|
Smith-class Destroyer
The ''Smith''-class destroyers were the first ocean-going destroyers in the United States Navy, and the first to be driven by steam turbines instead of the reciprocating engines fitted in the sixteen earlier and much smaller torpedo boat destroyers ordered in 1898. and are sometimes considered to be ''Flusser''-class ships. Also, since ''Flusser'' was completed first, some period documentation refers to the entire class as ''Flusser''s.Friedman, pp. 22–28, 454–455 The first three of the class were ordered under the Act of 29 June 1906 "to have the highest practical speed, and to cost, exclusive of armament, not to exceed seven hundred and fifty thousand dollars each". The remaining pair were ordered under the Act of 7 March 1907 "to have the highest practical speed, and to cost, exclusive of armament, not to exceed eight hundred thousand dollars each". All of the ships served as convoy escorts in World War I, and several attacked U-boats. The latter four vessels were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Flag 48 Stars
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
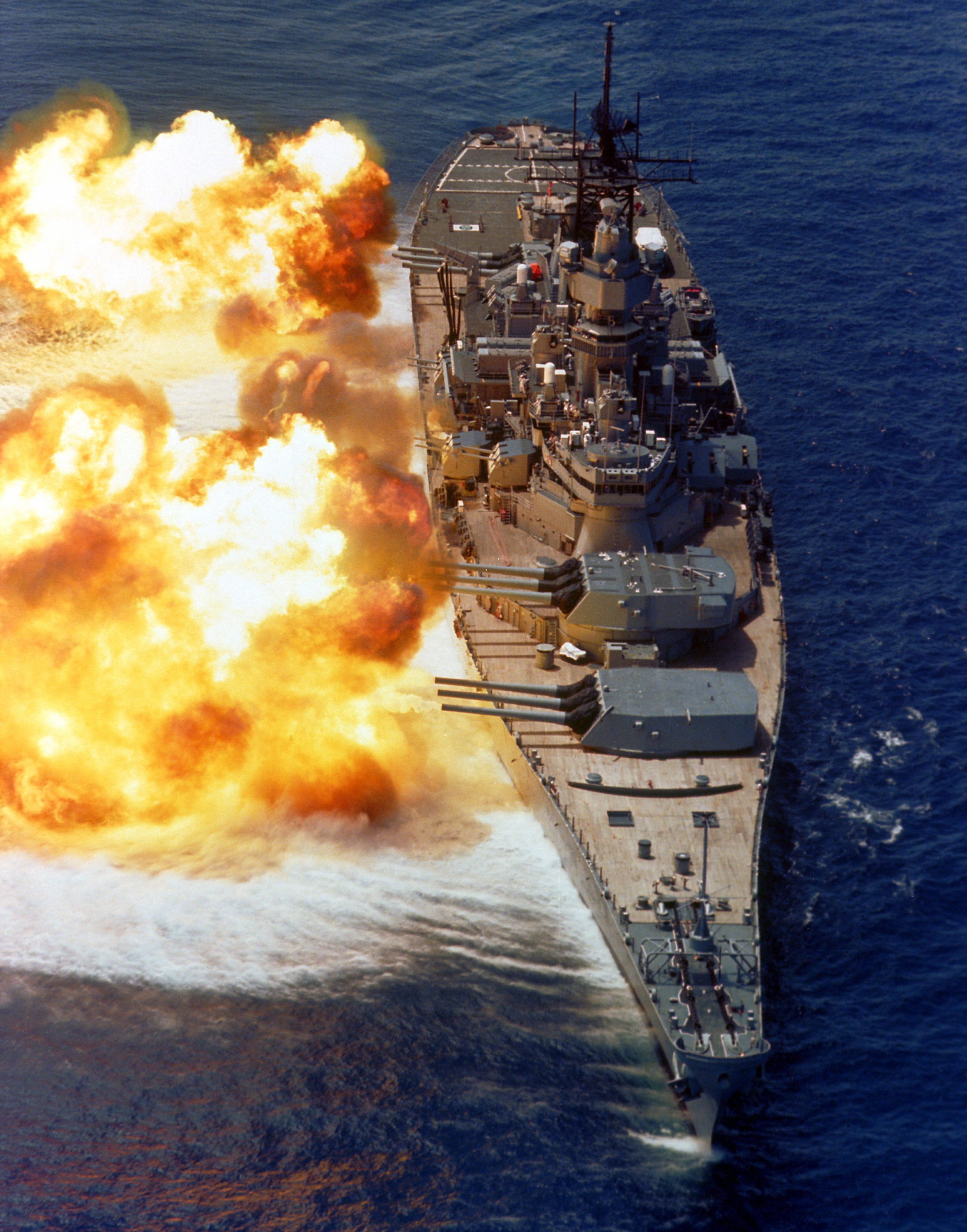
Battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ironclad warship,Stoll, J. ''Steaming in the Dark?'', Journal of Conflict Resolution Vol. 36 No. 2, June 1992. now referred to by historians as pre-dreadnought battleships. In 1906, the commissioning of into the United Kingdom's Royal Navy heralded a revolution in the field of battleship design. Subsequent battleship designs, influenced by HMS ''Dreadnought'', were referred to as "dreadnoughts", though the term eventually became obsolete as dreadnoughts became the only type of battleship in common use. Battleships were a symbol of naval dominance and national might, and for decades the battleship was a major factor in both diplomacy and military strategy.Sondhaus, L. ''Naval Warfare 1815–1914'', . A global arms race in battleship con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbinia
''Turbinia'' was the first steam turbine-powered steamship. Built as an experimental vessel in 1894, and easily the fastest ship in the world at that time, ''Turbinia'' was demonstrated dramatically at the Spithead Navy Review in 1897 and set the standard for the next generation of steamships, the majority of which would be turbine powered. The vessel is currently located at the Discovery Museum in Newcastle upon Tyne, North East England, while her original powerplant is located at the Science Museum in London. Development Charles Algernon Parsons invented the modern steam turbine in 1884, and having foreseen its potential to power ships, he set up the Parsons Marine Steam Turbine Company with five associates in 1893. To develop this, he had the experimental vessel ''Turbinia'' built in a light design of steel by the firm of Brown and Hood, based at Wallsend on Tyne in the North East of England. The Admiralty was kept informed of developments, and ''Turbinia'' was launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Charles Parsons
Sir Charles Algernon Parsons, (13 June 1854 – 11 February 1931) was an Anglo-Irish engineer, best known for his invention of the compound steam turbine, and as the eponym of C. A. Parsons and Company, C. A. Parsons and Company. He worked as an engineer on dynamo and turbine design, and power generation, with great influence on the naval and electrical engineering fields. He also developed optical equipment for searchlights and telescopes. Career and commercial activity Parsons was born into an Anglo-Irish family in London as the youngest son of the famous astronomer William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse. (The family seat is Birr Castle, County Offaly, Ireland, and the town of Birr, County Offaly, Birr was called Parsonstown, after the family, from 1620 to 1901.) With his three brothers, Parsons was educated at home in Ireland by private tutors (including John Purser (mathematician), John Purser), all of whom were well versed in the sciences and also acted as pract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Drive
A direct-drive mechanism is a mechanism design where the force or torque from a prime mover is transmitted directly to the effector device (such as the drive wheels of a vehicle) without involving any intermediate couplings such as a gear train or a belt.Asada, H., & Kanade, T. (1983) Design of direct-drive mechanical arms' in ''Journal of Vibration, Acoustics, Stress, and Reliability in Design'', Volume 105, Issue 3, pp.312-316 History In the late 19th century and early 20th century, some of the earliest locomotives and cars used direct drive transmissions at higher speeds. Direct-drive mechanisms for industrial arms began to be possible in the 1980s, with the use of rare-earth magnetic materials. The first direct-drive arm was built in 1981 at Carnegie Mellon University. Today the most commonly used magnets are neodymium magnets. Design Direct-drive systems are characterized by smooth torque transmission, and nearly-zero backlash.Bruno Siciliano, Oussama Khatib (Eds., 2008 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
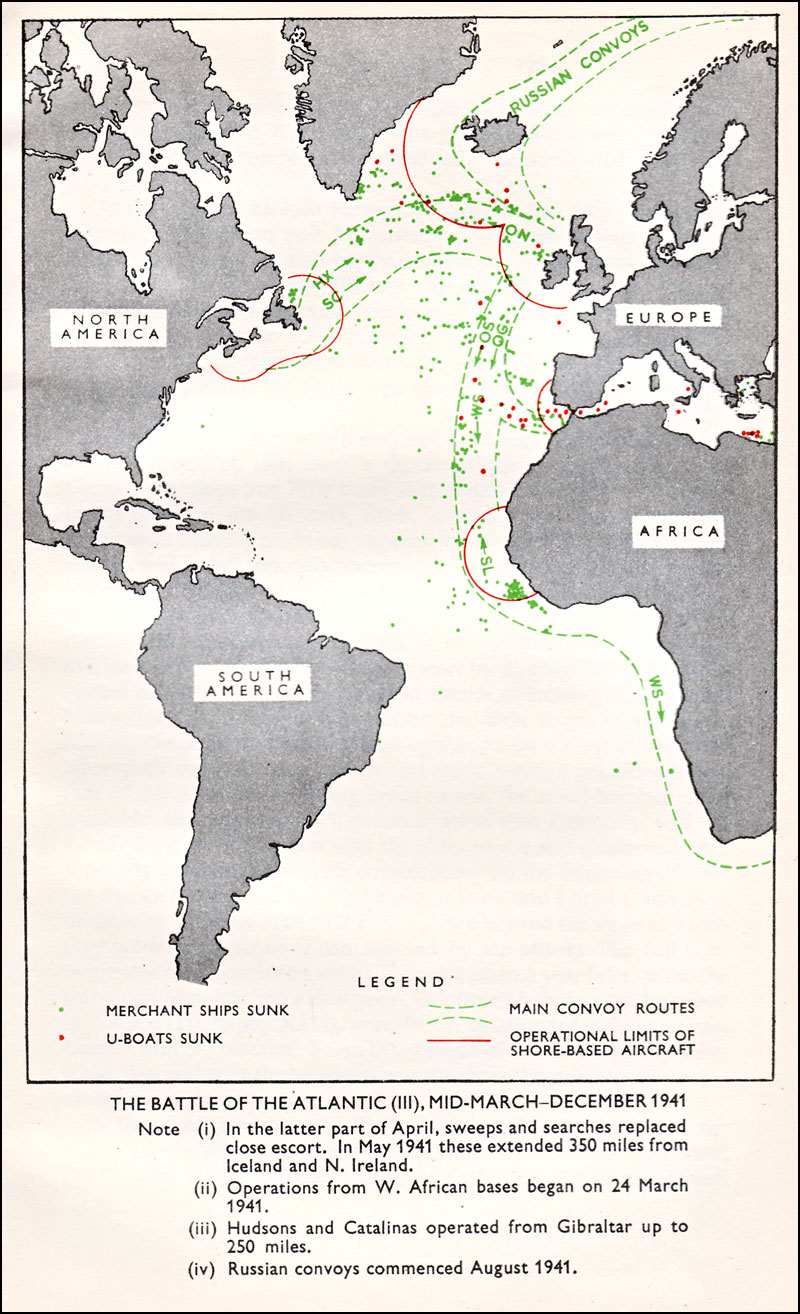
Convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used in a non-military sense, for example when driving through remote areas. Naval convoys Age of Sail Naval convoys have been in use for centuries, with examples of merchant ships traveling under naval protection dating to the 12th century. The use of organized naval convoys dates from when ships began to be separated into specialist classes and national navies were established. By the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, effective naval convoy tactics had been developed to ward off pirates and privateers. Some convoys contained several hundred merchant ships. The most enduring system of convoys were the Spanish treasure fleets, that sailed from the 1520s until 1790. When merchant ships sailed independently, a privateer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive hydraulic shock. Most depth charges use high explosive charges and a fuze set to detonate the charge, typically at a specific depth. Depth charges can be dropped by ships, patrol aircraft, and helicopters. Depth charges were developed during World War I, and were one of the first viable methods of attacking a submarine underwater. They were widely used in World War I and World War II, and remained part of the anti-submarine arsenals of many navies during the Cold War, during which they were supplemented, and later largely replaced, by anti-submarine homing torpedoes. A depth charge fitted with a nuclear warhead is also known as a " nuclear depth bomb". These were designed to be dropped from a patrol plane or deployed by an anti-submarine missile from a surface ship, or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-air Warfare
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, subsurface ( submarine launched), and air-based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements, and passive measures (e.g. barrage balloons). It may be used to protect naval, ground, and air forces in any location. However, for most countries, the main effort has tended to be homeland defence. NATO refers to airborne air defence as counter-air and naval air defence as anti-aircraft warfare. Missile defence is an extension of air defence, as are initiatives to adapt air defence to the task of intercepting any projectile in flight. In some countries, such as Britain and Germany during the Second World War, the Soviet Union, and modern NATO and the United States, ground-based air defence and air defence aircraft h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-submarine Warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations are typically carried out to protect friendly shipping and coastal facilities from submarine attacks and to overcome blockades. Successful ASW operations typically involved a combination of sensor and weapon technologies, along with effective deployment strategies and sufficiently trained personnel. Typically, sophisticated sonar equipment is used for first detecting, then classifying, locating, and tracking a target submarine. Sensors are therefore a key element of ASW. Common weapons for attacking submarines include torpedoes and naval mines, which can both be launched from an array of air, surface, and underwater platforms. ASW capabilities are often considered of significant strategic importance, particularly following provocative instances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of self-propelled Whitehead torpedoes. These were inshore craft created to counter both the threat of battleships and other slow and heavily armed ships by using speed, agility, and powerful torpedoes, and the overwhelming expense of building a like number of capital ships to counter an enemy's. A swarm of expendable torpedo boats attacking en masse could overwhelm a larger ship's ability to fight them off using its large but cumbersome guns. A fleet of torpedo boats could pose a similar threat to an adversary's capital ships, albeit only in the coastal areas to which their small size and limited fuel load restricted them. The introduction of fast torpedo boats in the late 19th century was a serious concern to the era's naval strategists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model T Ford
The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. The relatively low price was partly the result of Ford's efficient fabrication, including assembly line production instead of individual handcrafting. It was mainly designed by an American ( Childe Harold Wills) and two Hungarian engineers (Joseph A. Galamb, Eugene Farkas). The Model T was colloquially known as the "Tin Lizzie", "Leaping Lena" or "flivver". The Ford Model T was named the most influential car of the 20th century in the 1999 Car of the Century competition, ahead of the BMC Mini, Citroën DS, and Volkswagen Beetle. Ford's Model T was successful not only because it provided inexpensive transportation on a massive scale, but also because the car signified innovation for the rising middle class and became a powerful symbol of the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great White Fleet
The Great White Fleet was the popular nickname for the group of United States Navy battleships which completed a journey around the globe from December 16, 1907 to February 22, 1909 by order of President Theodore Roosevelt. Its mission was to make friendly courtesy visits to numerous countries while displaying new U.S. naval power to the world. One goal was to deter a threatened war with Japan since tensions were high in 1907. It familiarized the 14,500 officers and men with the logistical and planning needs for extended fleet action far from home. Hulls were painted a stark white, giving the armada its nickname. It consisted of 16 battleships divided into two squadrons, along with various small escorts.The Great White Fleet by Department of the Navy – Naval History and Heritage Comman [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |