|
Social Impact Incentives
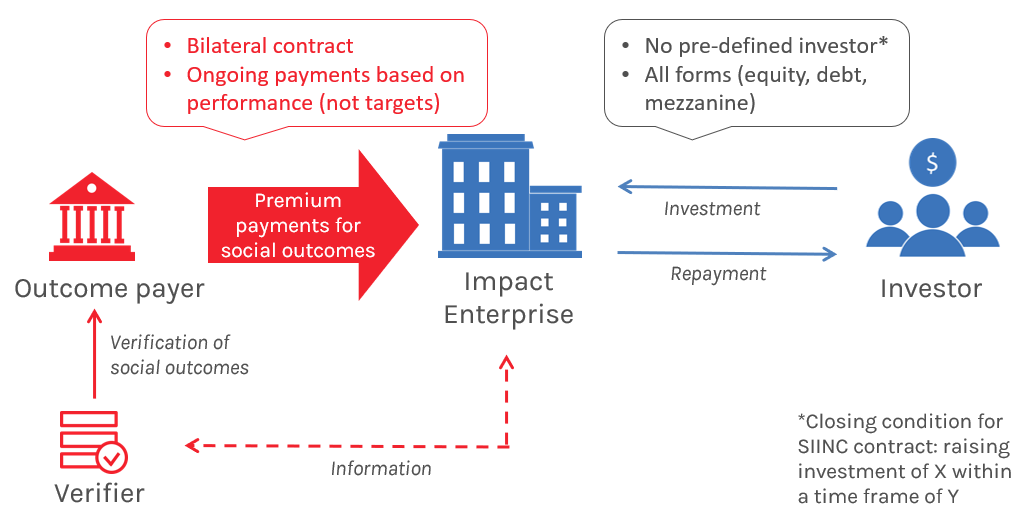
The Social Impact Incentives (SIINC) model is a blended finance instrument introduced for the first time in 2016. In the SIINC model, enterprises are provided with time-limited premium payments for achieving social impact, thus aligning profitability with their social impact and enabling them to attract growth capital. The SIINC agreement is a bilateral contract between an outcome funder (e.g. a development agency or a philanthropic organization) and an enterprise; an independent verifier assesses the impact performance and clears payments for disbursement; the investment between the enterprise and its investor is arranged via a separate contract. History SIINC was co-created by Roots of Impact and the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation in 2016 by exploring how to adapt pay-for-success models like impact bonds for market-based organizations. The Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation funded a pilot program in Latin America and the Caribbean which launched in 2016 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blended Finance
Blend finance is defined as "the strategic use of development finance and philanthropic funds to mobilize private capital flows to emerging and frontier markets", resulting in positive results for both investors and communities. Blended finance offers the possibility to scale up commercial financing for developing countries and to channel such financing toward investments with development impact. As such, blended finance is designed to support progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set forth by the United Nations. Meeting the SDGs will require an additional $2.5 trillion in private and public financing per year as of 2017 estimates, and an additional $13.5 trillion to implement the COP21 Paris climate accord. The concept of blended finance can contribute to raising the private financing needed. It was first recognized as a solution to the funding gap in the outcome document of the Third International Conference on Financing for Development in July 2015. Buildin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Agency For Development And Cooperation
The Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) is an office-level agency in the federal administration of Switzerland, and a part of the Federal Department of Foreign Affairs. Together with other federal offices, SDC is responsible for overall coordination of Swiss international development activities and cooperation with Eastern Europe, as well as humanitarian aid. According to the OECD, Switzerland's total official development assistance (ODA) increased in 2022 to USD 4.5 billion (preliminary data) due to an increase in in-donor refugee costs. This represented 0.56% of gross national income (GNI). History The SDC has been active in Burkina Faso since 1974. In 1993, the SDC ran an office in Eritrea, which closed in 2006 when the SDC stopped supporting its projects in Eritrea for political reasons. The SDC relaunched its support actions in Eritrea in 2017 and terminated it in 2025, after no progress in the field of migration was made in negotiations with the Eritrean go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter-American Development Bank
The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB or IADB) is an international development finance institution headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States of America. It serves as one of the leading sources of development financing for the countries of Latin America and the Caribbean. Established in 1959, the IDB supports Latin American and Caribbean economic, social, and institutional development and regional integration by lending to governments and sub-national agencies, developing new financial tools, creating enabling conditions for private-sector-led growth, convening and aligning countries around common interests, and bridging the region with the rest of the world. The IDB also provides extensive technical assistance to its borrowing member countries. It works across a range of sectors, including infrastructure, health, education, energy, citizen security, environmental sustainability, trade, transportation, housing, and small businesses. It works in conjunction with IDB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Ventures
New Ventures is a global program that provides services for the development of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) whose main goal is to generate a positive environmental or social change within their own communities. New Ventures were created in 1999 by the World Resources Institute, and it was established in emerging markets with a large biodiversity. It currently has centres in Brazil, China, Colombia, India, Indonesia and México. New Venture's reach varies in each country, but every Center offers free development services that provide SMEs with management tools and access to capital in order to make them grow and increase their positive impact. The project has assisted more than 600 enterprises worldwide. Global Centers Brazil New Ventures Brazil was created in 2002. It has assisted more than 10 enterprises. It organizes the "New Ventures Investor Forum" annually since 2004, which presents projects to global investors. The Center is currently directed by Marcelo Torres. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashoka (non-profit Organization)
Ashoka (formerly branded Ashoka: Innovators for the Public) is an American-based nonprofit organization that promotes social entrepreneurship by connecting and supporting individual social entrepreneurs. Ashoka invests in over 3,800 social entrepreneurs in over 90 countries worldwide. These individuals in turn become the people that others will try to follow by example. Social entrepreneurship also supports teens and gives them a way to flourish, to grow independently, while continuing to find support from those around them. An example of this independence is the way that young Asian teens, whose ultimate goal is to attend and eventually graduate from college use the business skills that they have learned will go a long way to meeting this ultimate goal. It is this change making experience that Ashoka offers everyone. globalization of social entrepreneurship benefits many. When jobs are created; not only does the economy benefit but society benefits as well from this entrepre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston Consulting Group
Boston Consulting Group, Inc. (BCG) is an American global management consulting firm founded in 1963 and headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts. It is one of the "Big Three (management consultancies), Big Three" (or MBB, the world's three largest management consulting firms by revenue) along with McKinsey & Company and Bain & Company. Since 2021, BCG has been led by the German executive Christoph Schweizer. History The firm was founded in 1963 as part of The Boston Safe Deposit and Trust Company. Bruce Henderson had been recruited from Arthur D. Little to establish the consulting arm operating as a subsidiary under the name Management and Consulting Division of the Boston Safe Deposit and Trust Company. Initially the division only advised clients of the bank, with billings for the first month at just US$500. Henderson hired his second consultant, Arthur P. Contas, in December 1963. In 1966, BCG opened its second office in Tokyo, Japan. In 1967, Henderson met Bill Bain (consulta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Impact Bond
A social impact bond (SIB), also known as pay-for-success financing, pay-for-success bond (US), social benefit bond (Australia), pay-for-benefit bond (Australia), social outcomes contract (UK), social impact partnership (Europe), social impact contract (Europe), or simply a social bond, is a type of outcomes-based contracting, whereby a contractor typically attempts to effect a policy of government but does not get paid by the government unless specified goals are achieved. The term was invented by Geoff Mulgan, chief executive of the Young Foundation. The first SIB was launched by UK-based Social Finance Ltd. in September 2010. By July 2019, 132 SIBs had been initiated in 25 countries, and they were worth more than $420m. , 23 countries use SIBs, with () 276 projects in place and capital raised to the value of $745m. History The social impact bond is a non-tradeable version of social policy bonds, first conceived by Ronnie Horesh, a New Zealand economist, in 1988. Since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Development Impact Bond
Development impact bonds (DIBs) are a performance-based investment instrument intended to finance development programmes in low resource countries, which are built off the model of social impact bond (SIB) model. In general, the model works the same: an investor provides upfront funding to the implementer of a program. An evaluator measures the results of the implementer's program. If these results hit a target set before the implementation period, an outcome payer agrees to provide investors a return on their capital. This ensures that investors are not simply engaging in concessionary lending. The first social impact bond was originated by Social Finance UK in 2010, supported by the Rockefeller Foundation, structured to reduce recidivism among inmates from Peterborough Prison. Based on the SIB model, a DIB creates a contract between private investors and donors or governments who have agreed upon a shared development goal. Investors advance fund development programmes with financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Impact ...
Social impact may refer to: *Social impact assessment *Social impact bond *Social impact theory *Social influence See also * Corporate social impact {{Disambig Impact Impact may refer to: * Impact (mechanics), a large force or mechanical shock over a short period of time * Impact, Texas, a town in Taylor County, Texas, US Science and technology * Impact crater, a meteor crater caused by an impact event * Imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |