|
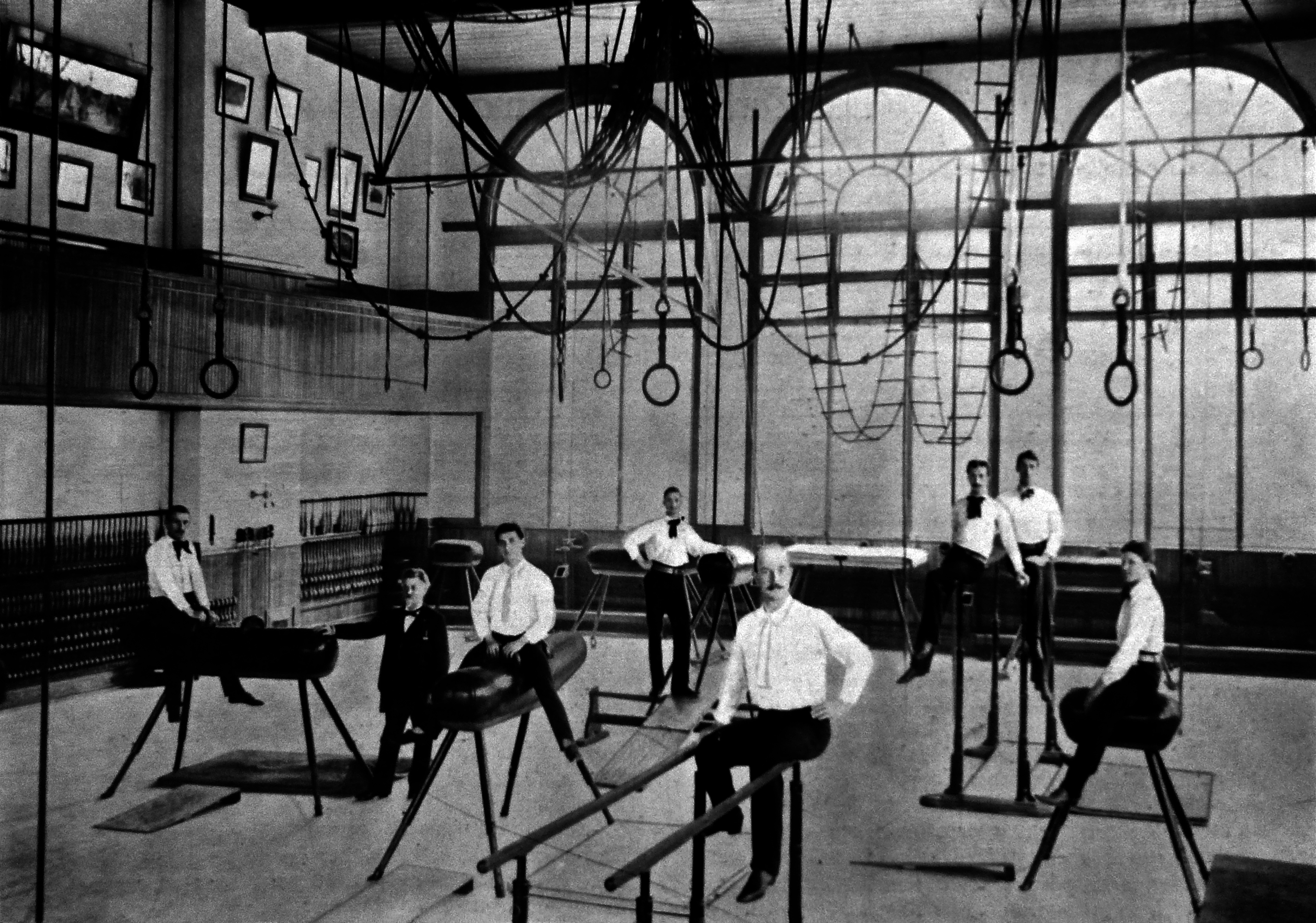
Sokol Movement
The Sokol movement (, ''falcon'') is an all-age gymnastics organization first founded in Prague in the Czech lands of Austria-Hungary in 1862 by Miroslav Tyrš and Jindřich Fügner. It was based upon the principle of " a strong mind in a sound body". The Sokol, through lectures, discussions, and group outings provided what Tyrš viewed as physical, moral, and intellectual training for the nation. This training extended to men of all ages and classes, and eventually to women. The movement also spread across all the regions populated by Slavic cultures, most of them part of either Austria-Hungary or the Russian Empire: present-day Slovakia, the Slovene Lands, Croatia, Serbia, Bulgaria, Poland (Polish Sokół movement), Ukraine, Belarus. In many of these nations, the organization also served as an early precursor to the Scouting movements. Though officially an institution "above politics", the Sokol played an important part in the development of Czech National Revival, Czech natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miroslav Tyrš
Miroslav Tyrš (born Friedrich Emanuel Tirsch, in Czech: Bedřich Tyrš; 17 September 1832 – 8 August 1884) was a Czech philosopher, art historian, sports organizer and together with Jindřich Fügner the cofounder of the Sokol movement. Early life Miroslav Tyrš was born Friedrich Emanuel Tirsch to a German doctor in Děčín. The family moved to Döbling near Vienna where his father, mother and two sisters died from tuberculosis leaving Miroslav orphaned at the age of six years. He was brought up by his Czech uncle in Kropáčova Vrutice near Mladá Boleslav and was assimilated into the Czech community.Robert Šimek: Miroslav Tyrš – Paže tuž, vlasti služ!, Profit.cz 201 In 1844, Tyrš, along with nine other scholars, undertook physical training with R. Stephany. He studied at the Gymnasium (school), gymnasium in Malá Strana, Prague and passed its final exam in Czech in 1850. At a time when students were required to take exams in the German language, yet Tyr� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, seventh largest EU country, covering a combined area of . It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordering seven countries. The territory is characterised by a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and Temperate climate, temperate transitional climate. The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Humans have been present on Polish soil since the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Glacial Period over 12,000 years ago. Culturally diverse throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marching
Marching refers to the organized, uniformed, steady walking forward in either rhythmic or route-step time; and, typically, it refers to overland movements on foot of military troops and units under field orders. Marching is often performed to march music and is typically associated with military and civilian ceremonial parades. It is a major part of military basic training in most countries and usually involves a system of drill commands. Purpose It is said that many ancient empires first developed marching as a way to move troops from one place to another without them getting mixed up with other troops. A soldier learning to march to drum cadences, martial music and shouted commands is considered an essential element of teaching military discipline. In the United States Marine Corps, close order drill is used to promote exercise, obeying orders, discipline, esprit de corps, confidence, and leadership. Military paces In the military venue there are various rhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles University
) , image_name = Carolinum_Logo.svg , image_size = 200px , established = , type = Public, Ancient , budget = 8.9 billion CZK , rector = Milena Králíčková , faculty = 4,057 , administrative_staff = 4,026 , students = 51,438 , undergrad = 32,520 , postgrad = 9,288 , doctoral = 7,428 , city = Prague , country = Czech Republic , campus = Urban , colors = , affiliations = Coimbra Group EUA Europaeum , website = Charles University ( cs, Univerzita Karlova, UK; la, Universitas Carolina; german: Karls-Universität), also known as Charles University in Prague or historically as the University of Prague ( la, Universitas Pragensis, links=no), is the oldest and largest university in the Czech Republic. It is one of the oldest universities in Europe in continuous operation. Today, the university consists of 17 faculties located in Prague, Hradec Králové, and Plzeň. Charles University belongs among the top three universities in Central and Eastern Europe. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romantic Nationalism
Romantic nationalism (also national romanticism, organic nationalism, identity nationalism) is the form of nationalism in which the state claims its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes such factors as language, race, ethnicity, culture, religion, and customs of the nation in its primal sense of those who were born within its culture. It can be applied to ethnic nationalism as well as civic nationalism. Romantic nationalism arose in reaction to dynastic or imperial hegemony, which assessed the legitimacy of the state from the top down, emanating from a monarch or other authority, which justified its existence. Such downward-radiating power might ultimately derive from a god or gods (see the divine right of kings and the Mandate of Heaven). Among the key themes of Romanticism, and its most enduring legacy, the cultural assertions of romantic nationalism have also been central in post-Enlightenment art and political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Ludwig Jahn
(11August 177815October 1852) was a German gymnastics educator and nationalist whose writing is credited with the founding of the German gymnastics ( Turner) movement as well as influencing the German Campaign of 1813, during which a coalition of German states effectively ended the occupation of Napoleon's First French Empire. His admirers know him as , roughly meaning "Father of Gymnastics ". Life was born in the village of in Brandenburg, Prussia. He studied theology and philology from 1796 to 1802 at the universities in , , and . After the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt in 1806, he joined the Prussian army. In 1809, he went to Berlin where he became a teacher at the and at the Plamann School. Brooding upon what he saw as the humiliation of his native land by Napoleon, conceived the idea of restoring the spirits of his countrymen by the development of their physical and moral powers through the practice of gymnastics. The first , or open-air gymnasium, was opened by in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turnverein
Turners (german: Turner) are members of German-American gymnastic clubs called Turnvereine. They promoted German culture, physical culture, and liberal politics. Turners, especially Francis Lieber, 1798–1872, were the leading sponsors of gymnastics as an American sport and the field of academic study. In Germany, a major gymnastic movement was started by ''Turnvater'' ("father of gymnastics") and nationalist Friedrich Ludwig Jahn in the early 19th century when Germany was occupied by Napoleon. The ''Turnvereine'' ("gymnastic unions"; from German ''turnen'' meaning “to practice gymnastics,” and ''Verein'' meaning “club, union”) were not only athletic but also political, reflecting their origin in similar ethnocentric "national gymnastic" organizations in Europe (such as the Czech Sokol), who were participants in various national movements for independence. The Turner movement in Germany was generally liberal in nature, and many Turners took part in the Revolutions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
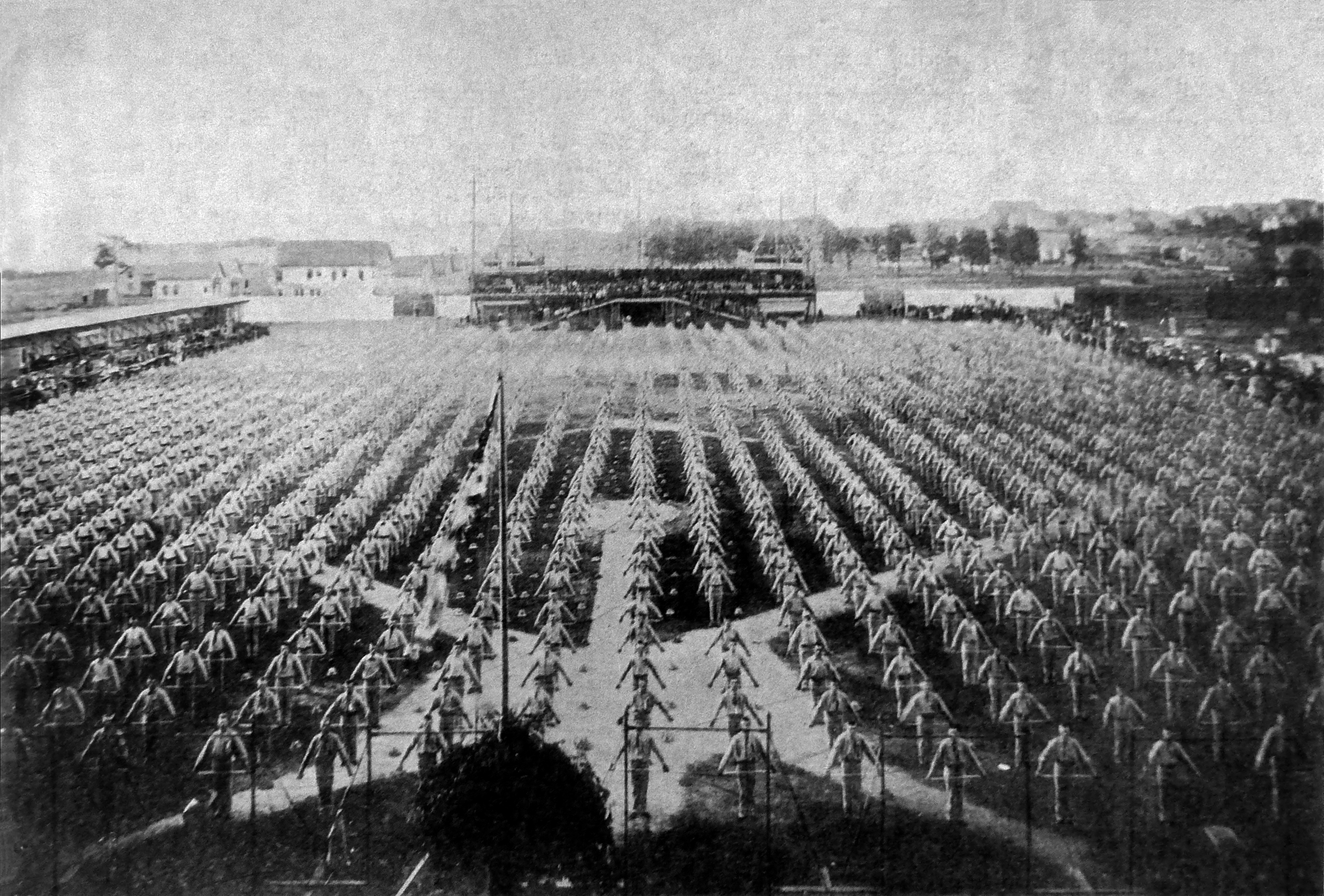
Group Of Sokols
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together. Groups of people * Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity * Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic identity * Religious group (other), a group whose members share the same religious identity * Social group, a group whose members share the same social identity * Tribal group, a group whose members share the same tribal identity * Organization, an entity that has a collective goal and is linked to an external environment * Peer group, an entity of three or more people with similar age, ability, experience, and interest Social science * In-group and out-group * Primary, secondary, and reference groups * Social group * Collectives Science and technology Mathematics * Group (mathematics), a set together with a binary operation satisfying certain algebraic conditions Chemistry * Functional group, a group of atoms whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Games
Mass games or mass gymnastics are a form of performing arts or gymnastics in which large numbers of performers take part in a highly regimented performance that emphasizes group dynamics rather than individual prowess. North Korea Mass games are now performed only in the Rungrado May Day Stadium but in the '90s there were mass games held at the Kim Il-sung Stadium and in the Pyongyang Gymnasium. Mass Games can basically be described as a synchronized socialist-realist spectacular, featuring over 100,000 participants in a 90-minute display of gymnastics, dance, acrobatics, and dramatic performance, accompanied by music and other effects, all wrapped in a highly politicized package. Students practiced every day from January onwards. The 90-minute performance is held every evening at 7pm and features the 'largest picture in the world' a giant mosaic of individual students each holding a book whose pages links with their neighbours’ to make up one gigantic scene. When the stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech National Revival
The Czech National Revival was a cultural movement which took place in the Czech lands during the 18th and 19th centuries. The purpose of this movement was to revive the Czech language, culture and national identity. The most prominent figures of the revival movement were Josef Dobrovský and Josef Jungmann. Background Following the Battle of White Mountain in 1620, Czech lands experienced Germanisation politics spearheaded by the Habsburg Emperors. The oppression was also connected with religion – up to 95% of the inhabitants of Bohemia were Protestants (''See Hussite'') when the Habsburgs took power. Although the Habsburgs had promised freedom of religion, they started rampant anti-Reformation and re-Catholicization efforts which made most of the Czech elites flee the country. This violent re-Catholicization has been suggested to be one of the reasons behind today's widespread Czech atheism. During the two following centuries Czech had been more or less eradicated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scouting
Scouting, also known as the Scout Movement, is a worldwide youth Social movement, movement employing the Scout method, a program of informal education with an emphasis on practical outdoor activities, including camping, woodcraft, aquatics, hiking, Backpacking (wilderness), backpacking, and sports. Another widely recognized movement characteristic is the Scout uniform, by intent hiding all differences of social standing in a country and encouraging equality, with neckerchief and campaign hat or comparable headwear. Distinctive uniform insignia include the fleur-de-lis and the trefoil, as well as Scout badge, merit badges and other patches. In 1907, Robert Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell, Robert Baden-Powell, a Lieutenant General in the British Army, held a Brownsea Island Scout camp, Scouting encampment on Brownsea Island in England. Baden-Powell wrote ''Scouting for Boys'' (London, 1908), partly based on his earlier military books. The Scout Movement of both Boy Scouts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)