|
Slovak Expeditionary Army Group
The Slovak Expeditionary Army Group was an element of the military forces of the Slovak Republic that fought under Nazi German command on the Eastern Front during World War II. Background The Slovak Republic was a puppet state established on 14 March 1939. It possessed a small army of its own, largely made up of parts inherited from the old Czechoslovak Army. The 1st Slovak Infantry Division took part in the German invasion of Poland in September 1939. In the aftermath of the German invasion of France, the German government consolidated its control of the Slovak regime. On 21 June 1941, the Slovak government not informed about the invasion of Russia and offered to participate in the German invasion of the Soviet Union. Germany accepted the following day. The Slovak Army was called up, as the regime sought to demonstrate its indispensability to Nazi Germany and its greater loyalty than Hungary. History The Slovak Expeditionary Army Group of about 45,000 men entered the Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Forces Of The Slovak Republic
The Slovak Ground Forces (), also known as the Slovak Army, are the land forces of the Slovak Armed Forces. Organization * Ground Forces Command, in Trenčín ** 71st Command Support Battalion, in Trenčín ** 103rd Nuclear, Biological and Chemical Defence Battalion, in Rožňava ** 22nd Reconnaissance Regiment , in Prešovhttps://www.mosr.sk/data/att/161762.pdf *** 64th Battalion of Unmanned aerial vehicles & Electronic Warfare, in Prešov *** 65th Reconnaissance Battalion, in Prešov ** 1st Mechanized Brigade, in Topoľčany *** 103rd Command Support Company, in Topoľčany *** 11th Mechanized Battalion, in Martin ( BVP-2) *** 12th Mechanized Battalion, in Nitra (BVP-2) *** 13th Mechanized Battalion, in Levice (BVP-2) *** 14th Logistic Battalion, in Topoľčany ** 2nd Mechanized Brigade, in Prešov *** 67th Command Support Company, in Prešov *** 14th Tank Battalion, in Trebišov ( T-72M1 and Leopard 2A4) *** 21st Mechanized Battalion, in Trebišov ( BVP-1) *** 22nd Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustín Malár
Augustín Malár (18 July 1894 – 28 February 1945) was a Slovak general during World War II. During the interwar period, Malár was one of the few successful higher officers of Slovak nationality in the Czechoslovak Army. After the German occupation of Bohemia and Moravia and the establishment of the First Slovak Republic in March 1939, he became one of the highest and most experienced officers in the newly created Slovak Army. After the Slovak puppet state declared war on the USSR, the so-called Fast Division or Slovak Motorized Division was deployed on the Eastern Front. Malár became commander of the unit at the turn of 1941 and 1942. During this time he earned promotion to general and received the German Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. Later he served as military attaché to Italy and Germany, and in 1944 he was appointed as a commander of the East Slovak Army, the two best Slovak divisions which were intended to defend Slovakia against Soviet offensives. The planner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Logistics
Military logistics is the discipline of planning and carrying out the movement, supply, and maintenance of military forces. In its most comprehensive sense, it is those aspects or military operations that deal with: * Design, development, Military acquisition, acquisition, storage, distribution, maintenance, evacuation, and disposition of materiel. * Transport of personnel. * Acquisition or construction, maintenance, operation and disposition of facilities. * Acquisition or furnishing of services. * Medical and health service support. Etymology and definition The word "logistics" is derived from the Greek adjective meaning "skilled in calculating", and its corresponding Latin word . In turn this comes from the Greek , which refers to the principles of thought and action. Another Latin root, ''log-'', gave rise around 1380 to , meaning to lodge or dwell, and became the French verb , meaning "to lodge". Around 1670, the French King Louis XIV created the position of , an office ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antisemitic Canard
Antisemitic tropes, also known as antisemitic canards or antisemitic libels, are " sensational reports, misrepresentations or fabrications" about Jews as an ethnicity or Judaism as a religion. Since the 2nd century, malicious allegations of Jewish guilt have become a recurring motif in antisemitic tropes, which take the form of libels, stereotypes or conspiracy theories. They typically present Jews as cruel, powerful or controlling, some of which also feature the denial or trivialization of historical atrocities against Jews. These tropes have led to pogroms, genocides, persecutions and systemic racism for Jews throughout history. Antisemitic tropes mainly evolved in monotheistic societies, whose religions were derived from Judaism, many of which were traceable to Christianity's early days. These tropes were mirrored by 7th-century Quranic claims that Jews were "visited with wrath from Allah" due to their supposed practice of usury and disbelief in his revelations. In medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Bolshevik
Jewish Bolshevism, also Judeo–Bolshevism, is an antisemitic and anti-communist conspiracy theory that claims that the Russian Revolution of 1917 was a Jewish plot and that Jews controlled the Soviet Union and international communist movements, often in furtherance of a plan to destroy Western civilization. It was one of the main Nazi beliefs that served as an ideological justification for the German invasion of the Soviet Union and the Holocaust. After the Russian Revolution, the antisemitic canard was the title of the pamphlet ''The Jewish Bolshevism'', which featured in the racist propaganda of the anti-communist White movement forces during the Russian Civil War (1918–1922). During the 1930s, the Nazi Party in Germany and the German American Bund in the United States propagated the antisemitic theory to their followers, sympathisers, and fellow travellers. Nazi Germany used the trope to implement anti-Slavic policies and initiate racial war against Soviet Union, portrayi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbarossa Decree
The Military Justice Decree (), commonly known as the Barbarossa decree, was one of the criminal orders of the ''Wehrmacht'' issued by ''Generalfeldmarschall'' Wilhelm Keitel on 13 May 1941. The decree declared that the upcoming Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union, would be a war of extermination and endorsed war crimes against Soviet civilians. The Barbarossa decree was laid out by Adolf Hitler during a high-level meeting with military officials on 30 March 1941, where he declared the political and intellectual elites of the Soviet Union would be eradicated by German forces, in order to ensure a long-lasting German victory. Hitler underlined that executions would not be a matter for military courts, but for the organised action of the military. The decree was issued by Keitel a few weeks before Operation Barbarossa, exempting punishable offences committed by enemy civilians from the jurisdiction of military justice. Suspects were to be brought before a ''Wehr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut Für Zeitgeschichte
The Institute of Contemporary History (''Institut für Zeitgeschichte'') in Munich was conceived in 1947 under the name ''Deutsches Institut für Geschichte der nationalsozialistischen Zeit'' ("German Institute of the History of the National Socialist Era"). Founded by the German government and the State of Bavaria at the suggestion of the Allied Forces, it was established in 1949 and renamed in 1952. Its purpose is the analysis of contemporary German history. History The institute is funded by the German government, and the German states of Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg, Brandenburg, Hesse, Lower Saxony, North Rhine-Westphalia and Saxony. The first director of the institute was Hans Rothfels, the second director was Martin Broszat. Representatives of the supporting states are also members of the institute's board. Since 1953, the institute has been publishing the journal ' (''Contemporary History Quarterly''), which is regarded as one of the most important publications of Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
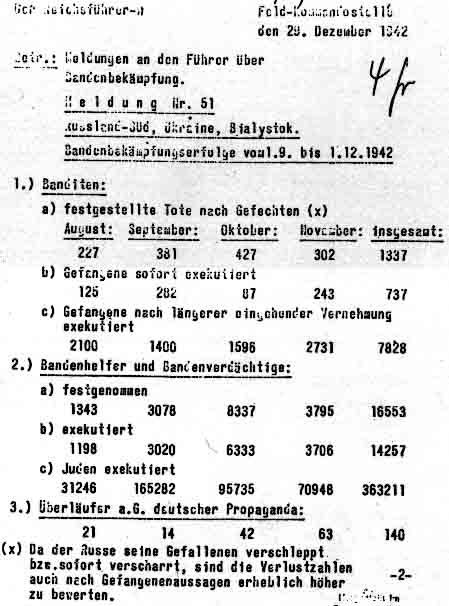
Bandenbekämpfung
In Military history of Germany, German military history, (), also referred to as Nazi security warfare during World War II, refers to the concept and military doctrine of Counterinsurgency, countering Resistance movement, resistance or insurrection in the Rear (military), rear area during wartime with extreme brutality. The doctrine provided a rationale for disregarding the established Law of war, laws of war and for targeting any number of groups, from Guerrilla warfare, armed guerrillas to civilians, as "bandits" or "members of gangs". As applied by the German Empire and later Nazi Germany, it became instrumental in the crimes against humanity committed by the two regimes, including the Herero and Nama genocide and the Holocaust. Historian Alex J. Kay estimates that around one million civilians died as a result of German anti-partisan warfare—excluding actual partisans—among the 13 to 14 million people murdered by the Nazis during World War II. Background According to his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuban Bridgehead
The Kuban Bridgehead (), also known as the "Goth's head position" (), was a German military position on the Taman Peninsula, Russia, between the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea. Existing from January to October 1943, the bridgehead formed after the Germans were pushed out of the Caucasus. The heavily fortified position was intended as a staging area for the ''Wehrmacht'' which was to be used to renew attacks towards the oil wells of the Caucasus. Axis positions in the bridgehead were repeatedly subjected to large Soviet offensives, but none ever comprehensively broke the Axis defensive lines. The bridgehead was abandoned when the Red Army breached the Panther–Wotan line, forcing an evacuation of the German forces across the Kerch Strait to Crimea. Prelude Case Blue (''Fall Blau''), launched 28 June 1942, saw Army Group South divided into two Army Groups, Army Group A and Army Group B, the former participating in the Battle of the Caucasus. Throughout the operation the German si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group B
Army Group B () was the name of four distinct German Army Group, army group commands that saw action during World War II. The first Army Group B was created on 12 October 1939 (from the former Army Group North) and fought in the Battle of France on the northern flank. It was responsible for a part of the German invasion of Belgium (1940), German invasion of Belgium and the majority of the German invasion of the Netherlands. In the later stage of that campaign ("Fall Rot, Case Red"), it again advanced on the German right flank towards the Somme (river), Somme river, the city of Paris and the France–Spain border, Franco-Spanish border. After 16 August 1940, it was deployed to East Prussia and to the General Government in Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), German-occupied Poland. When Operation Barbarossa began on 22 June 1941, Army Group B was renamed on the same day to become "Army Group Center". The second Army Group B came into existence on 9 July 1942, when Army Group South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Mobile Infantry Division (Slovak Republic)
The 1st Mobile Infantry Division also known as the Slovak Fast Division and as the Rapid Division, was an infantry division of the Slovak Expeditionary Army Group that fought on the Eastern Front during World War II. History The division was formed as the Rapid Group on 23 June 1941. A month later on 23 July 1941, the Rapid Group was reorganized into a division after the Battle of Lypovec. During the Battle of the Caucasus, the division was encircled at Saratowskaya, but managed to escape to the Kuban bridgehead. However, the division was forced to leave behind all their heavy equipment and weapons in order to escape. The division was then destroyed during the Melitopol offensive with 2,600 soldiers of the division becoming prisoners of war. The division was reformed in early 1944. The reformed division was used to protect communication lines. The division participated in the Odessa Offensive The Odessa Offensive Operation (Russian language, Russian: Одесская Наст ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |