|
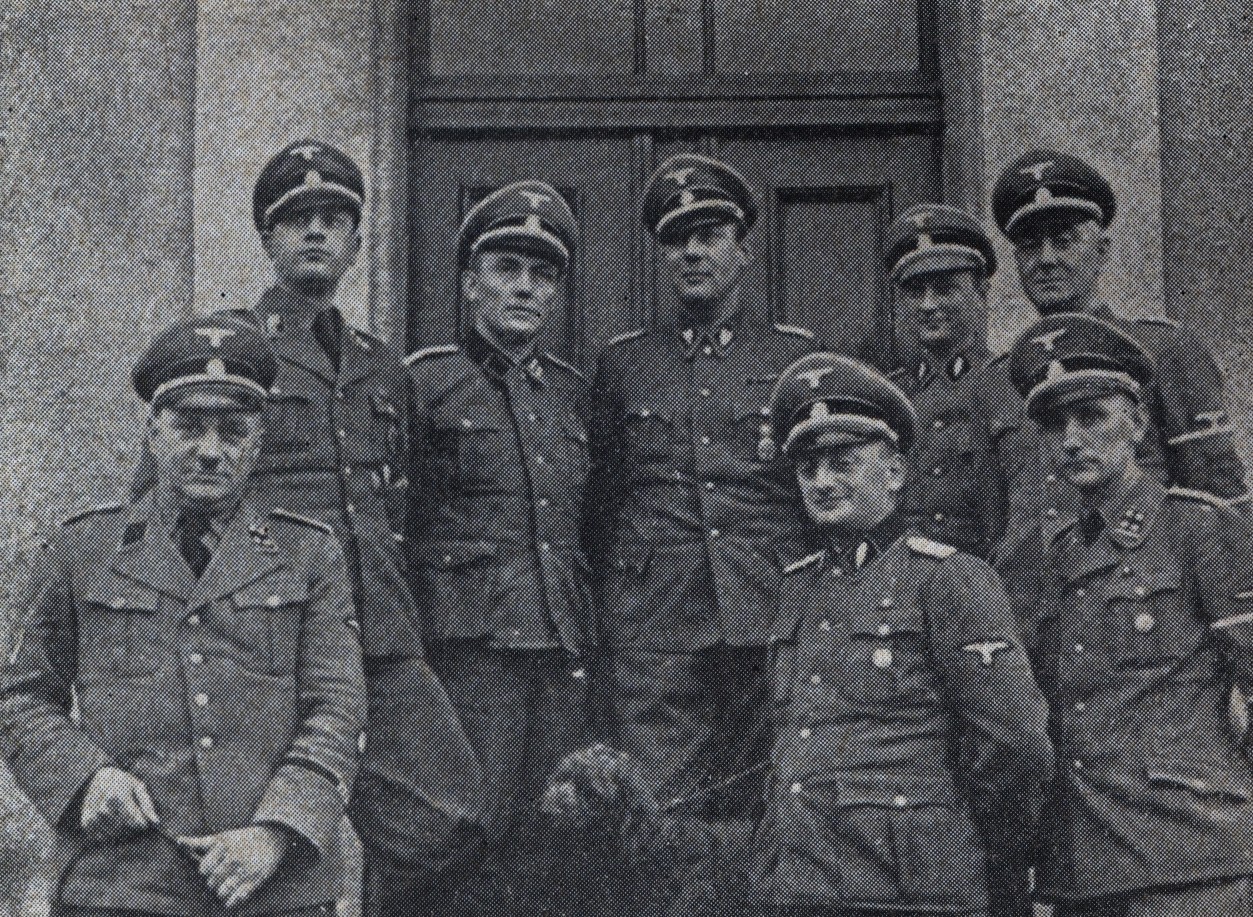
Sonderdienst
''Sonderdienst'' (german: Special Services) were the Nazi German paramilitary formations created in semicolonial General Government during the occupation of Poland in World War II. They were based on similar '' SS'' formations called ''Volksdeutscher Selbstschutz'' operating in the '' Warthegau'' district of German-annexed western part of Poland in 1939. ''Sonderdienst'' were founded on 6 May 1940 by '' Gauleiter'' Hans Frank who stationed in occupied Kraków. Initially, they were made up of ethnic German '' Volksdeutsche'' who lived in Poland before the attack and joined the invading force thereafter. However, after the 1941 Operation Barbarossa they also included Soviet prisoners of war who volunteered for special training, such as the Trawniki men (German: ''Trawnikimänner'') deployed at all major killing sites of the " Final Solution". Many of those men did not know German and required translation by their native commanders. The ''Abteilung Sonderdienst'' (Department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of the Holocaust. As a member of a reserve battalion during World War I, Himmler did not see active service, and did not fight. He studied agriculture in university, and joined the Nazi Party in 1923 and the SS in 1925. In 1929, he was appointed by Adolf Hitler. Over the next 16 years, he developed the SS from a 290-man battalion into a million-strong paramilitary group, and set up and controlled the Nazi concentration camps. He was known for good organisational skills and for selecting highly competent subordinates, such as Reinhard Heydrich in 1931. From 1943 onwards, he was both Chief of German Police and Minister of the Interior, overseeing all internal and external police and security forces, including the Gestapo (Secret State Police). H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gau (country Subdivision)
''Gau'' (German language, German , nl, gouw , fy, gea or ''goa'' ) is a Germanic languages, Germanic term for a region within a country, often a former or current province. It was used in the Middle Ages, when it can be seen as roughly corresponding to an England, English shire. The administrative use of the term was revived as a subdivision during the period of Nazi Germany in 1933–1945. It still appears today in regional names, such as the Rheingau or Allgäu. Middle Ages Etymology The Germanic word is reflected in Gothic language, Gothic ''gawi'' (neuter; genitive ''gaujis'') and early Old High German ''gewi, gowi'' (neuter) and in some compound names ''-gawi'' as in Gothic (e.g. ''Durgawi'' "Canton of Thurgau", ''Alpagawi'' "Allgäu"), later ''gâi, gôi'', and after loss of the stem suffix ''gaw, gao'', and with motion to the feminine as ''gawa'' besides ''gowo'' (from ''gowio''). Old Saxon shows further truncation to ''gâ, gô''. As an equivalent of Latin ''pagus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selbstschutz
''Selbstschutz'' (German for "self-protection") is the name given to different iterations of ethnic-German self-protection units formed both after the First World War and in the lead-up to the Second World War. The first incarnation of the ''Selbstschutz'' was a German paramilitary organisation formed after World War I for ethnic Germans who lived outside Germany in the territories occupied by Germany and Austria-Hungary following the conclusion of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. The purpose of these units was to protect local ethnic-German communities and, indirectly, to serve German security interests in southern Ukraine. Another iteration of the ''Selbstschutz'' concept was established in Silesia and aimed at returning Polish-inhabited territories back to Germany following the rebirth of Poland. In 1921, the units of ''Selbstschutz'' took part in the fights against the Polish Third Silesian Uprising. The third incarnation operated in territories of Central and Eastern Europe befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Tannenberg
Operation Tannenberg (german: Unternehmen Tannenberg) was a codename for one of the anti-Polish extermination actions by Nazi Germany that were directed at the Poles during the opening stages of World War II in Europe, as part of the ''Generalplan Ost'' for the German colonization of the East. The shootings were conducted with the use of a proscription list (''Sonderfahndungsbuch Polen''), compiled by the Gestapo in the span of two years before the 1939 invasion. The top secret lists identified more than 61,000 members of the Polish elite: activists, intelligentsia, scholars, clergy, actors, former officers and others, who were to be interned or shot. Members of the German minority living in Poland assisted in preparing the lists.Unterne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abwehr
The ''Abwehr'' ( German for ''resistance'' or ''defence'', but the word usually means ''counterintelligence'' in a military context; ) was the German military-intelligence service for the '' Reichswehr'' and the ''Wehrmacht'' from 1920 to 1944. Although the 1919 Treaty of Versailles prohibited the Weimar Republic from establishing an intelligence organization of their own, they formed an espionage group in 1920 within the Ministry of Defence, calling it the ''Abwehr''. The initial purpose of the ''Abwehr'' was defence against foreign espionage: an organizational role which later evolved considerably. Under General Kurt von Schleicher (prominent in running the ''Reichswehr'' from 1926 onwards) the individual military services' intelligence units were combined and, in 1929, centralized under Schleicher's ''Ministeramt'' within the Ministry of Defence, forming the foundation for the more commonly understood manifestation of the ''Abwehr''. Each ''Abwehr'' station throughout Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jungdeutsche Partei
''Jungdeutsche Partei in Polen'' (JDP), or the Young German Party in Poland ( pl, Partia Młodoniemiecka w Polsce), was a Nazi German extreme right-wing political party founded in 1931 by members of the ethnic German minority residing in the Second Polish Republic. The party was opposed not only to collaboration with Poland, but also, with other German organizations in Poland. Its leader was Rudolf Wiesner (pictured, fourth from the left), a committed Nazi. He was replaced by Max Wambeck from NSDAP on 22 November 1938. After the invasion of Poland Wambeck (fluent in Polish, known as Maksymilian Wambeck locally) served as '' SS-Obersturmführer'' in Chodzież in the '' Gnesen Gau'' (Polish Gniezno County) interrogating and torturing Armia Krajowa resistance members. Activities Sponsored financially by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany, the ''Jungdeutsche Partei'' members trained in propaganda, sabotage and espionage activities against the Polish state, smuggled mili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutscher Volksverband
''Deutscher Volksverband in Polen'' (DVV), or the German People's Union in Poland, was a Nazi German extreme right-wing political party founded in 1924 in central Poland by members of the ethnic German minority who did not wish to join the minority bloc in the Polish parliament Sejm. DVV was headed by August Utta, and financially supported by the Reich Ministry of Finance. ''Deutscher Volksverband'' was most active in the Łódź and Tomaszów area. The German Foreign Ministry aggressively supported the DVV Party through its own consulate in Poland for a number of reasons, one of them being the presence of the explicitly pro-Polish ''Deutscher Kultur– und Wirtschaftsbund'' (DKWB) organization in Łódź, which was critical of the revisionist Weimar government. DVV members denounced the "Lodzer Mensch" from the DKWB as puppets of the Polish government collaborating with the Jews and committing high treason against the German Reich. In 1935 August Utta was replaced by Ludwig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Minority In Poland
The registered German minority in Poland at the 2011 national census consisted of 148,000 people, of whom 64,000 declared both German and Polish ethnicities and 45,000 solely German ethnicity.Przynależność narodowo-etniczna ludności – wyniki spisu ludności i mieszkań 2011'. GUS. Materiał na konferencję prasową w dniu 29. 01. 2013. p. 3. At a 2002 census there were 152,900 people declaring German ethnicity. The German language is spoken in certain areas in Opole Voivodeship, where most of the minority resides, and in Silesian Voivodeship. German-speakers first came to these regions (present-day Opole and Silesian Voivodeships) during the Late Middle Ages. However, there are no localities in either Upper Silesia or Poland as a whole where German could be considered a language of everyday communication. The predominant home or family language of Poland's German minority in Upper Silesia used to be the Silesian German language (mainly ''Oberschlesisch'' dialect, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of the Second World War. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a significant number of ethnic Poles lived outside the country's borders. When, after several regional conflicts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |