|
Song (state)
Song was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty with its capital at Shangqiu. The state was founded soon after King Wu of Zhou conquered the Shang dynasty to establish the Zhou dynasty in 1046 BC. It was conquered by the state of Qi in 286 BC, during the Warring States period. Confucius is traditionally considered to have been a descendant of a Song nobleman who moved to the state of Lu. Origin King Zhou of Shang, King Zhou of Shang, Di Xin was the younger brother of Jizi, Zi Qi—who was said in legends to have ruled Gija Joseon in the 11th century BCE—and Zi Yan (), later rulers of Zhou's vassal state Song, father of Wu Geng. After King Wu of Zhou overthrew King Zhou of Shang, the last ruler of Shang, marking the transition to the Zhou dynasty, the victor was honor-bound by a stricture of feudal etiquette known as to allow the defeated house of Shang dynasty, Shang to continue offering sacrifices to their ancestors. As a result, for a time Shang be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (Ancient China)
Ancient Chinese states () were dynastic polities of China within and without the Zhou cultural sphere prior to Qin's wars of unification. They ranged in size from large estates, to city-states to much vaster territories with multiple population centers. Many of these submitted to royal authority, but many did not—even those that shared the same culture and ancestral temple surname as the ruling house. Prior to the Zhou conquest of Shang, these ancient states were already extant as units of the preceding Shang dynasty, Predynastic Zhou or polities of other cultural groups. Once the Zhou had established themselves, they made grants of land and relative local autonomy to kinfolk in return for military support and tributes, under a system known as '' fengjian''. The rulers of the states were collectively the ''zhuhou'' (). Over the course of the Zhou dynasty ( 1046–256 ), the ties of family between the states attenuated, the power of the central government waned, and the state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Lu
Lu (; 249 BC) was a vassal state during the Zhou dynasty of ancient China located around modern Shandong. Founded in the 11th century BC, its rulers were from a cadet branch of the House of Ji () that ruled the Zhou dynasty. The first duke was Boqin, a son of the Duke of Zhou, who was brother of King Wu of Zhou and regent to King Cheng of Zhou. Lu was the home state of Confucius as well as Mozi, and, as such, has an outsized cultural influence among the states of the Eastern Zhou and in history. The '' Annals of Spring and Autumn'', for instance, was written with the Lu rulers' years as their basis. Another great work of Chinese history, the '' Zuo Zhuan'' or ''Commentary of Zuo'', was traditionally considered to have been written in Lu by Zuo Qiuming. Geography The state's capital was in Qufu and its territory mainly covered the central and southwest regions of what is now Shandong Province. It was bordered to the north by the powerful state of Qi and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
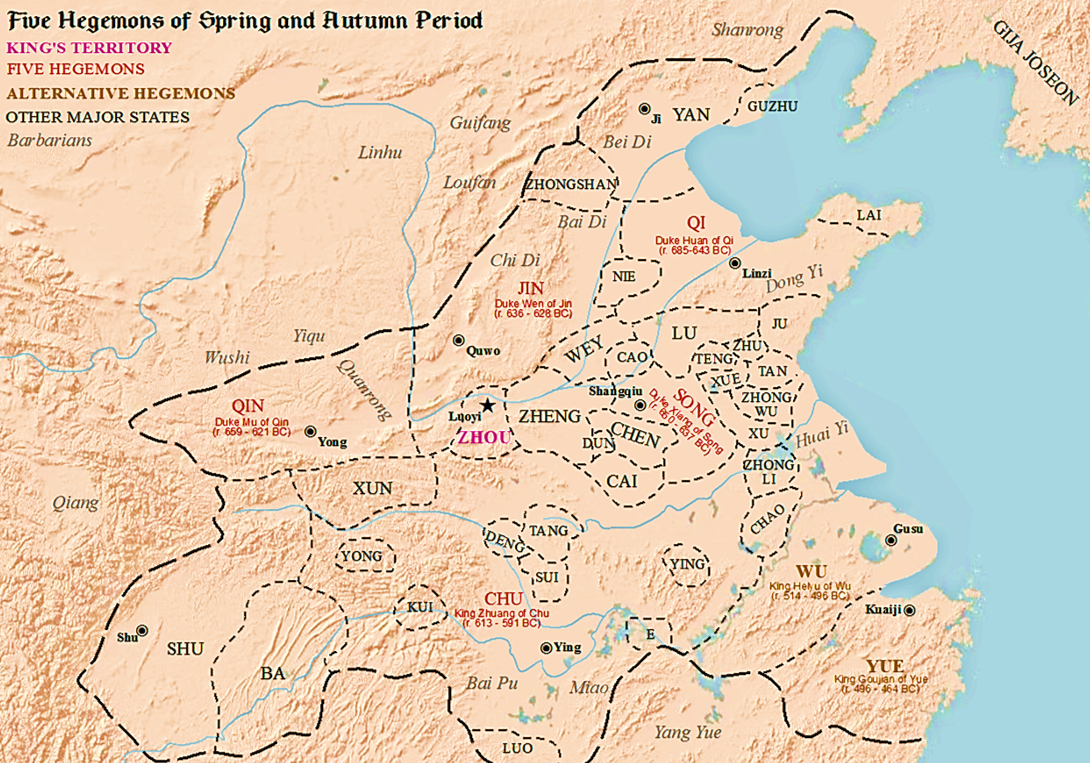
Five Hegemons
The Five Hegemons (), also referred to as the Five Hegemons of the Spring and Autumn period (), refers to several especially powerful rulers of Chinese states of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history (770–476 BCE), sometimes alternatively referred to as the "Age of Hegemons". There are various lists of five rulers of those certain states which rose to power over the other states of this time period, states which were also formed during the period of dissolution of a once real and strong central state, namely the empire of the Zhou dynasty. The Hegemons mobilized the remnants of the Zhou empire, according to shared mutual political and martial interests. An especially prominent Hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi. Pronunciation and meaning In ancient Chinese, (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ) '' has a similar meaning and pronunciation to (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ), which means 'the eldest son born to the principal wife in a family', or 'senator'. Both and can be translated as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Xiang Of Song
Duke Xiang of Song (宋襄公) (died 637 BC) was the leader in the state of Song in the Spring and Autumn period. His personal name was Zifu (子茲甫) and he took his throne in 650 BC. After the death of the Hegemon of China, Duke Huan of Qi, in 643 BC, Duke Xiang intervened in the War of Qi's succession on the behalf of his ally Prince Zhao. Forming an alliance with Cao, Wey, and Zou, Duke Xiang and his troops invaded Qi and eventually defeated Prince Zhao's rival brothers, crowning him as "Duke Xiao of Qi". With his influence on the rise, Duke Xiang saw a chance to become the next hegemon of China and made war with Chu. In 641 BC, he made a covenant with Cao and Zhu, two small states. Then he ordered the viscount of Zeng to be sacrificed as a victim, because the later came too late for their first covenant, though he appeared in their another covenant. In 638 BC he attacked the state of Zheng and met the troops from Chu, who were running to save Zheng. Instead of giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Zheng
Zheng (; ; Old Chinese: *') was a vassal state in China during the Zhou dynasty (1046–221 BCE) located in the centre of ancient China in modern-day Henan Province on the North China Plain about east of the royal capital at Luoyang. It was the most powerful of the vassal states at the beginning of the Eastern Zhou (771–701 BCE), and was the first state to clearly establish a code of law in its late period of 543 BCE. Its ruling house had the ancestral name Ji (姬), making them a branch of the Zhou royal house, who held the rank of '' Bo'' (), a kinship term meaning "elder". Foundation Zheng was founded in 806 BC when King Xuan of Zhou, the penultimate king of the Western Zhou, made his younger brother Prince You () Duke of Zheng and granted him lands within the royal domain in the eponymous Zheng in modern-day Hua County, Shaanxi on the Wei River east of Xi'an. Prince You, known posthumously as Duke Huan of Zheng, established what would be the last bastion of Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Zhuang Of Zheng
Duke Zhuang of Zheng (; 757–701 BC) was the third ruler of the State of Zheng during the Spring and Autumn period in ancient China. His ancestral name was Ji (姬), given name Wusheng (寤生), which means "difficult birth" with breech presentation. In 743 BC, he became the duke of Zheng, and later defeated his younger brother Gongshu Duan, who had led a rebellion against him. Duke Zhuang led military campaigns in the name of the Zhou king against the Rong people and other Zhou states. Early life and rise to power Born as the first of two sons and groomed for the throne, Zheng's mother nevertheless preferred her second son, the reason being that she suffered through an extraordinarily painful time when giving birth to Zheng. When Duke Zheng ascended to the dukedom over the violent objections of his mother, she began plotting to get Gongshu Duan into power. First she asked Zheng to give Gongshu Duan the city of Duan as a fiefdom. Duan, at that time, was the second largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnatic Primogeniture
Primogeniture () is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit all or most of their parent's estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relative. In most contexts, it means the inheritance of the firstborn son (agnatic primogeniture); it can also mean by the firstborn daughter (matrilineal primogeniture), or firstborn child (absolute primogeniture). Its opposite analogue is partible inheritance. Description The common definition given is also known as male-line primogeniture, the classical form popular in European jurisdictions among others until into the 20th century. In the absence of male-line offspring, variations were expounded to entitle a daughter or a brother or, in the absence of either, to another collateral relative, in a specified order (e.g., male-preference primogeniture, Salic primogeniture, semi-Salic primogeniture). Variations have tempered the traditional, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnatic Seniority
Agnatic seniority is a patrilineality, patrilineal principle of inheritance where the order of succession to the throne prefers the monarch's younger brother over the monarch's own sons. A monarch's children (the next generation) succeed only after the males of the elder generation have all been exhausted. Agnatic seniority excludes females of the dynasty and their descendants from the succession. Contrast Primogeniture#Agnatic primogeniture, agnatic primogeniture, where the king's sons stand higher in succession than his brothers. Description In hereditary monarchy, monarchies, particularly in more ancient times, seniority was a much-used principle of order of succession. The Ottoman Empire evolved from an elective succession (following the principle of agnatic seniority) to a succession inherited by the law of agnatic seniority. In succession based on rotation (close to seniority), all (male) members of the dynasty were entitled to the monarchy, in principle. However, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weizi Of Song
Weizi (), also spelled Wei Tsze, was the first ruler of Song. He was the subject of Chapter 18 of the ''Analects'' of Confucius. Weizi was the eldest son of Di Yi. He was first enfeoffed at Wei (微), hence Lord of Wei (微子). He was also a half-brother of the last Shang king, Di Xin (better known as King Zhou of Shang). Di Xin gave himself over to drinking, women and abandoned morals. Weizi tried to persuade him not to do so, but Di Xin ignored. Subsequently, Weizi resigned and withdrew from the court. When Zhou dynasty conquered the Shang kingdom, Weizi submitted and presented the ritual utensils to King Wu of Zhou. He was pardoned by King Wu. After Rebellion of the Three Guards was put down, Weizi was enfeoffed as Duke of Song and granted land at Shangqiu (商邱 'the hill of Shang'), where the capital of the new State of Song was built. After his death, he was succeeded by his younger brother Yan (衍), historically known as Weizhong (). Weizi was honored by Confuciu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Zhou
Dan, Duke Wen of Zhou, commonly known as the Duke of Zhou, was a member of the royal family of the early Zhou dynasty who played a major role in consolidating the kingdom established by his elder brother King Wu. He was renowned for acting as a capable and loyal regent for his young nephew King Cheng, and for successfully suppressing the Rebellion of the Three Guards and establishing firm rule of the Zhou dynasty over eastern China. He is also a Chinese culture hero, with the authorship of the ''I Ching'' and the ''Classic of Poetry'' having traditionally been attributed to him, as well as the establishment of the '' Rites of Zhou''. Life His personal name was Dan (). He was the fourth son of King Wen of Zhou and Queen Tai Si. His eldest brother Bo Yikao predeceased their father (supposedly a victim of cannibalism); the second-eldest defeated the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye around 1046 BC, ascending the throne as King Wu. King Wu distributed many fiefs to his r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yinxu
Yinxu (; ) is a Chinese archeological site corresponding to Yin, the final capital of the Shang dynasty (). Located in present-day Anyang, Henan, Yin served as the capital during the Late Shang period () which spanned the reigns of 12 Shang kings and saw the emergence of oracle bone script, the earliest known Chinese writing. Along with oracle bone script and other material evidence for the Shang's existence, the site was forgotten for millennia. Its rediscovery in 1899 resulted from an investigation into oracle bones that were discovered being sold nearby. The rediscovery of Yinxu marked the beginning of decades of intensive excavation and study. It is one of China's oldest and largest archeological sites, and was selected by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in 2006. Yinxu is located in northern Henan, near modern Anyang and the borders Henan shares with Hebei and Shanxi. Public access to the site is permitted. Traditional history According to the 2nd century ''Shuowen Jiezi'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Geng
Wu Geng or Wugeng (Chinese language, Chinese: ''Wǔgēng''), a.k.a. ''Lùfù'', was an ancient Chinese people, Chinese Chinese nobility, noble who was the son of King Zhou of Shang, King Zhou, the last chinese king, king of the Shang dynasty, Shang. After his father executed Bigan by cutting out his heart, Wugeng fled to Feng, the capital of the Zhou state, together with his uncles Weizi and Weizhong to plead King Wu of Zhou for help. Shortly afterward King Wu attacked the Shang and defeated King Zhou at the Battle of Muye, thus establishing the Zhou dynasty. Wugeng was allowed to stay in Yin, the old Shang capital, and rule it as a princedom and a vassal lord to King Wu. After King Wu of Zhou, King Wu's death and the ascension of his young son King Cheng of Zhou, Cheng, Wugeng joined the Rebellion of the Three Guards, failed rebellion of the Three Guards against the regent Duke of Zhou. He in turn was joined by the "Dongyi, Eastern Barbarian" states of ancient China, states. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |