|
Slovak Jews
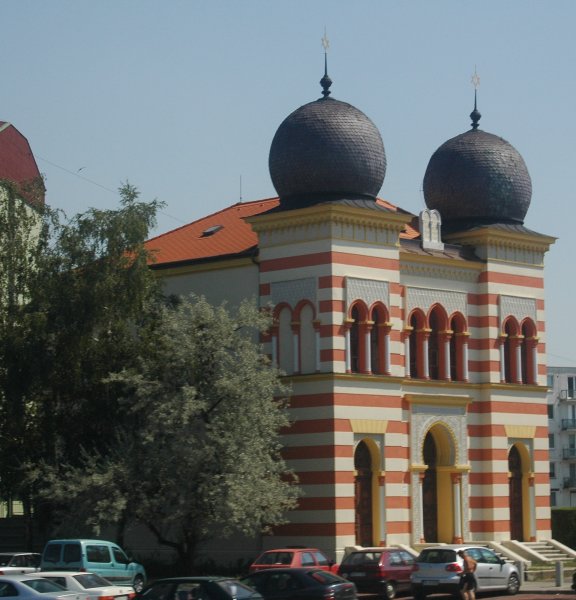
The history of the Jews in Slovakia goes back to the 11th century, when the first Jews settled in the area. Early history In the 14th century, about 800 Jews lived in Bratislava, the majority of them engaged in commerce and money lending. In the early 15th century, a Jewish cemetery was established at Tisinec and was in use until 1892. In 1494, a blood libel caused sixteen Jews to be burned at the stake in Trnava, and in 1526, after the Battle of Mohács, Jews were expelled from all major towns. In 1529, thirty Jews were burned at the stake in Pezinok. In the late 17th century and early 18th century, Jews began to return to their original cities and establish organized communities, though they were barred from many trading industries and often in conflict with non-Jews. In 1683, hundreds of Jews from Moravia fled to the Hungarian Kingdom, seeking refuge from Kuruc riots and restrictions on their living imposed in Moravia. In 1700, a leading yeshiva was established in Bratisl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Language
Slovak ( ; endonym: or ), is a West Slavic language of the Czech-Slovak languages, Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script and formerly in Cyrillic script. It is part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Slovak is closely related to Czech language, Czech, to the point of very high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish language, Polish. Like other Slavic languages, Slovak is a fusional language with a complex system of morphology (linguistics), morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German language, German, as well as other Slavic languages. History The Czech–Slovak gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
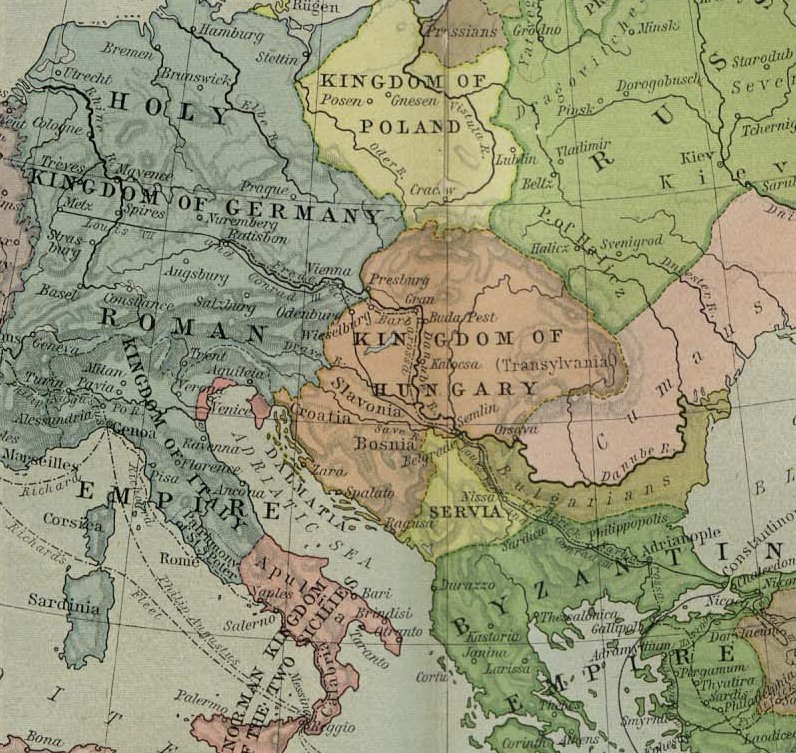
Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor
Joseph II (13 March 1741 – 20 February 1790) was Holy Roman Emperor from 18 August 1765 and sole ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 29 November 1780 until his death. He was the eldest son of Empress Maria Theresa and her husband, Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Francis I, and the brother of Marie Antoinette, Leopold II, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold II, Maria Carolina of Austria, and Maria Amalia, Duchess of Parma. He was thus the first ruler in the Austrian dominions of the union of the Houses of House of Habsburg, Habsburg and House of Lorraine, Lorraine, styled Habsburg-Lorraine. Joseph was a proponent of enlightened absolutism like his brother Leopold II, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold II; however, his commitment to secularizing, liberalizing and modernizing reforms resulted in significant opposition, which resulted in failure to fully implement his programs. Meanwhile, despite making some territorial gains, his reckless foreign policy badly isolated Austria. He has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovakism
Czechoslovakism (, ) is a concept which underlines reciprocity of the Czech people, Czechs and the Slovak people, Slovaks. It is best known as an ideology which holds that there is one Czechoslovak nation, though it might also appear as a political program of two nations living in one common state. The climax of Czechoslovakism fell on 1918-1938, when as a one-nation-theory it became the official political doctrine of Czechoslovak Republic (1918-1938), Czechoslovakia; its best known representative was Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk, Tomáš Masaryk. Today Czechoslovakism as political concept or ideology is almost defunct; its remnant is a general sentiment of cultural affinity, present among many Czechs and Slovaks. Antecedents Except some 70 years of Great Moravia in the early Medieval era, until the 20th century the peoples in the basins of Upper Elbe, Morava (river), Morava, Váh, Nitra (river), Nitra and Hornád have never lived in a common state. Throughout ages they were gradual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Irredentism
Hungarian irredentism or Greater Hungary ( ) are irredentist political ideas concerning redemption of territories of the historical Kingdom of Hungary. The objective is to at least regain control over Hungarian-populated areas in Hungary's neighbouring countries. Hungarian historiography uses the term "Historic Hungary" (). "Whole Hungary" () is also commonly used by supporters of this ideology. The Treaty of Trianon defined the current borders of Hungary and, compared against the claims of the pre-war Kingdom, post-Trianon Hungary had approximately 72% less land stake and about two-thirds fewer inhabitants, almost 5 million of these being of Hungarian ethnicity. However, only 54% of the inhabitants of the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary were Hungarians before World War I. Following the treaty's instatement, Hungarian leaders became inclined towards revoking some of its terms. This political aim gained greater attention and was a serious national concern up through the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Antisemitism
Economic antisemitism is antisemitism that uses stereotypes and canards that are based on negative perceptions or assertions of the economic status, occupations, or economic behavior of Jews, at times leading to various governmental policies, regulations, taxes, and laws that target or disproportionately impact the economic status, occupations, or behavior of Jews. Relationship to religious antisemitism Leon Poliakov writes that economic antisemitism is not a distinct form of antisemitism but merely a manifestation of theological antisemitism (without the theological causes of economic antisemitism, there would be no economic antisemitism). On the other hand, Derek Penslar contends that in the modern era, economic antisemitism is "distinct and nearly constant" but theological antisemitism is "often subdued". Stereotypes and canards Derek Penslar describes modern economic antisemitism as a "double helix of intersecting paradigms, the first associating the Jew with paupers an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Antisemitism
Religious antisemitism is the aversion to or discrimination against Jews as a whole based on religious doctrines of supersession, which expect or demand the disappearance of Judaism and the conversion of Jews to other faiths. This form of antisemitism has frequently served as the basis for false claims and religious antisemitic tropes against Judaism. Sometimes, it is called theological antisemitism. Some scholars have argued that modern antisemitism is primarily based on nonreligious factors, John Higham (historian), John Higham is emblematic of this school of thought. However, this interpretation has been challenged. In 1966, Charles Glock and Rodney Stark first published public opinion polling data, which showed that most Americans based their stereotypes of Jews on religion. Since then, further opinion polling in America and Europe has supported this conclusion. Origins Father Edward Flannery, in his 1965 book ''The Anguish of the Jew: Twenty-Three Centuries of Antisemiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Nationalism
Slovak nationalism is an ethnic nationalist ideology that asserts that the Slovaks are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of the Slovaks. History Modern Slovak nationalism first arose in the 19th century in response to Magyarization of Slovak-inhabited territories in the Kingdom of Hungary. It was based on two main ideas: a historical state right based on a continuity with the early medieval Great Moravian Empire and an identity associated with the Slavs. Ethnic and civic nationalism During the century-long period spanning from Slovakia's semi-independence as part of democratic Czechoslovakia in 1918, to the liberal democratic independent republic of the early 2020s, Slovak nationalism had gradually evolved into several different ideological strands. One is the continued ethnic nationalism, focused mainly on the Slovak ethnic majority and Slovakia as a primarily Slovak nation state. This nationalism occurs both in moderate and radical forms. The other major strand is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Emancipation
Jewish emancipation was the process in various nations in Europe of eliminating Jewish disabilities, to which European Jews were then subject, and the recognition of Jews as entitled to equality and citizenship rights. It included efforts within the community to integrate into their societies as citizens. It occurred gradually between the late 18th century and the early 20th century. Jewish emancipation followed after the Age of Enlightenment and the concurrent Haskalah, or Jewish Enlightenment. Various nations repealed or superseded previous discriminatory laws applied specifically against Jews where they resided. Before the emancipation, most Jews were isolated in residential areas from the rest of the society; emancipation was a major goal of European Jews of that time, who worked within their communities to achieve integration in the majority societies and broader education. Many became active politically and culturally within wider European civil society as Jews gained f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolog Judaism
Neologs (, "Neolog faction") are one of the two large communal organizations among Hungarian Jewry. Socially, the liberal and modernist Neologs had been more inclined toward integration into Hungarian society since the Era of Emancipation in the 19th century. This was their main feature, and they were largely the representative body of urban, assimilated middle- and upper-class Jews. Religiously, the Neolog rabbinate was influenced primarily by Zecharias Frankel's Positive-Historical School, from which Conservative Judaism evolved as well, although the formal rabbinical leadership had little sway over the largely assimilationist communal establishment and congregants. Their rift with the traditionalist and conservative Orthodox Jews was institutionalized following the 1868–1869 Hungarian Jewish Congress, and they became a separate communal organization. The Neologs remained organizationally independent in those territories ceded under the terms of the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Status Quo (Hungarian Jews)
The Schism in Hungarian Jewry (, "Orthodox-Neolog Schism"; , trans. ''Die Teilung in Ungarn'', "The Division in Hungary") was the institutional division of the Jewish community in the Kingdom of Hungary between 1869 and 1871, following a failed attempt to establish a national, united representative organization. The founding congress of the new body was held during an ongoing conflict between the traditionalist Orthodox party and its modernist Neolog rivals, which had been raging for decades. The traditionalists, fearing their opponents would dominate the new body, seceded and then lobbied the government to allow the formation of an independent Orthodox supracommunal organization with a policy of strict separation from the Neologs. When faced with the need to choose between the two, a third faction of "Status Quo" congregations emerged, refusing to join either and remaining fully autonomous, without a higher authority. While a large proportion of communities retained a cohesive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodox Judaism
Orthodox Judaism is a collective term for the traditionalist branches of contemporary Judaism. Theologically, it is chiefly defined by regarding the Torah, both Torah, Written and Oral Torah, Oral, as literally revelation, revealed by God in Judaism, God on Mount Sinai (Bible), Mount Sinai and faithfully transmitted ever since. Orthodox Judaism therefore advocates a strict observance of Jewish Law, or ''halakha'', which is to be Posek, interpreted and determined only according to traditional methods and in adherence to the continuum of received precedent through the ages. It regards the entire ''halakhic'' system as ultimately grounded in immutable revelation, essentially beyond external and historical influence. More than any theoretical issue, obeying the Kosher, dietary, Tumah and taharah, purity, ethical and other laws of ''halakha'' is the hallmark of Orthodoxy. Practicing members are easily distinguishable by their lifestyle, refraining from doing 39 Melakhot, numerous rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |