|
South American Dreadnought Race
A naval arms race among Argentina, Brazil, and Chile—the ABC countries, wealthiest and most powerful countries in South America—began in the early twentieth century when the Brazilian government ordered three dreadnoughts, formidable battleships whose capabilities far outstripped older vessels in the world's navies. In 1904, the Brazilian legislature allocated substantial funds to improve the country's naval forces. Proponents of this plan believed that they needed a strong navy to become an international power and counter Argentine–Chilean naval arms race, recent expansions of the Argentine and Chilean navies. The revolutionary design of the 1906 British warship prompted the Brazilians to alter these plans and redirect their money into constructing three dreadnoughts. These warships, the most powerful in the world, entered service at a time when dreadnoughts were an important factor in a nation's international prestige and therefore brought global attention to Brazil. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazilian Battleship Minas Geraes Firing A Broadside 3
Brazilian commonly refers to: * Brazil, a country * Brazilians, its people * Brazilian Portuguese, its dialect Brazilian may also refer to: * "The Brazilian", a 1986 instrumental music piece by Genesis * Brazilian Café, Baghdad, Iraq (1937) * Brazilian cuisine ** Churrasco, or Brazilian barbecue * Brazilian-cut bikini, a swimsuit revealing the buttocks * Bikini waxing#Brazilian waxing, Brazilian waxing, a style of pubic hair removal * Mamelodi Sundowns F.C., a South African football club nicknamed ''The Brazilians'' See also * Brazil (other) * ''Brasileiro'', a 1992 album by Sergio Mendes * Brazilian jiu-jitsu, a martial art and combat sport system * Culture of Brazil * Football in Brazil {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
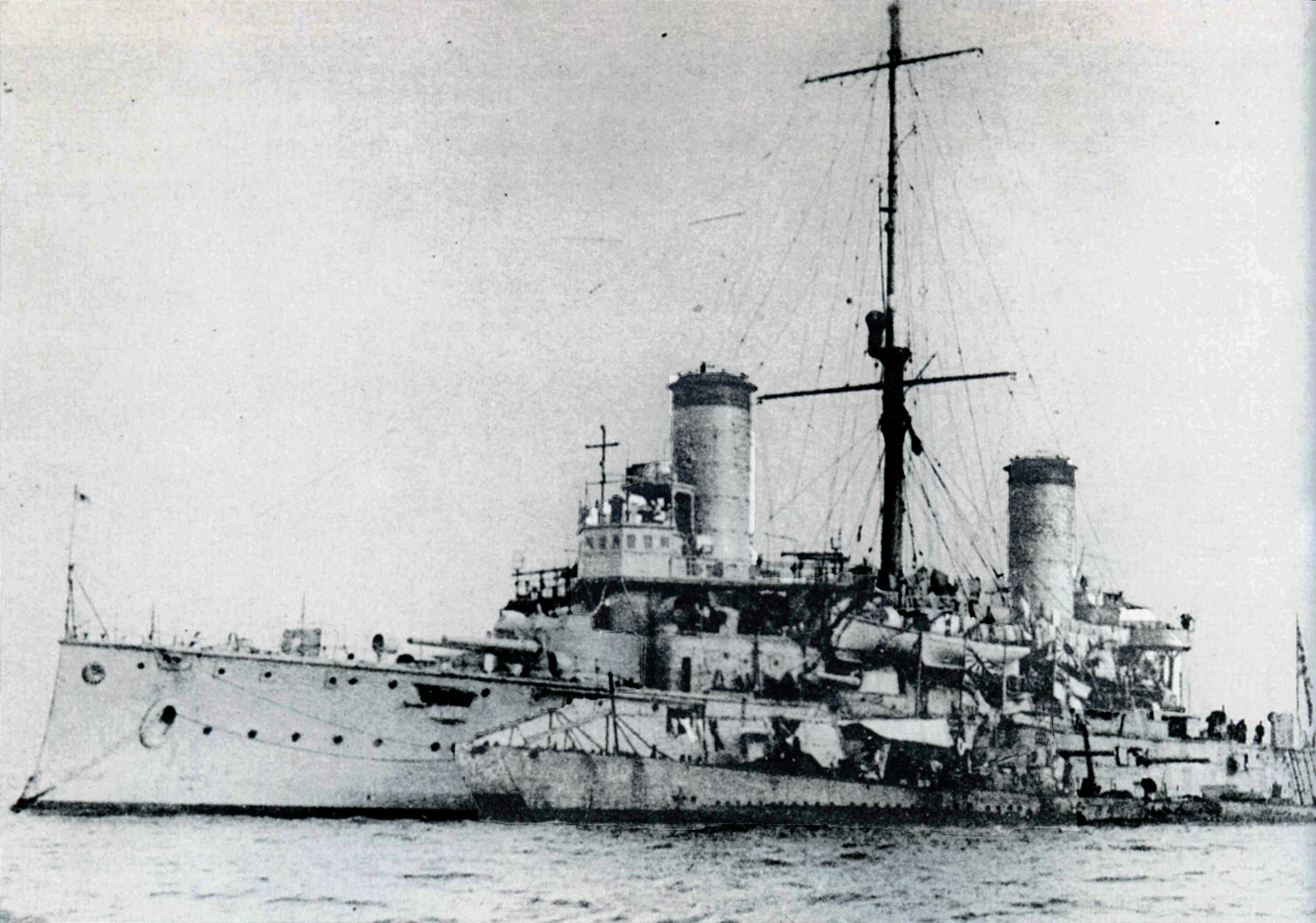
Japanese Cruiser Nisshin
, also transliterated as ''Nissin'', was a armored cruiser of the Imperial Japanese Navy, built in the first decade of the 20th century by Gio. Ansaldo & C., Sestri Ponente, Italy, where the type was known as the . The ship was originally ordered by the Royal Italian Navy in 1901 as ''San Rocco'' and sold the next year to the Argentine Navy who renamed her ''Mariano Moreno'' during the Argentine–Chilean naval arms race, but the lessening of tensions with Chile and financial pressures caused the Argentinians to sell her before delivery. At that time tensions between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire were rising, and the ship was offered to both sides before she was purchased by the Japanese. During the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05, ''Nisshin'' participated in the Battle of the Yellow Sea and was damaged in the subsequent Battle of Tsushima. In addition, she frequently bombarded the defenses of Port Arthur. The ship played a limited role in World War I and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
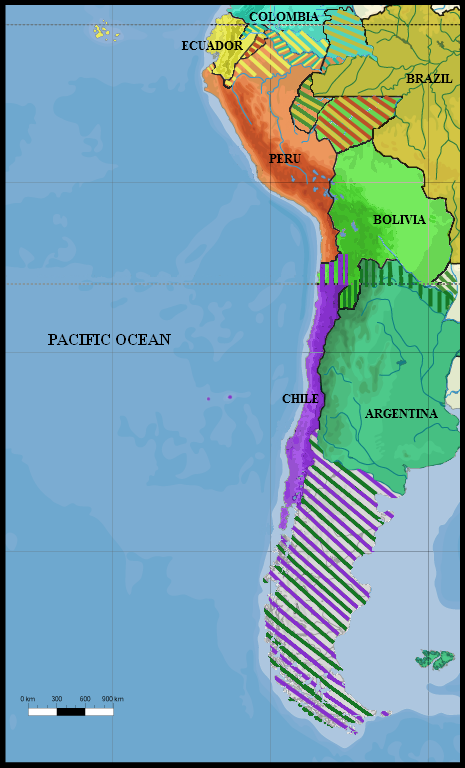
Puna De Atacama Dispute
The Puna de Atacama dispute, sometimes referred to as Puna de Atacama Lawsuit ( Spanish: ''Litigio de la Puna de Atacama''), was a border dispute involving Argentina, Chile and Bolivia in the 19th century over the arid high plateau of Puna de Atacama located about 4500 meters above the sea around the current borders of the three countries. The dispute originated with the Chilean annexation of the Bolivian Litoral Department in 1879 during the War of the Pacific. That year, the Chilean Army occupied San Pedro de Atacama, the main settlement of the current Chilean part of Puna de Atacama. By 1884, Bolivia and its ally Peru had lost the war, and Argentina communicated to the Chilean government that the border line in the Puna was still a pending issue between Argentina and Bolivia. Chile answered that the Puna de Atacama still belonged to Bolivia. The same year, Argentina occupied Pastos Grandes in the Puna. Bolivia had still not signed any peace treaty with Chile until the Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilean Civil War Of 1891
The Chilean Civil War of 1891 (also known as Revolution of 1891) was a civil war in Chile fought between forces supporting Congress of Chile, Congress and forces supporting the President of Chile, President, José Manuel Balmaceda from 16 January 1891 to 18 September 1891. The war saw a confrontation between the Chilean Army and the Chilean Navy, siding with the president and the congress, respectively. This conflict ended with the defeat of the Chilean Army and the presidential forces, and with President Balmaceda committing suicide as a consequence of the defeat. In Chilean historiography the war marks the end of the Liberal Republic and the beginning of the History of Chile during the Parliamentary Era (1891–1925), Parliamentary Era. Causes The Chilean Civil War grew out of political disagreements between the president of Chile, José Manuel Balmaceda, and the Chilean congress. In 1889, the congress became distinctly hostile to the administration of Balmaceda, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Pacific
The War of the Pacific (), also known by War of the Pacific#Etymology, multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Treaty of Defensive Alliance (Bolivia–Peru), Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Atacama Desert border dispute, Chilean claims on Litoral Department, coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia. The direct cause of the war was a nitrate taxation dispute between Bolivia and Chile, with Peru being drawn in due to its secret alliance with Bolivia. Some historians have pointed to deeper origins of the war, such as the interest of Chile and Peru in the nitrate business, a long-standing rivalry between Chile and Peru for regional hegemony, as well as the political and economical disparities between the stability of Chile and the volatility of Peru and Bolivia. In February 1878, Bolivia increased taxes on the Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of self-propelled Whitehead torpedoes. These were inshore craft created to counter both the threat of battleships and other slow and heavily armed ships by using speed, agility, and powerful torpedoes, and the overwhelming expense of building a like number of capital ships to counter an enemy. A swarm of expendable torpedo boats attacking en masse could overwhelm a larger ship's ability to fight them off using its large but cumbersome guns. A fleet of torpedo boats could pose a similar threat to an adversary's capital ships, albeit only in the coastal areas to which their small size and limited fuel load restricted them. The introduction of fast torpedo boats in the late 19th century was a serious concern to the era's naval strategists, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARA Patagonia (1885)
ARA ''Patagonia'' was an armoured cruiser that served in the Argentine Navy between 1886 and 1927. Design ''Patagonia'' was a steam-sail armoured cruiser with steel hull and wooden planking, and armoured conning tower. It was propelled by two compound horizontal engines, and two masts with brick sails. It was equipped with two searchlights, two small steam boats, and five smaller boats with oars. As designed, its main battery was one 250mm Armstrong gun at the bow, and one 150mm Armstrong gun at the stern and on each side; with Vavasseur mountings protected with armoured shields. The secondary battery had four 87.5 mm and two 65.2mm Armstrong guns. It also mounted eight Nordenfelt machine guns and six Gardner machine guns. In 1899, the 250mm gun and two 150mm guns were removed, and the remainder of its artillery was redistributed. History ''Patagonia'' was ordered in 1885 to the shipyard Stabilimento Tecnico Triestino in Trieste at a cost of £ 100,000; this tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironclad Warship
An ironclad was a steam-propelled warship protected by steel or iron armor constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shells. The first ironclad battleship, , was launched by the French Navy in November 1859, narrowly preempting the British Royal Navy. However, Britain built the first completely iron-hulled warships. Ironclads were first used in warfare in 1862 during the American Civil War, when they operated against wooden ships, and against each other at the Battle of Hampton Roads in Virginia. Their performance demonstrated that the ironclad had replaced the unarmored ship of the line as the most powerful warship afloat. Ironclad gunboats became very successful in the American Civil War. Ironclads were designed for several uses, including as high-seas battleships, long-range cruisers, and coastal defense ships. Rapid development of warship design in the late 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
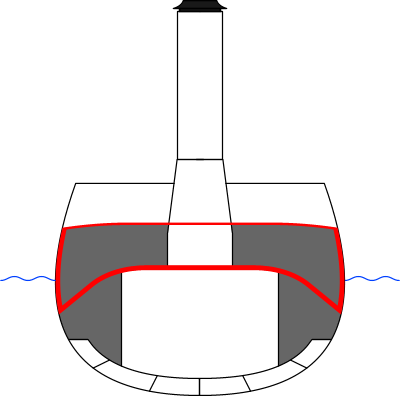
Central Battery Ship
The central battery ship, also known as a centre battery ship in the United Kingdom and as a casemate ship in European continental navies, was a development of the (high- freeboard) broadside ironclad of the 1860s, given a substantial boost due to the inspiration gained from the Battle of Hampton Roads, the first battle between ironclads fought in 1862 during the American Civil War. One of the participants was the Confederate casemate ironclad , essentially a central battery ship herself, albeit a low-freeboard one. The central battery ships had their main guns concentrated in the middle of the ship in an armoured citadel. The concentration of armament amidships meant the ship could be shorter and handier than a broadside type like previous warships. In this manner the design could maximize the thickness of armour in a limited area while still carrying a significant broadside. These ships meant the end of the armoured frigates with their full-length gun decks. In the UK, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and Patagonian Desert, deserts, Plateaus, tablelands, and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The northern limit of the region is not precisely defined; the Colorado River, Argentina, Colorado and Barrancas River, Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes considered part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armored Cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a pre-dreadnought battleship and fast enough to outrun any battleship it encountered. For many decades, naval technology had not advanced far enough for designers to produce a cruiser that combined an armored belt with the long-range and high speed required to fulfill its mission. For this reason, beginning in the 1880s and 1890s, many navies preferred to build protected cruisers, which only relied on a lightly armored deck (ship), deck to protect the vital parts of the ship. However, by the late 1880s, the development of modern rapid-fire breech-loading cannons and high-explosive shells made the reintroduction of side armor a necessity. The invention of Case-hardening, case-hardened armor in the mid-1890s offered effective protection with less weight than previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of cruiser of the late 19th century, took their name from the armored deck, which protected vital machine-spaces from fragments released by explosive shells. Protected cruisers notably lacked a belt of armour along the sides, in contrast to armored cruisers which carried both deck and belt armour. Outside of a handful of very large designs in the major navies (which preceded the revival of armored cruisers), the majority of protected cruisers were of 'second-' or 'third-class' types, lighter in displacement and mounting fewer and/or lighter guns than armored cruisers. By the early 20th-century, with the advent of increasingly lighter yet stronger armour, even smaller vessels could afford some level of both belt and deck armour. In the place of protected cruisers, these new ' light armored cruisers' would evolve into light cruisers and heavy cruisers, the former especially taking on many of the roles originally envisioned for protected cruisers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |