|
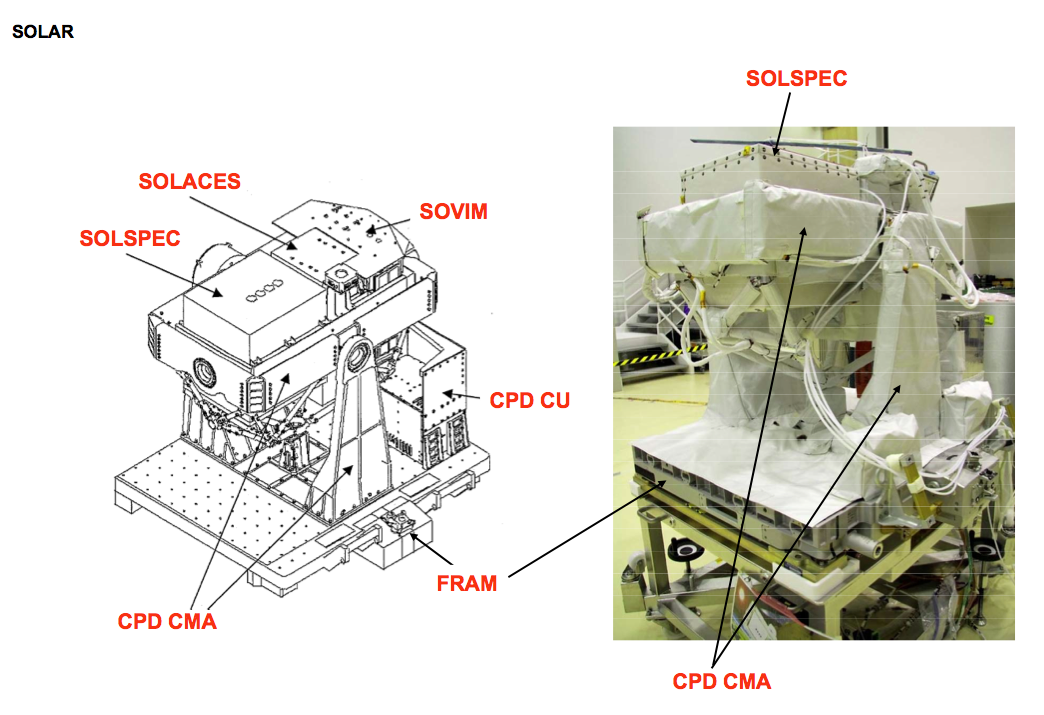
Solar (ISS Facility)
SOLAR was an European Space Agency, ESA science observatory on the Columbus (ISS module), Columbus Laboratory, which is part of the International Space Station. SOLAR was launched with Columbus in February 2008 aboard STS-122. It was externally mounted to Columbus with the European Technology Exposure Facility (EuTEF). SOLAR has three main space science instruments: SOVIMSOLSPECand SOL-ACES. Together they provide detailed measurements of the Sun's irradiance, spectral irradiance. The SOLAR platform and its instruments are controlled from thBelgian User Support and Operations Centre(B.USOC), located at thBelgian Institute for Space Aeronomy(BISA) in Uccle, Belgium. Instruments *SOVIM (''So''lar ''V''ariability and ''I''rradiance ''M''onitor) instrument is based on an earlier instrument (SOVA) which flew aboard the European Retrievable Carrier, launched on STS-46 in 1992. It is designed to measure solar radiation with wavelengths from 200 nanometers - 100 micrometers. This covers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-122 Sun Monitoring On The External Payload Facility Of Columbus (Solar)
STS-1 (Space Transportation System-1) was the first orbital spaceflight of NASA's Space Shuttle program. The first Space Shuttle orbiter, orbiter, Space Shuttle Columbia, ''Columbia'', launched on April 12, 1981, and returned on April 14, 1981, 54.5 hours later, having orbited the Earth 37 times. ''Columbia'' carried a crew of two—commander John Young (astronaut), John W. Young and pilot Robert Crippen, Robert L. Crippen. It was the first American crewed space flight since the Apollo–Soyuz, Apollo–Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) in 1975. STS-1 was also the maiden test flight of a new American spacecraft to carry a crew, though it was preceded by Approach and Landing Tests, atmospheric testing (ALT) of the orbiter and ground testing of the Space Shuttle system. The launch occurred on the 20th anniversary of Vostok 1, the first human spaceflight, performed by Yuri Gagarin for the Soviet Union, USSR. This was a coincidence rather than a celebration of the anniversary; a technical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure Spectrum, spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. In visible light a spectrometer can separate white light and measure individual narrow bands of color, called a spectrum. A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors. Spectrometers were History_of_spectroscopy, developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. The capability of spectroscopy to determine Analytical_chemistry#Spectroscopy, chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in Astronomical spectroscopy, astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of Astronomical_spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missions To The Sun
Mission (from Latin 'the act of sending out'), Missions or The Mission may refer to: Geography Australia *Mission River (Queensland) Canada *Mission, British Columbia, a district municipality *Mission, Calgary, Alberta, a neighbourhood * Okanagan Mission, a neighbourhood in Kelowna, British Columbia, commonly called "the Mission" *Mission River, a short river located at the delta of the Kaministiquia River of northern Ontario, Canada * Mission Ridge (British Columbia), a ridge in BC * Mission Ridge Ski Area, a Ski Area near the ridge in BC * Mission Lake, a lake in Saskatchewan United States * Mission, Delaware, an unincorporated community * Mission, Kansas, a city * Mission, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Mission, Minnesota, an unincorporated community * Mission, Oregon, an unincorporated community and census-designated place * Mission, South Dakota, a city * Mission, Texas, a city * Mission District, San Francisco, a neighborhood in San Francisco, Califo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Facilities On The International Space Station
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Greek natural philo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and electronic structure of matter to be investigated at the atomic, molecular and macro scale, and over astronomical distances. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Current applications of spectroscopy include biomedical spectroscopy in the areas of tissue analysis and medical imaging. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Research On The ISS
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOLAR ESA
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun ** Solar eclipse, an eclipse of a sun in which it is obstructed by the moon ** Solar System, the planetary system made up by the Sun and the objects orbiting it * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from ''Mesmer'', 2017 * "Solar", a song by Sault from ''Air'', 2022 * ”Solar”, a song by Stam1na from ''Taival'', 2018 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbus Extern
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to: * Christopher Columbus (1451–1506), the Italian explorer * Columbus, Ohio, the capital city of the U.S. state of Ohio * Columbus, Georgia, a city in the U.S. State of Georgia Columbus may also refer to: Places Extraterrestrial * Columbus (crater), a crater on Mars * ''Columbus'' (ISS module), the European module for the International Space Station * ''Columbus'' (spacecraft), a program to develop a European space station 1986–1991 Italy * Columbus (Rome), a residential district United States * Columbus, Arkansas * Columbus, Georgia, the 119th-most populous city in the United States, and the 2nd-largest in Georgia after Atlanta * Columbus, Illinois * Columbus, Indiana, known for modern architecture * Columbus, Kansas * Columbus, Kentucky * Columbus, Minnesota * Columbus, Mississippi * Columbus, Missouri * Columbus, Montana * Columbus, Nebraska * Columbus, New Jersey * Colum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cygnus NG-12
NG-12, previously known as OA-12, was the thirteenth flight of the Northrop Grumman robotic resupply spacecraft Cygnus (spacecraft), Cygnus and its twelfth Commercial Resupply Services flight to the International Space Station (ISS) for NASA. The mission launched on 2 November 2019 at 13:59:47 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC). This was the first launch of Cygnus under the Commercial Resupply Services 2 (CRS-2) contract. Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems, Orbital ATK and NASA jointly developed a new space transportation system to provide commercial cargo resupply services to the International Space Station (ISS). Under the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) program, then Orbital Sciences Corporation, Orbital Sciences designed and built Antares (rocket), Antares, a medium-class launch vehicle; Cygnus (spacecraft), Cygnus, an advanced maneuvering spacecraft, and a Pressurized Cargo Module which is provided by Orbital's industrial partner Thales Alenia Space. Northr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Rotation
Solar rotation varies with latitude. The Sun is not a solid body, but is composed of a gaseous plasma. Different latitudes rotate at different periods. The source of this differential rotation is an area of current research in solar astronomy. The rate of surface rotation is observed to be the fastest at the equator (latitude ) and to decrease as latitude increases. The solar rotation period is 25.67 days at the equator and 33.40 days at 75 degrees of latitude. The Carrington a system for tracking the Sun's rotation, as seen from at the current UTC time of , is CR . Surface rotation as an equation The differential rotation rate of the photosphere can be approximated by the equation: :\omega=A+B\,\sin^2(\varphi)+C\,\sin^4(\varphi) where \omega is the angular velocity in degrees per day, \varphi is the solar latitude, A is angular velocity at the equator, and B, C are constants controlling the decrease in velocity with increasing latitude. The values of A, B, and C differ d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |