unknown. There are a number of global examples of large marine conservation ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing Industry
The fishing industry includes any industry or activity concerned with taking, culturing, processing, preserving, storing, transporting, marketing or selling fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including recreational, subsistence and commercial fishing, and the related harvesting, processing, and marketing sectors.FAO Fisheries Section: Glossary''Fishing industry.''Retrieved 28 May 2008. The commercial activity is aimed at the delivery of fish and other seafood products for human consumption or as input factors in other industrial processes. The livelihood of over 500 million people in developing countries depends directly or indirectly on fisheries and aquaculture. The fishing industry is struggling with environmental and welfare issues, including overfishing and occupational safety. Additionally, the combined pressures of climate change, biodiversity loss and overfishing endanger the livelihoods and food security of a substant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom Trawling
Bottom trawling is trawling (towing a trawl, which is a fishing net) along the seafloor. It is also referred to as "dragging". The scientific community divides bottom trawling into benthic trawling and demersal trawling. Benthic trawling is towing a net at the very bottom of the ocean and demersal trawling is towing a net just above the benthic zone. Bottom trawling can be contrasted with midwater trawling (also known as pelagic trawling), where a net is towed higher in the water column. Midwater trawling catches pelagic fish such as anchovies and mackerel, whereas bottom trawling targets both bottom-living fish ( groundfish) and semi-pelagic species such as cod, squid, shrimp, and rockfish. Trawling is done by a trawler, which can be a small open boat with only or a large factory trawler with . Bottom trawling can be carried out by one trawler or by two trawlers fishing cooperatively ( pair trawling). Global catch from bottom trawling has been estimated at over 30 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for lime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenpeace
Greenpeace is an independent global campaigning network, founded in Canada in 1971 by Irving Stowe and Dorothy Stowe, immigrant environmental activists from the United States. Greenpeace states its goal is to "ensure the ability of the Earth to nurture life in all its diversity" and focuses its campaigning on worldwide issues such as climate change, deforestation, overfishing, commercial whaling, genetic engineering, and anti-nuclear issues. It uses direct action, lobbying, research, and ecotage to achieve its goals. The network comprises 26 independent national/regional organisations in over 55 countries across Europe, the Americas, Africa, Asia and the Pacific, as well as a co-ordinating body, Greenpeace International, based in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. The global network does not accept funding from governments, corporations, or political parties, relying on three million individual supporters and foundation grants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaice
Plaice is a common name for a group of flatfish that comprises four species: the European, American, Alaskan and scale-eye plaice. Commercially, the most important plaice is the European. The principal commercial flatfish in Europe, it is also widely fished recreationally, has potential as an aquaculture species, and is kept as an aquarium fish. Also commercially important is the American plaice. The term ''plaice'' (plural ''plaice'') comes from the 14th-century Anglo-French ''plais''. This in turn comes from the late Latin ''platessa'', meaning flatfish, which originated from the Ancient Greek ''platys'', meaning broad. Plaice species European plaice The European plaice (''Pleuronectes platessa'') is a right-eyed flounder belonging to the family Pleuronectidae. It is a commercially important flatfish that lives on the sandy bottoms of the European shelf. It ranges geographically from the Barents Sea to the Mediterranean. European plaice are characterised by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sole (fish)
Sole is a fish belonging to several families. Generally speaking, they are members of the family Soleidae, but, outside Europe, the name ''sole'' is also applied to various other similar flatfish, especially other members of the sole suborder Soleoidei as well as members of the flounder family. In European cookery, there are several species which may be considered ''true soles'', but the common or Dover sole '' Solea solea'', often simply called ''the sole'', is the most esteemed and most widely available. Etymology of the word The word ''sole'' in English, French, and Italian comes from its resemblance to a sandal, Latin ''solea''. In other languages, it is named for the tongue, e.g. el, γλώσσα, german: Seezunge, nl, zeetong or ', hu, nyelvhal, es, lenguado, zh, 龍脷 ("dragon tongue"), ar, لسان الثور lisan Ath-thawr (for the common sole) meaning 'the tongue of ox' in Qosbawi accent. A partial list of common names for species referred to as sole includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatfish
A flatfish is a member of the ray-finned demersal fish order Pleuronectiformes, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through or around the head during development. Some species face their left sides upward, some face their right sides upward, and others face either side upward. Many important food fish are in this order, including the flounders, soles, turbot, plaice, and halibut. Some flatfish can camouflage themselves on the ocean floor. Taxonomy Over 800 described species are placed into 16 families. Broadly, the flatfishes are divided into two suborders, Psettodoidei and Pleuronectoidei, with > 99% of the species diversity found within the Pleuronectoidei. The largest families are Soleidae, Bothidae and Cynoglossidae with more than 150 species each. There also exist two monotypic families ( Paralichthodidae and Oncopteridae). Some families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Worm
Any worm that lives in a marine environment is considered a marine worm. Marine worms are found in several different phyla, including the Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida (segmented worms), Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, and Phoronida. For a list of marine animals that have been called "sea worms", see sea worm. Reproduction Marine worms exhibit numerous types of reproduction, both sexually and asexually. Asexually many are able to reproduce via budding or regeneration. This regeneration is most notably studied in Plathelminths or Triclad, known for being one of the earliest animals to be studied for its regenerative capabilities. Marine worms will also sexually reproduce, internally and externally, with some releasing spawn into the ocean currents. This is in opposition to the much more internal and invasive method displayed by flat-worms called Penis fencing where hermaphroditic organisms will flight to try and impregnate their opponent while avoiding becoming impregnate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |