|
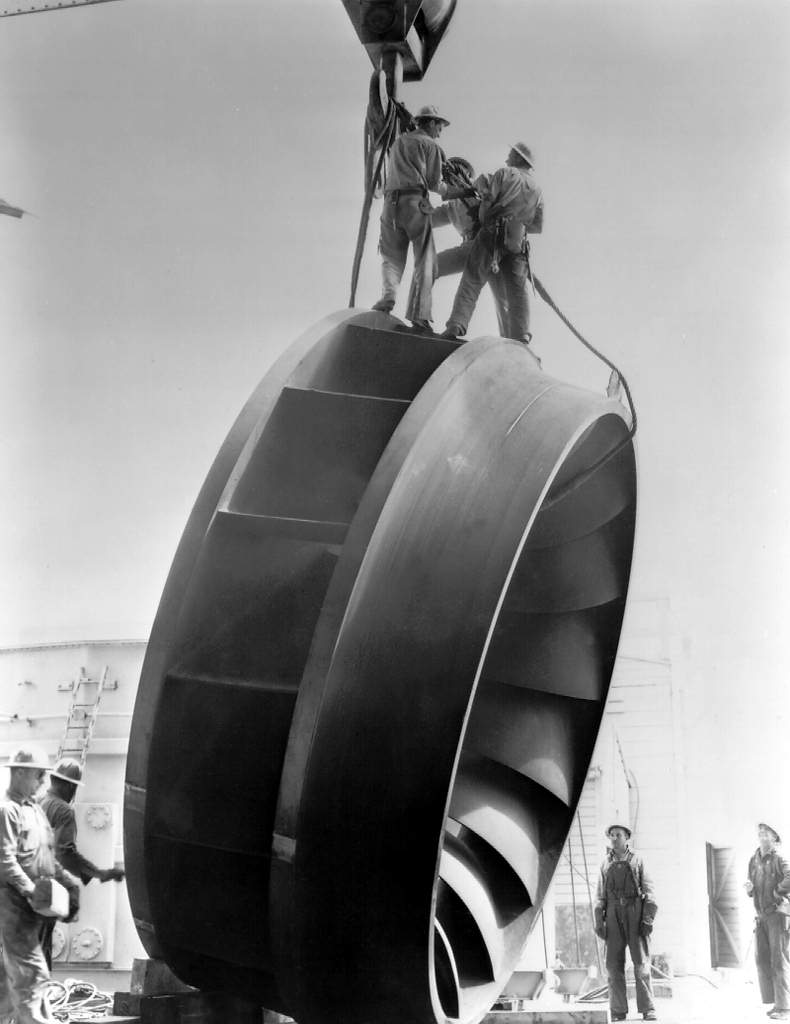
Slip Factor
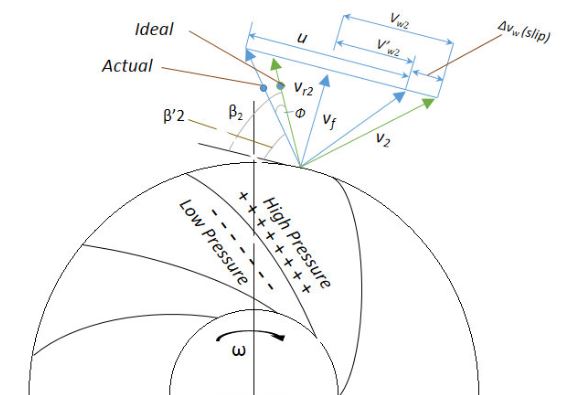
In turbomachinery, the slip factor is a measure of the fluid slip in the impeller of a compressor or a turbine, mostly a centrifugal machine. Fluid slip is the deviation in the angle at which the fluid leaves the impeller from the impeller's blade/vane angle. Being quite small in axial impellers (inlet and outlet flow in the same direction), slip is a very important phenomenon in radial impellers and is useful in determining the accurate estimation of work input or the energy transfer between the impeller and the fluid, rise in pressure and the velocity triangles at the impeller exit. A simple explanation for the fluid slip can be given as: Consider an impeller with ''z'' number of blades rotating at angular velocity ω. A difference in pressure and velocity during the course of clockwise flow through the impeller passage can be observed between the trailing and leading faces of the impeller blades. High pressure and low velocity are observed at the leading face of the impeller's bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbomachinery
Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor (turbine), rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and gas compressor, compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid.Logan, Earl. "Handbook of turbomachinery". 1995. Marcel Deckker.Vandad Talimi (Original author unknown). "Mechanical Equipment and Systems". 2013. Memorial University of Newfoundland. http://www.engr.mun.ca/~yuri/Courses/MechanicalSystems/Turbomachinery.pdf These two types of machines are governed by the same basic relationships including Newton's Laws of Motion, Newton's second Law of Motion and Euler's pump and turbine equation for compressible fluids. Centrifugal pumps are also turbomachines that transfer energy from a rotor to a fluid, usually a liquid, while turbines and compressors usually work with a gas. History The first turbomachines could be identified as water wheels, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impeller
An impeller or impellor is a rotor used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid. It is the opposite of a turbine, which extracts energy from, and reduces the pressure of, a flowing fluid. In pumps An impeller is a rotating component of a centrifugal pump that accelerates fluid outward from the center of rotation, thus transferring energy from the motor that drives the pump to the fluid being pumped. The velocity achieved by the impeller transfers into pressure when the outward movement of the fluid is confined by the pump casing. An impeller is usually a short cylinder with an open inlet (called an eye) to accept incoming fluid, vanes to push the fluid radially, and a splined, keyed, or threaded bore to accept a drive shaft. It can be cheaper to cast an impeller and its spindle as one piece, rather than separately. This combination is sometimes referred to simply as the "rotor." Types Open impellers An open impeller has a hub with attached vanes and is moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Transfer
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity Triangle
In turbomachinery, a velocity triangle or a velocity diagram is a triangle representing the various components of velocities of the working fluid in a turbomachinery, turbomachine. Velocity triangles may be drawn for both the inlet and outlet sections of any turbomachine. The vector (mathematics and physics), vector nature of velocity is utilized in the triangles, and the most basic form of a velocity triangle consists of the tangential velocity, the absolute velocity and the relative velocity of the fluid making up three sides of the triangle. Velocities involved A general velocity triangle consists of the following vectors: *''V'' : Absolute velocity of the fluid. *''U'' : Blade Linear velocity. *''Vr'': Relative velocity of the fluid after contact with rotor (turbine), rotor. *''Vw'': Tangential component of ''V'' (absolute velocity), called ''Whirl velocity''. *''Vf'': Flow velocity (axial component in case of axial machines, radial component in case of radial machines). The fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies. Velocity is a physical vector quantity; both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The scalar absolute value ( magnitude) of velocity is called , being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the SI ( metric system) as metres per second (m/s or m⋅s−1). For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an ''acceleration''. Constant velocity vs acceleration To have a ''constant velocity'', an object must have a constant speed in a constant direction. Constant dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddy (fluid Dynamics)
In fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current (water), current created when the fluid is in a Turbulence, turbulent flow regime. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream side of the object. Fluid behind the obstacle flows into the void creating a swirl of fluid on each edge of the obstacle, followed by a short reverse flow of fluid behind the obstacle flowing upstream, toward the back of the obstacle. This phenomenon is naturally observed behind large emergent rocks in swift-flowing rivers. An eddy is a movement of fluid that deviates from the general flow of the fluid. An example for an eddy is a vortex which produces such deviation. However, there are other types of eddies that are not simple vortices. For example, a Rossby wave is an eddy which is an undulation that is a deviation from mean flow, but doesn't have the local closed streamlines of a vortex. Swirl and eddies in engineering The propensity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's axis than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strength of the compensating force is proportional to the fluid's viscosity. In general, viscosity depends on a fluid's state, such as its temperature, pressure, and rate of deformation. However, the dependence on some of these properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is the thin layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface formed by the fluid flowing along the surface. The fluid's interaction with the wall induces a no-slip boundary condition (zero velocity at the wall). The flow velocity then monotonically increases above the surface until it returns to the bulk flow velocity. The thin layer consisting of fluid whose velocity has not yet returned to the bulk flow velocity is called the velocity boundary layer. The air next to a human is heated resulting in gravity-induced convective airflow, airflow which results in both a velocity and thermal boundary layer. A breeze disrupts the boundary layer, and hair and clothing protect it, making the human feel cooler or warmer. On an aircraft wing, the velocity boundary layer is the part of the flow close to the wing, where viscous forces distort the surrounding non-viscous flow. In the Earth's atmosphere, the atmospheric b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slip Factor1
Slip or SLIP may refer to: Science and technology Biology * Slip (fish), also known as Black Sole * Slip (horticulture), a small cutting of a plant as a specimen or for grafting * Muscle slip, a branching of a muscle, in anatomy Computing and telecommunications * SLIP (programming language), (Symmetric LIst Processing language) * Slip (telecommunication), a positional displacement in a sequence of transmitted symbols * Serial Line Internet Protocol, a mostly obsolete encapsulation of the Internet Protocol Earth science * Silicic-dominated Large Igneous Province (SLIP), a geological feature consisting of a large area of igneous rocks of a certain type * Slip, the relative movement of geological features present on either side of a fault plane * Land slip or landslide, commonly called a slip in New Zealand Materials * Slip (ceramics), an aqueous suspension of minerals * Slip (materials science), the process by which a dislocation motion produces plastic deformation Mechanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Compressors
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor. Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transport the fluid through a pipe. The main distinction is that the focus of a compressor is to change the density or volume of the fluid, which is mostly only achievable on gases. Gases are compressible, while liquids are relatively incompressible, so compressors are rarely used for liquids. The main action of a pump is to pressurize and transport liquids. Many compressors can be staged, that is, the fluid is compressed several times in steps or stages, to increase discharge pressure. Often, the second stage is physically smaller than the primary stage, to accommodate the already compressed gas without reducing its pressure. Each stage further compresses the gas and increases its pressure and also temperature (if inter cooling between stages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |