|
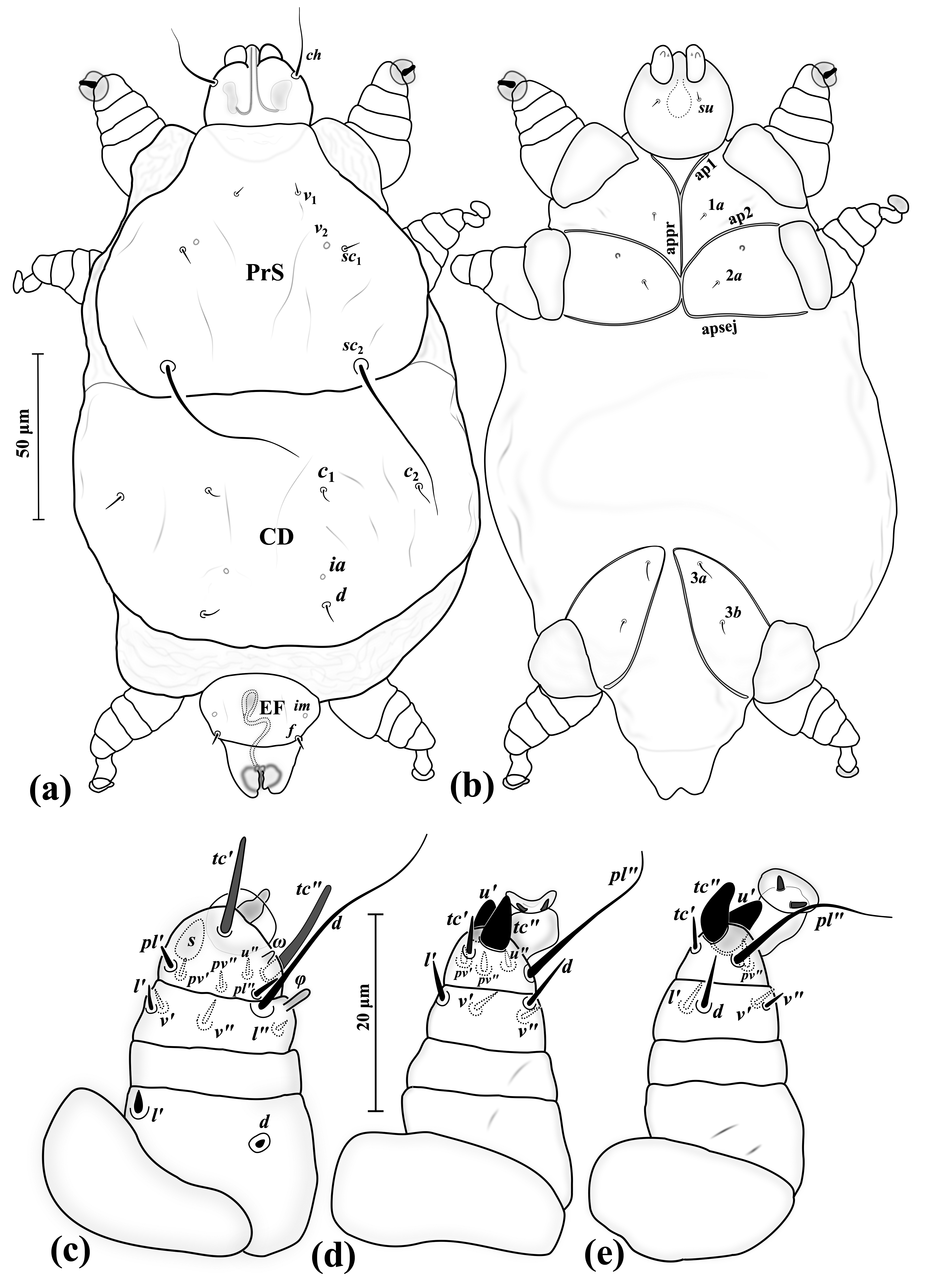
Soricidex Dimorphus
''Soricidex'' is a genus of tiny mites that live on the head and body of its host species, the common shrew (''Sorex araneus The common shrew (''Sorex araneus''), also known as the Eurasian shrew, is the most common shrew, and one of the most common mammals, throughout Northern Europe, including Great Britain, but excluding Ireland. It is long and weighs , and has ve ...''). Only one species has been formally described, ''Soricidex dimorphus'', but V. Bukva mentions two more undescribed species from his collection. ''S. dimorphus'' exhibits sexual dimorphism, a feature unseen in its family, Demodecidae. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q48998552 Acari genera Parasitic acari Parasitic arthropods of mammals Trombidiformes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnid
Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, whip spiders and Uropygi, vinegaroons. Adult arachnids have eight Arthropod leg, legs attached to the cephalothorax. In some species the frontmost pair of legs has converted to a sensory function, while in others, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. Almost all Extant taxon, extant arachnids are terrestrial animal, terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 110,000 named species, of which 51,000 are species of spiders. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acari
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group invalid as a clade. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive '' Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy Mites are not a defined taxon, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombidiformes
Trombidiformes is a large, diverse order of mites. Taxonomy In 1998, Trombidiformes was divided into the Sphaerolichida and the Prostigmata. The group has few synapomorphies by which it can be defined, unlike the other major group of acariform mites, Sarcoptiformes. Its members include medically important mites (such as ''Demodex'', the chiggers, and scrub-itch mites) and many agriculturally important species, including the spider mites (Tetranychidae). The superfamily Eriophyoidea, traditionally considered members of the Trombidiformes, have been found to be basal mites in genomic analyses, sister to the clade containing Sarcoptiformes and Trombidiformes. The 2004 classification retained the two suborders, comprising around 125 families and more than 22,000 described species. In the 2011 revised classification, the order now contains 151 families, 2235 genera and 25,821 species, and there were another 10 species with 24 species that present only as fossils. These 151 famili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demodecidae
Demodecidae is a family of parasitic and commensal mites, living on various species of mammals. Each species of mite is usually only found on a single mammal species, whereas a mammal species can have several different species of demodecid mites living on it. Many species of mites are restricted to very limited areas of their body, e.g. the Meibomian glands Meibomian glands (also called tarsal glands, palpebral glands, and tarsoconjunctival glands) are sebaceous glands along the rims of the eyelid inside the tarsal plate. They produce meibum, an oily substance that prevents evaporation of the ey ..., the ear canal, the tongue etc. The family was formerly named ''Demodicidae''. References Trombidiformes Acari families {{Acari-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soricidex Dimorphus
''Soricidex'' is a genus of tiny mites that live on the head and body of its host species, the common shrew (''Sorex araneus The common shrew (''Sorex araneus''), also known as the Eurasian shrew, is the most common shrew, and one of the most common mammals, throughout Northern Europe, including Great Britain, but excluding Ireland. It is long and weighs , and has ve ...''). Only one species has been formally described, ''Soricidex dimorphus'', but V. Bukva mentions two more undescribed species from his collection. ''S. dimorphus'' exhibits sexual dimorphism, a feature unseen in its family, Demodecidae. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q48998552 Acari genera Parasitic acari Parasitic arthropods of mammals Trombidiformes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group invalid as a clade. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are Predation, predators or Parasitism, parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive ''Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy Mites are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorex Araneus
The common shrew (''Sorex araneus''), also known as the Eurasian shrew, is the most common shrew, and one of the most common mammals, throughout Northern Europe, including Great Britain, but excluding Ireland. It is long and weighs , and has velvety dark brown fur with a pale underside. It is one of the rare venomous mammals. Juvenile shrews have lighter fur until their first moult. The common shrew has small eyes, a pointed, mobile snout and red-tipped teeth. It has a life span of approximately 14 months. Shrews are active day and night, taking short periods of rest between relatively long bursts of activity. Territory Common shrews are found throughout the woodlands, grasslands, and hedgelands of Britain, Scandinavia, and Eastern Europe. Each shrew establishes a home range of 370 to 630 m2 (440 to 750 yd²). Males often extend the boundaries during the breeding season to find females. Shrews are extremely territorial and will aggressively defend their home ranges from othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acari Genera
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group invalid as a clade. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive '' Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy Mites are not a defined taxon, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |