|
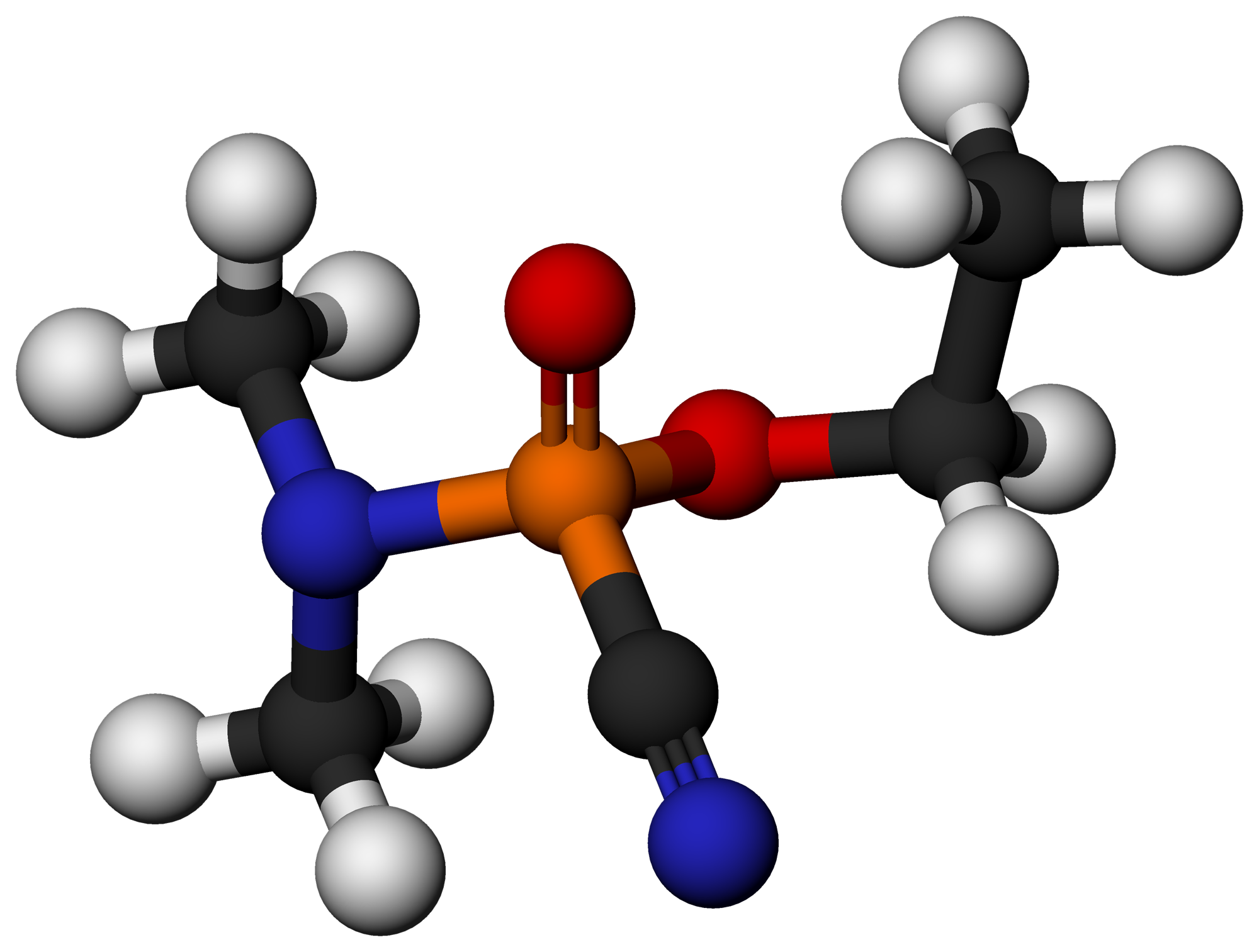
Soman Structural Formulae Stereoisomers V
Soman (or GD, EA 1210, Zoman, PFMP, A-255, systematic name: ''O''-pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate) is an extremely toxic chemical substance. It is a nerve agent, interfering with normal functioning of the mammalian nervous system by inhibiting the enzyme cholinesterase. It is an inhibitor of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. As a chemical weapon, it is classified as a weapon of mass destruction by the United Nations according to UN Resolution 687. Its production is strictly controlled, and stockpiling is outlawed by the Chemical Weapons Convention of 1993 where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance. Soman was the third of the so-called ''G-series'' nerve agents to be discovered along with GA (tabun), GB (sarin), and GF (cyclosarin). When pure, soman is a volatile, corrosive, and colorless liquid with a faint odor like that of mothballs or rotten fruit. More commonly, it is a yellow to brown color and has a strong odor described as similar to cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Agent
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemistry, organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison. Poisoning by a nerve agent leads to constriction of pupils, profuse salivation, convulsions, and involuntary urination and defecation, with the first symptoms appearing in seconds after exposure. Death by asphyxiation or cardiac arrest may follow in minutes due to the loss of the body's control over Respiration (physiology), respiratory and other muscles. Some nerve agents are readily vaporized or aerosolized, and the primary portal of entry into the body is the respiratory system. Nervous agents can also be absorbed through the skin, requiring that those likely to be subjected to su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
50.html" title="Click for more on -> 100%;">50">
|
50.html" style="text-decoration:none;">100%;">50
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... 50.html" style="text-decoration:none;"> [...More Info...] 50.html" style="text-decoration:none;"> [...Related Items...] 50" target=_blank style="text-decoration:none;"> OR: [Wikipedia] 50" target=_blank style="text-decoration:none;"> [Google] 50" target=_blank style="text-decoration:none;"> [Baidu] |
Richard Kuhn
Richard Johann Kuhn (; 3 December 1900 – 31 July 1967) was an Austrian-German biochemist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1938 "for his work on carotenoids and vitamins". Biography Early life Kuhn was born in Vienna, Austria, where he attended grammar school and high school. His interest in chemistry surfaced early; however he had many interests and decided late to study chemistry. Between 1910 and 1918 he was a schoolmate of Wolfgang Pauli, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for 1945. Beginning in 1918, Kuhn attended lectures at the University of Vienna in chemistry. He finished his chemistry studies at University of Munich and received his doctoral degree in 1922 with Richard Willstätter for a scientific work on enzymes. After graduating, Kuhn continued his scientific career, first in Munich, then at the ETH Zurich and from 1929 onwards at the University of Heidelberg, where he was head of the chemistry department beginning in 1937. In 1928 he mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, industrial buildings, for vector control, and control of insect parasites of animals and humans. Acaricides, which kill mites and ticks, are not strictly insecticides, but are usually classified together with insecticides. Some insecticides (including common bug sprays) are effective against other non-insect arthropods as well, such as scorpions, spiders, etc. Insecticides are distinct from insect repellents, which repel but do not kill. Sales In 2016 insecticides were estimated to account for 18% of worldwide pesticide sales. Worldwide sales of insecticides in 2018 were estimated as $ 18.4 billion, of which 25% were neonicotinoids, 17% were pyrethroids, 13% were diamides, and the rest were many other classes which sold for less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabun (nerve Agent)
Tabun (military designation GA) is an extremely toxic compound of the organophosphate family. It is not present in nature. At room temperature, the pure compound is a clear and viscous liquid. However, impurities imparted during its manufacture are almost always present, turning it into a yellow or brown liquid. Exposed to environs, it slowly volatizes into the atmosphere, with the vapor having a slight fruity or almond-like odor. As the compound has a much higher molecular mass (162 g/mol) compared to air, Tabun gas tends to accumulate in low-lying areas. It is a potent inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase, a key enzyme within the human body as well as in other animals. Acetylcholinesterase is responsible for breaking down acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter released into the synaptic cleft by motor neurons. The presence of acetylcholine within the cleft signals the post-synaptic (downstream) motor neuron to contract the neuron's associated muscle fibers, and vice versa. By irreversibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IG Farben
I. G. Farbenindustrie AG, commonly known as IG Farben, was a German Chemical industry, chemical and Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical conglomerate (company), conglomerate. It was formed on December 2, 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies: Agfa-Gevaert, Agfa, BASF, Bayer, :de:Chemische Fabrik Griesheim-Elektron, Griesheim-Elektron, Hoechst AG, Hoechst, and Weiler-ter-Meer. It was seized by the Allies of World War II, Allies after World War II and split into its constituent companies; parts in East Germany were nationalized. IG Farben was once the largest company in Europe and the largest chemical and pharmaceutical company in the world. IG Farben scientists made fundamental contributions to all areas of chemistry and the pharmaceutical industry. Otto Bayer discovered the polyaddition for the synthesis of polyurethane in 1937, and three company scientists became List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates: Carl Bosch and Friedrich Bergius in 1931 "for their contribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerhard Schrader
Gerhard Schrader (25 February 1903 – 10 April 1990) was a German chemist specializing in the discovery of new insecticides, hoping to make progress in the fight against hunger in the world. Schrader is best known for his accidental discovery of nerve agents including sarin and tabun. Sarin is partially named after him: It was named in honor of its discoverers, Schrader, Otto Ambros, , and Hans-Jürgen von der Linde. Schrader was born in Bortfeld, near Wendeburg, Germany. He attended gymnasium in Braunschweig and later studied chemistry at Braunschweig University of Technology. He was later employed at the Bayer AG division of IG Farben. From 1926 onwards, Schrader was in the employment of the large German industrial conglomerate IG Farben in the discovery of new inseciticides, focusing his efforts on the organophosphates, a class of compounds that interact with acetylcholine esterases present in nerve cells and thus inhibit nerve impulse transfer in animals, leading to deat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva Protocol
The Protocol for the Prohibition of the Use in War of Asphyxiating, Poisonous or other Gases, and of Bacteriological Methods of Warfare, usually called the Geneva Protocol, is a treaty prohibiting the use of chemical and biological weapons in international armed conflicts. It was signed at Geneva on 17 June 1925 and entered into force on 8 February 1928. It was registered in ''League of Nations Treaty Series'' on 7 September 1929. The Geneva Protocol is a protocol to the Convention for the Supervision of the International Trade in Arms and Ammunition and in Implements of War signed on the same date, and followed the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907. It prohibits the use of "asphyxiating, poisonous or other gases, and of all analogous liquids, materials or devices" and "bacteriological methods of warfare". This is now understood to be a general prohibition on chemical weapons and biological weapons between state parties, but has nothing to say about production, storage or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosgene
Phosgene is an organic chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. It can be thought of chemically as the double acyl chloride analog of carbonic acid, or structurally as formaldehyde with the hydrogen atoms replaced by chlorine atoms. In 2013, about 75–80 % of global phosgene was consumed for isocyanates, 18% for polycarbonates and about 5% for other fine chemicals. Phosgene is extremely poisonous and was used as a chemical weapon during World War I, where it was responsible for 85,000 deaths. It is a highly potent pulmonary irritant and quickly filled enemy trenches due to it being a heavy gas. It is classified as a Schedule 3 substance under the Chemical Weapons Convention. In addition to its industrial production, small amounts occur from the breakdown and the combustion of organochlorine compounds, such as chloroform. Structure and basic properties Phosgene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |