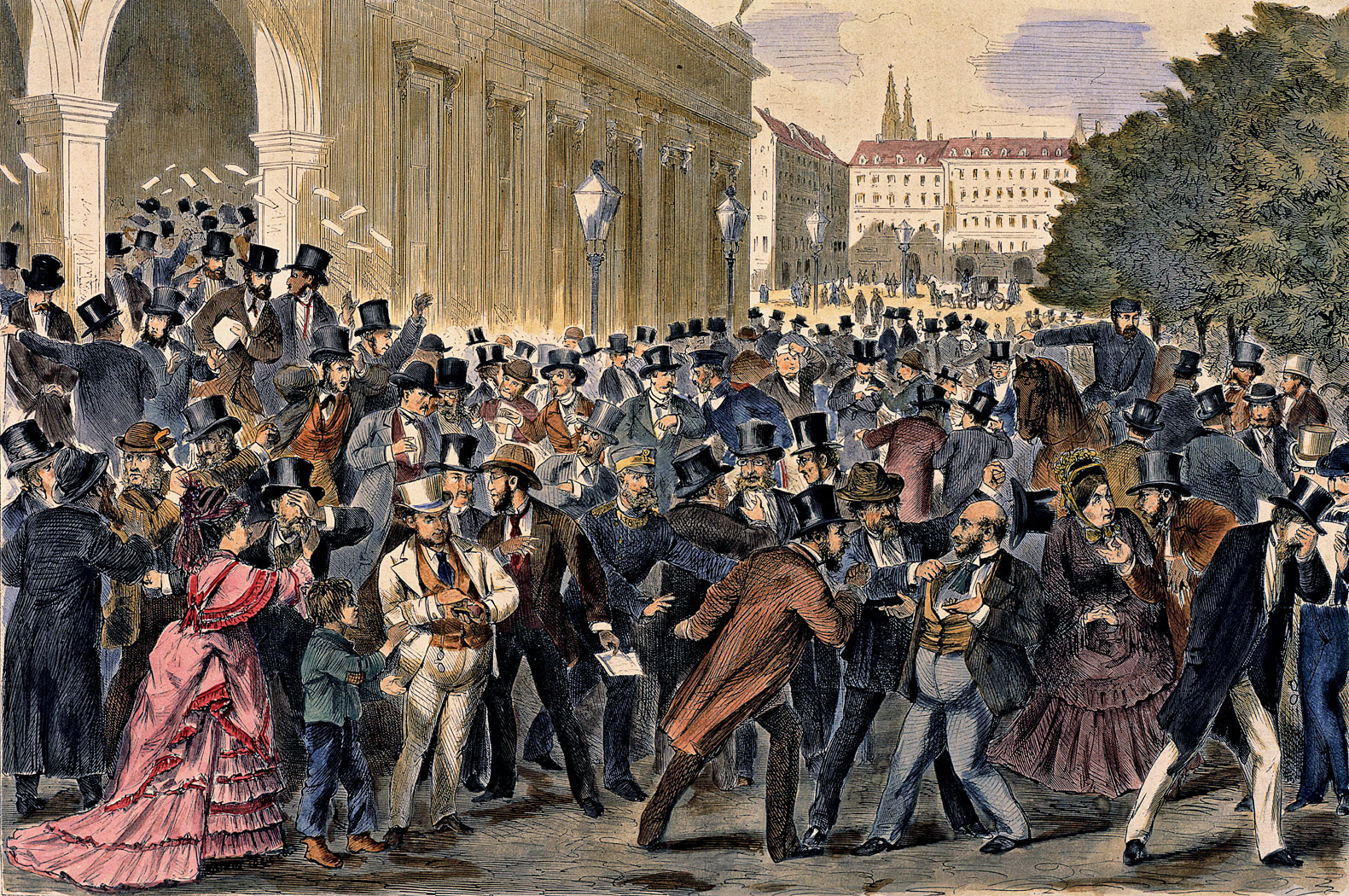|
Social Crisis
A social crisis (or alternately a societal crisis) is a crisis in which the basic structure of a society experiences some drastic interruption or decline. Overview A social crisis can be sudden and immediate, or it can be some gross societal inequity which might take decades to develop, or it could be a wide range of scenarios or situations which fall somewhere between those conceptual modes. This can include *a ''political'' crisis such as a coup d'etat, or mass civil disorder, due to political and/or social disorder, due to military conflict, or mass protests, or dysfunction within any part of or the central body of government. *an ''economic'' crisis which can range from or include a possible financial crisis, currency crisis, or any economic shock, or any breakdown or major dysfunctions within the economic system, *or a major upheaval due to a ''natural disaster'', which can include severe weather, or epidemics, or drought, or famine, or other events related to the natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Disorder
Civil disorder, also known as civil disturbance, civil unrest, civil strife, or turmoil, are situations when law enforcement and security forces struggle to Public order policing, maintain public order or tranquility. Causes Any number of things may cause civil disorder, whether it is a single cause or a combination of causes; however, most are born from political grievances, economic inequality, economic disparities, social discord, but historically have been the result of long-standing oppression by a group of people towards another. Civil disorder arising from political grievances can include a range of events, from a simple protest to a mass civil disobedience. These events can be spontaneous, but can also be planned. These events can turn violent when agitators and law enforcers overreact. Civil disorder has in history arisen from economic disputes, political reasons (such as in opposition to oppressive or tyrannical government forces), religious opposition, racial oppre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with Bank run#Systemic banking crises, banking panics, and many recessions coincided with these panics. Other situations that are often called financial crises include stock market crashes and the bursting of other financial Economic bubble, bubbles, currency crisis, currency crises, and sovereign defaults. Financial crises directly result in a loss of paper wealth but do not necessarily result in significant changes in the real economy (for example, the crisis resulting from the famous tulip mania bubble in the 17th century). Many economists have offered theories about how financial crises develop and how they could be prevented. There is little consensus and financial crises continue to occur from time to time. It is apparent however that a consistent feature of bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency Crisis
A currency crisis is a type of financial crisis, and is often associated with a real economic crisis. A currency crisis raises the probability of a banking crisis or a default crisis. During a currency crisis the value of foreign denominated debt will rise drastically relative to the declining value of the home currency. Generally doubt exists as to whether a country's central bank has sufficient foreign exchange reserves to maintain the country's fixed exchange rate, if it has any. The crisis is often accompanied by a speculative attack in the foreign exchange market. A currency crisis results from chronic balance of payments deficits, and thus is also called a balance of payments crisis. Often such a crisis culminates in a devaluation of the currency. Financial institutions and the government will struggle to meet debt obligations and economic crisis may ensue. Causation also runs the other way. The probability of a currency crisis rises when a country is experiencing a banki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Disaster
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or Hazard#Natural hazard, hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides - including submarine landslides, tropical cyclones, volcanism, volcanic activity and wildfires. Additional natural hazards include blizzards, dust storms, firestorms, hails, ice storms, sinkholes, thunderstorms, tornadoes and tsunamis. A natural disaster can cause list of natural disasters by death toll, loss of life or property damage, damage property. It typically causes economic damage. How bad the damage is depends on how well people are Emergency management, prepared for disasters and how strong the buildings, roads, and other Infrastructure, structures are. Scholars have argued the term "natural disaster" is unsuitable and should be abandoned. Instead, the simpler term ''disaster'' could be used. At the same time, the type of haz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Disorder
Civil disorder, also known as civil disturbance, civil unrest, civil strife, or turmoil, are situations when law enforcement and security forces struggle to Public order policing, maintain public order or tranquility. Causes Any number of things may cause civil disorder, whether it is a single cause or a combination of causes; however, most are born from political grievances, economic inequality, economic disparities, social discord, but historically have been the result of long-standing oppression by a group of people towards another. Civil disorder arising from political grievances can include a range of events, from a simple protest to a mass civil disobedience. These events can be spontaneous, but can also be planned. These events can turn violent when agitators and law enforcers overreact. Civil disorder has in history arisen from economic disputes, political reasons (such as in opposition to oppressive or tyrannical government forces), religious opposition, racial oppre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with Bank run#Systemic banking crises, banking panics, and many recessions coincided with these panics. Other situations that are often called financial crises include stock market crashes and the bursting of other financial Economic bubble, bubbles, currency crisis, currency crises, and sovereign defaults. Financial crises directly result in a loss of paper wealth but do not necessarily result in significant changes in the real economy (for example, the crisis resulting from the famous tulip mania bubble in the 17th century). Many economists have offered theories about how financial crises develop and how they could be prevented. There is little consensus and financial crises continue to occur from time to time. It is apparent however that a consistent feature of bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Societal Collapse
Societal collapse (also known as civilizational collapse or systems collapse) is the fall of a complex human society characterized by the loss of cultural identity and of social complexity as an Complex adaptive system, adaptive system, the downfall of government, and the rise of violence. Possible causes of a societal collapse include natural catastrophe, war, pandemic, pestilence, famine, economic collapse, population decline or overshoot (population), overshoot, mass migration, Competence (human resources), incompetent leaders, and sabotage by rival civilizations. A collapsed society may revert to a more primitive state, be absorbed into a stronger society, or completely disappear. Virtually all civilizations have suffered such a fate, regardless of their size or complexity. Most never recovered, such as the Western and Eastern Roman Empires, the Spanish conquest of the Maya, Maya civilization, and the History of Easter Island#Destruction of society and population, Easter Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |